GCSE Chemistry Revision "Introducing Electrolysis"
Summary
TLDRThis video from freesis lessons explores the principles of electrolysis, focusing on why ionic compounds like lead bromide conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water. It explains the processes occurring at the cathode and anode, detailing reduction and oxidation reactions. The video promises further content on specific electrolysis examples and their applications in extracting reactive metals, hinting at the educational resources available for deeper understanding.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Ionic compounds like lead bromide (PbBr2) are formed from the reaction between lead and bromine, resulting in lead ions (Pb2+) and bromide ions (Br-).
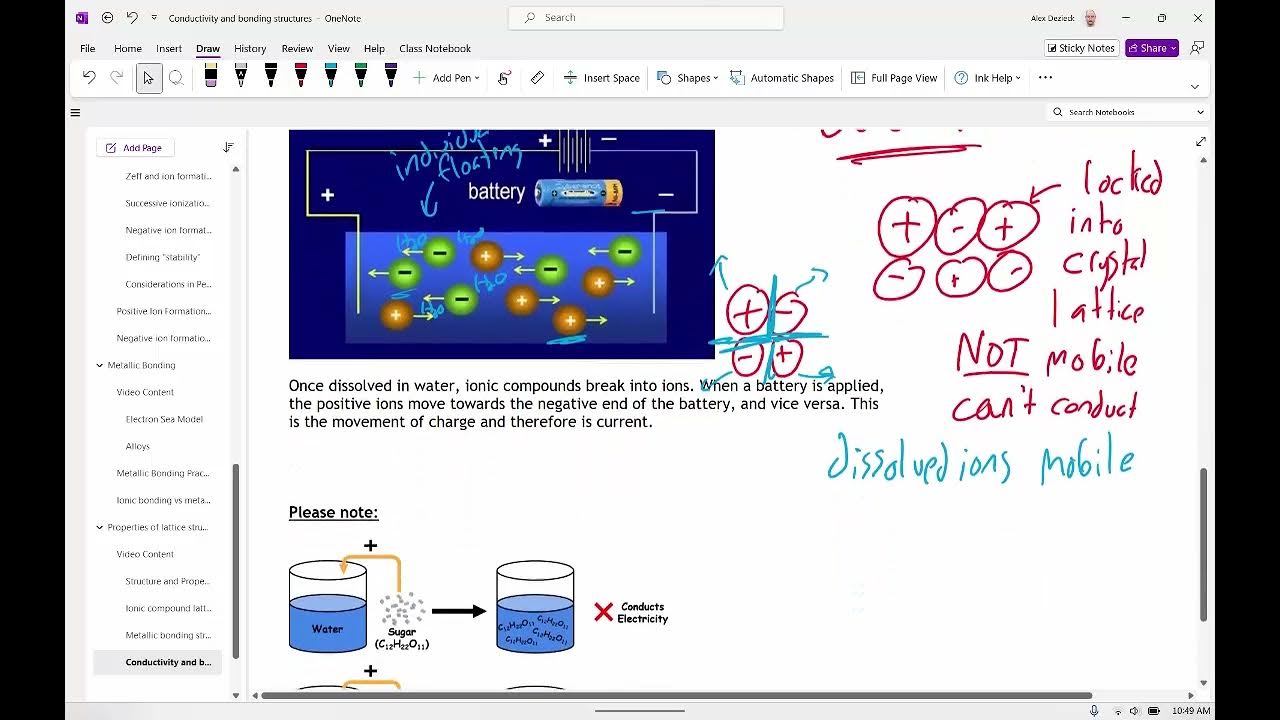
- 🌐 Solid ionic compounds do not conduct electricity because the ions are locked in place by strong electrostatic forces.
- 💧 When ionic compounds are molten or dissolved in water, the ions are free to move, allowing the substance to conduct electricity, making them electrolytes.
- ⚡️ Electrolysis involves passing an electric current through a molten ionic compound, causing chemical reactions at the electrodes.
- 🔋 The negative electrode, or cathode, is where positive ions gain electrons (reduction), while the positive electrode, or anode, is where negative ions lose electrons (oxidation).
- 🔄 During electrolysis of lead bromide, lead ions are reduced to lead atoms at the cathode, and bromide ions are oxidized to bromine molecules at the anode.
- 🔬 The process of electrolysis can be used to extract reactive metals, such as aluminum, from their compounds.
- 📚 The video script is part of a series that will explore specific examples of electrolysis, which are important for higher-tier students.
- 📘 The script mentions a vision workbook with questions on electrolysis, which can be accessed by viewers for further practice.
- 🎓 Understanding the concepts of reduction and oxidation is crucial for higher-tier students studying electrolysis.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video from freesis lessons?
-The main focus of the video is to explain why ionic compounds can conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water, describe the reactions at the positive and negative electrodes during electrolysis, and identify these reactions as reduction or oxidation.
What is the difference between solid ionic compounds and molten or dissolved ionic compounds in terms of electrical conductivity?
-Solid ionic compounds cannot conduct electricity because the ions are locked in place and not free to move. In contrast, molten or dissolved ionic compounds can conduct electricity because the forces of attraction are broken, allowing the ions to move freely.
What is the term for a liquid or solution that can conduct electricity due to the presence of ions?
-Such liquids or solutions are called electrolytes.
What happens to the lead ions during electrolysis of molten lead bromide?
-The lead ions (Pb2+) are attracted to the negative electrode, or cathode, where they gain electrons to form lead atoms, which is a reduction reaction.
What occurs with the bromide ions during the electrolysis of molten lead bromide?
-The bromide ions (Br-) are attracted to the positive electrode, or anode, where they lose an electron to form bromine atoms, which is an oxidation reaction.
Why are the reactions at the electrodes during electrolysis called reduction and oxidation?
-The reactions are called reduction and oxidation because reduction refers to the gain of electrons by the lead ions at the cathode, while oxidation refers to the loss of electrons by the bromide ions at the anode.
What is the role of the cathode in an electrolysis cell?
-The cathode is the negative electrode where reduction reactions occur, and it is where cations (positively charged ions) are attracted to gain electrons.
What is the role of the anode in an electrolysis cell?
-The anode is the positive electrode where oxidation reactions occur, and it is where anions (negatively charged ions) are attracted to lose electrons.
How do bromine atoms behave when formed at the anode during electrolysis?
-Bromine atoms pair up to form bromine molecules (Br2), which is the typical behavior of bromine when it is produced in this manner.
What can be extracted using electrolysis, as hinted in the video?
-Electrolysis can be used to extract reactive metals such as aluminum from their compounds.
Where can viewers find additional questions on electrolysis to practice and reinforce their understanding?
-Viewers can find plenty of questions on electrolysis in the vision workbook, which can be accessed by clicking on the provided link in the video description.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)