Y1 22) Types of Market Failure
Summary
TLDRMarket failure occurs when the free market fails to allocate resources efficiently, leading to suboptimal outcomes. Key causes include externalities (both positive and negative), information failures, and issues like income inequality and monopoly power. Public goods and common resources are often under or over-consumed, exacerbating the problem. Additionally, market failures can arise from imperfect mobility in the labor market. The video highlights these causes and suggests that intervention may be needed to correct the inefficiencies caused by these market imperfections, urging viewers to explore each cause in more detail through subsequent videos.
Takeaways
- 😀 Market failure occurs when the free market fails to allocate scarce resources at the socially optimal level.
- 😀 It's crucial to understand the concept of allocated efficiency in a free market before delving into market failure.
- 😀 Externalities, both negative and positive, can cause market failure because they are not accounted for in market transactions.
- 😀 Consumers and firms tend to ignore the impacts on third parties, leading to inefficient resource allocation.
- 😀 Merit and demerit goods are those whose true benefits or harms may not be fully understood, causing consumers to make irrational decisions.
- 😀 Public goods face the free rider problem, meaning firms have little incentive to supply them, leading to under-provision.
- 😀 Common access resources often experience overconsumption and overproduction due to negative externalities and self-interest.
- 😀 Income inequality can lead to market failure if the disparity becomes too high and is seen as unfair, based on equity concerns.
- 😀 Monopoly power is another source of market failure, as it leads to higher prices and lower quantities than socially optimal.
- 😀 Factor immobility, such as workers being geographically or structurally immobile, can prevent efficient resource allocation in the labor market.
- 😀 Understanding the causes of market failure, such as externalities, income inequality, and monopoly power, is essential for analyzing economic inefficiency.
Q & A
What is market failure?
-Market failure occurs when the free market fails to allocate scarce resources efficiently at the socially optimal level, leading to inefficiencies in production or consumption.
Why is understanding 'socially optimal level of output' important in the context of market failure?
-Understanding the 'socially optimal level of output' is crucial because it refers to the level of production or consumption that maximizes societal welfare. Without this understanding, it’s difficult to assess whether market failure is occurring.
How do externalities contribute to market failure?
-Externalities, whether negative (e.g., pollution) or positive (e.g., vaccination), cause market failure because producers and consumers ignore the effects their actions have on third parties, leading to overproduction or underproduction of goods.
What is the free rider problem, and how does it affect public goods?
-The free rider problem occurs when individuals or businesses benefit from public goods without paying for them. This results in insufficient supply of public goods because private firms have no incentive to produce them.
What role does imperfect information play in market failure?
-Imperfect information leads to irrational decision-making by consumers, as they cannot accurately assess the benefits or risks of goods and services. This misinformed decision-making causes resources to be allocated inefficiently.
What are merit and demerit goods, and how do they lead to market failure?
-Merit goods are those that are better for us than we realize, while demerit goods are worse for us than we think. The market fails when consumers don’t fully understand the true value or harm of these goods, leading to inefficient resource allocation.
How does income inequality contribute to market failure?
-Income inequality can be seen as a source of market failure when the disparity in wealth becomes so great that it leads to unfair outcomes, causing social and economic imbalances that are not addressed by the market alone.
What is monopoly power, and why does it lead to market failure?
-Monopoly power occurs when a single firm dominates the market, reducing competition. This leads to market failure because monopolies can set high prices and produce lower quantities than would be socially optimal.
How does factor immobility contribute to market failure?
-Factor immobility, such as when workers cannot move easily between jobs or regions, prevents resources from being allocated efficiently. This mismatch between demand and available labor leads to inefficiencies in the labor market.
What are common access resources, and how do they contribute to market failure?
-Common access resources, like natural resources or public spaces, are often overused because they are not owned by anyone in particular. This leads to depletion or degradation of the resource due to overconsumption, contributing to market failure.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Y1/IB 22) Negative Externalities in Production and Consumption

Y1/IB 23) Positive Externalities in Consumption and Production

High Resistance vs Low Resistance Liquidity - ICT Concepts
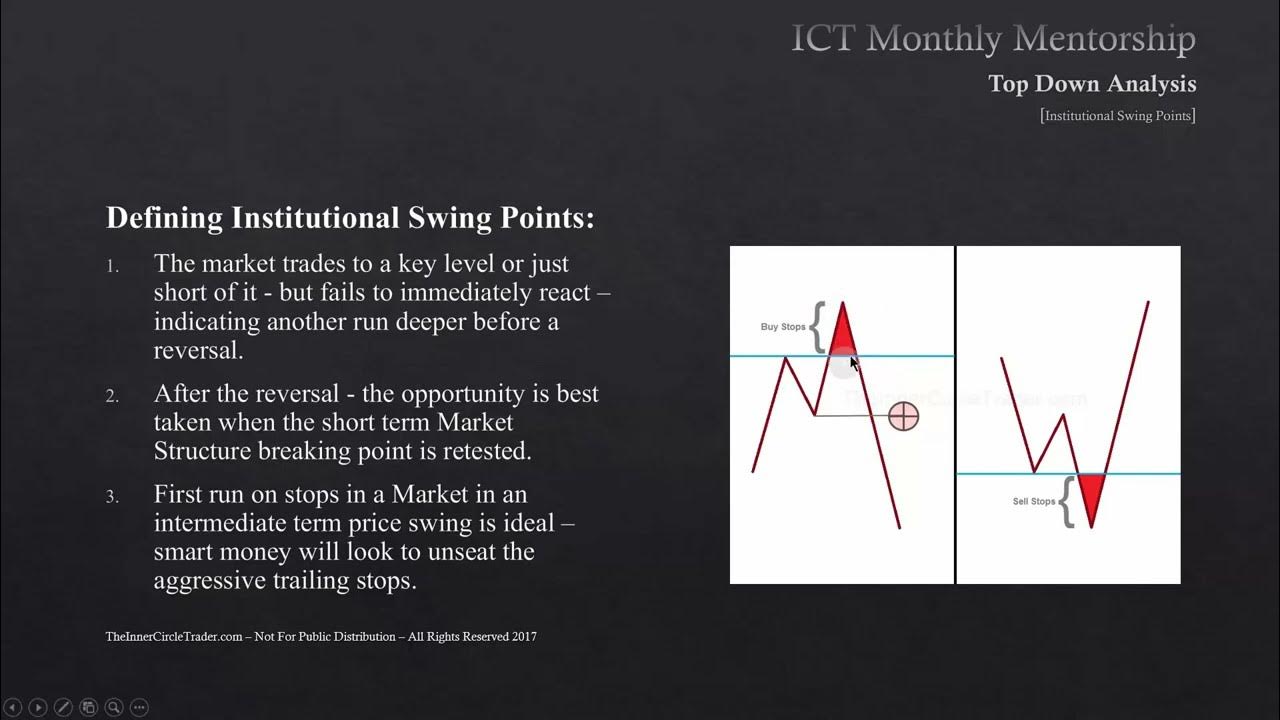
ICT Mentorship Core Content - Month 05 - Defining Institutional Swing Points

The Difference Between Cardiac Arrest, Heart Attack, and Heart Failure - 3D Animation

10 Prinsip Ekonomi - Kuliah Online Ekonomi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
