Double Angle Identities & Formulas of Sin, Cos & Tan - Trigonometry
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the key double angle formulas in trigonometry, providing clear step-by-step derivations and applications for sine, cosine, and tangent. It covers the formulas for sine (2θ = 2sin(θ)cos(θ)), cosine (2θ = cos²(θ) - sin²(θ)), and tangent (2θ = 2tan(θ) / (1 - tan²(θ))). Through detailed examples using right triangles, the video demonstrates how to calculate these double angle values for different angles. Viewers will gain a deeper understanding of how to apply these formulas in solving problems involving trigonometric functions.
Takeaways
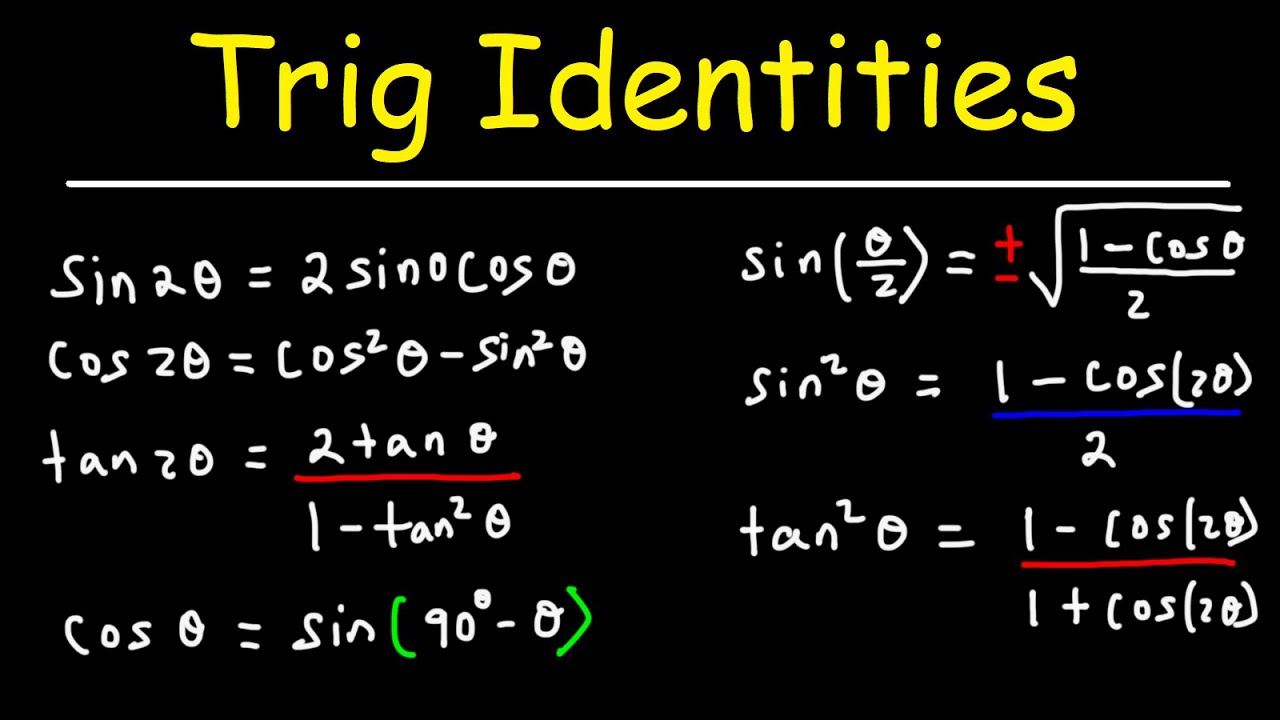
- 😀 The sine double angle formula is: sin(2θ) = 2 sin(θ) cos(θ).
- 😀 The cosine double angle formula is: cos(2θ) = cos²(θ) - sin²(θ). It can also be written as cos(2θ) = 2 cos²(θ) - 1 or cos(2θ) = 1 - 2 sin²(θ).
- 😀 The tangent double angle formula is: tan(2θ) = (2 tan(θ)) / (1 - tan²(θ)).
- 😀 To apply the sine double angle formula, simply multiply the sine and cosine of the angle and double the result.
- 😀 The cosine double angle formula can be derived using the sum of angles identity for cosine: cos(α + β) = cos(α) cos(β) - sin(α) sin(β).
- 😀 Tangent of a double angle can be calculated using the quotient identity for tangent: tan(2θ) = sin(2θ) / cos(2θ).
- 😀 Trigonometric identities simplify the process of finding values for double angles in trigonometric functions.
- 😀 When given values for sine, cosine, and tangent of an angle, you can easily find the values for sine, cosine, and tangent of double angles.
- 😀 For example, with sin(θ) = 3/5, cos(θ) = 4/5, the sine of the double angle sin(2θ) = 24/25, cosine of the double angle cos(2θ) = 7/25, and tangent of the double angle tan(2θ) = 24/7.
- 😀 The formulas help simplify complex expressions, such as 2 sin(75°) cos(75°) becoming sin(150°) = 1/2, and cos²(15°) - sin²(15°) simplifying to cos(30°) = √3/2.
Q & A
What is the double angle formula for sine?
-The double angle formula for sine is given by: sine(2θ) = 2 sine(θ) cosine(θ).
How is the double angle formula for cosine derived?
-The double angle formula for cosine is derived using the sum of angles formula for cosine: cosine(α + β) = cosine(α) cosine(β) - sine(α) sine(β). When α and β are both equal to θ, this becomes cosine(2θ) = cosine²(θ) - sine²(θ).
What is the double angle formula for tangent?
-The double angle formula for tangent is: tangent(2θ) = 2 tangent(θ) / (1 - tangent²(θ)).
How do you find sine(2θ) when sine(θ) = 3/5?
-To find sine(2θ), use the formula sine(2θ) = 2 sine(θ) cosine(θ). Given sine(θ) = 3/5 and cosine(θ) = 4/5, you substitute these values into the formula: sine(2θ) = 2 * (3/5) * (4/5) = 24/25.
How do you calculate cosine(2θ) when sine(θ) = 3/5 and cosine(θ) = 4/5?
-To calculate cosine(2θ), use the formula cosine(2θ) = cosine²(θ) - sine²(θ). With cosine(θ) = 4/5 and sine(θ) = 3/5, substitute into the formula: cosine(2θ) = (4/5)² - (3/5)² = 16/25 - 9/25 = 7/25.
What is the value of tangent(2θ) when sine(2θ) = 24/25 and cosine(2θ) = 7/25?
-To find tangent(2θ), use the quotient identity: tangent(2θ) = sine(2θ) / cosine(2θ). With sine(2θ) = 24/25 and cosine(2θ) = 7/25, tangent(2θ) = (24/25) / (7/25) = 24/7.
Why is the first method of finding tangent(2θ) easier than the second method?
-The first method, using sine(2θ) and cosine(2θ) directly, is simpler because it involves straightforward division of the two values. The second method involves a more complex formula and additional steps, including squaring and multiplying fractions.
How do you solve for sine(2θ) when cosine(θ) = 5/13 in quadrant IV?
-First, draw a right triangle in quadrant IV where cosine(θ) = adjacent/hypotenuse = 5/13. Using the Pythagorean theorem, find that sine(θ) = -12/13. Then, use the formula sine(2θ) = 2 sine(θ) cosine(θ) to calculate sine(2θ) = 2 * (-12/13) * (5/13) = -120/169.
How is cosine(2θ) calculated when cosine(θ) = 5/13 and sine(θ) = -12/13 in quadrant IV?
-To find cosine(2θ), use the formula cosine(2θ) = cosine²(θ) - sine²(θ). With cosine(θ) = 5/13 and sine(θ) = -12/13, substitute these values: cosine(2θ) = (5/13)² - (-12/13)² = 25/169 - 144/169 = -119/169.
What is the exact value of the expression 2 sine(75°) cosine(75°)?
-Using the double angle formula for sine, 2 sine(75°) cosine(75°) = sine(2 * 75°) = sine(150°). Since sine(150°) = 1/2, the exact value of the expression is 1/2.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführen5.0 / 5 (0 votes)