Types of Tissue Part 3: Muscle Tissue
Summary
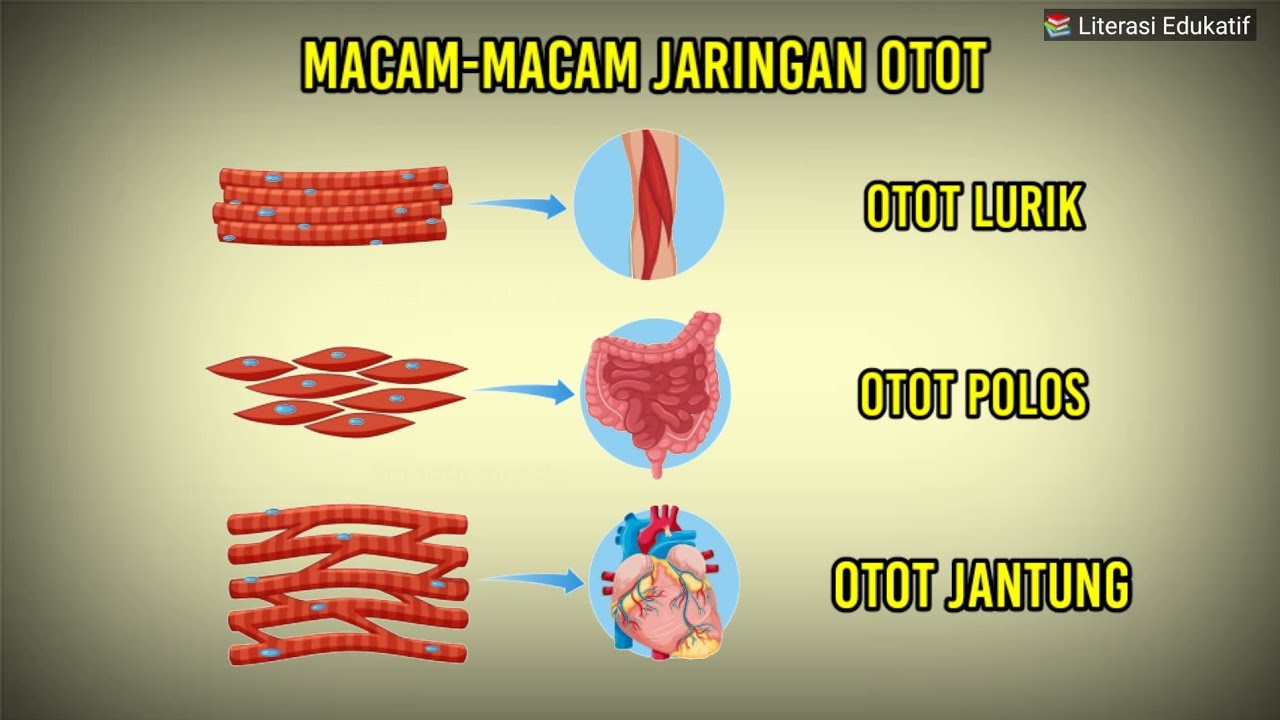
TLDRProfessor Dave's video script delves into the three types of muscles in the human body: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Skeletal muscles, the most abundant, are voluntary and help in movement and posture. Cardiac muscles, found only in the heart, are involuntary and essential for pumping blood. Smooth muscles, present in organs, regulate various bodily functions automatically. The script explores the structure and function of each, highlighting the specialized cells and tissues that enable muscle contraction and our body's movement.
Takeaways
- 💪 Skeletal muscles are the most abundant and are responsible for voluntary movements, posture, and maintaining body temperature.
- 🦴 Skeletal muscle fibers are multinucleated and contain myofibrils, which are made up of sarcomeres responsible for contraction.
- 🫀 Cardiac muscle, found only in the heart, is responsible for pumping blood and is innervated by the autonomic nervous system.
- 🔗 Cardiac muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, are short and branched with intercalated discs for rapid electrical signal transmission.
- 🌀 Smooth muscle is found in most organs and is responsible for regulating various bodily functions like digestion and blood pressure.
- 🔁 Smooth muscle is organized in layers and is not striated, with myofilaments scattered throughout the cell cytoplasm.
- 🧬 All three muscle types are similar in structure but differ in function, with skeletal muscle being under voluntary control and cardiac and smooth muscles being involuntary.
- 🏋️♂️ Skeletal muscle attachments can be direct to bones or indirect via tendons or aponeurosis, allowing for a wide range of movement.
- 🌡️ Skeletal muscles play a role in thermoregulation by releasing heat as a byproduct of contraction.
- 🤖 The autonomic nervous system controls the contraction of cardiac and smooth muscles, which operate without conscious thought.
Q & A
What are the three types of muscles in the human body?
-The three types of muscles in the human body are skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle.
What is the primary function of skeletal muscles?
-Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movements, maintaining posture, and forming sphincters in the digestive and urinary tracts.
How are skeletal muscles different from cardiac and smooth muscles in terms of structure?
-Skeletal muscle cells are multinucleated, long, cylindrical, and have a striated appearance due to the organization of myofilaments into sarcomeres.
What is the role of the endomysium in skeletal muscles?
-The endomysium is a sheath of connective tissue that surrounds each muscle fiber in skeletal muscles.
How does the structure of cardiac muscle cells differ from skeletal muscle cells?
-Cardiac muscle cells, or cardiomyocytes, are short, branched, and have one or two centrally located nuclei. They also contain intercalated discs with gap junctions for rapid electrical conduction.
Why is cardiac muscle considered an involuntary muscle?
-Cardiac muscle is innervated by the autonomic nervous system and contracts automatically without conscious control, making it an involuntary muscle.
In which part of the body is cardiac muscle found, and what is its main function?
-Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart, and its main function is to contract and push blood out to the rest of the body.
What are some functions of smooth muscle in the body?
-Smooth muscle regulates blood pressure, controls the passage of air in the airways, moves material through the digestive tract, expels urine from the bladder, and has various roles in the reproductive system.
How does the organization of smooth muscle fibers differ from that of skeletal and cardiac muscles?
-Smooth muscle fibers are typically organized into two layers: a longitudinal layer that runs parallel to the organ's long axis and a circular layer that runs around the organ's circumference.
Why is smooth muscle not striated like skeletal and cardiac muscles?
-Smooth muscle is not striated because it lacks the organized arrangement of myofibrils and sarcomeres; instead, its myofilaments are scattered throughout the cytoplasm.
How is the autonomic nervous system involved in the functioning of smooth muscle?
-The autonomic nervous system innervates smooth muscle, causing it to contract and relax automatically, without voluntary control.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)