High Resistance vs Low Resistance Liquidity - ICT Concepts
Summary
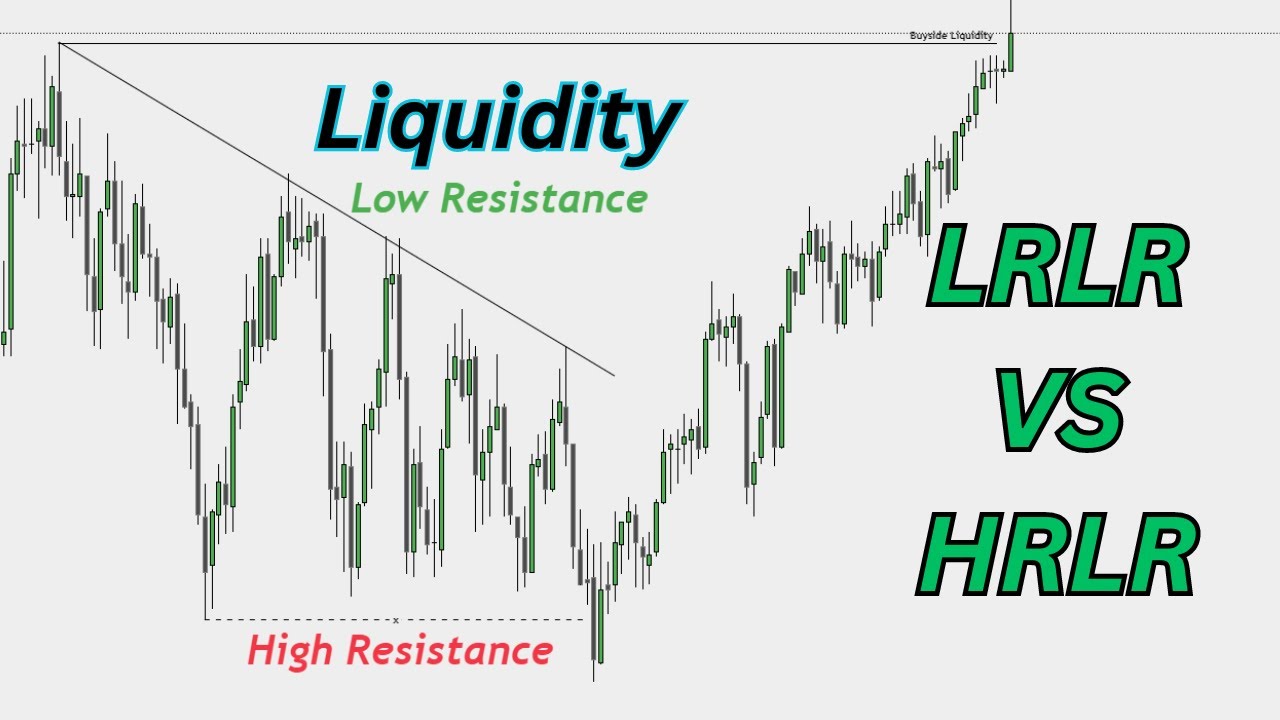
TLDRThis video explains the concepts of low resistance and high resistance liquidity in trading, with a focus on failure swings and their implications for market entry and stop loss strategies. Low resistance liquidity occurs when price fails to sweep previous highs or lows, while high resistance liquidity involves sweeping liquidity before a reversal. The video demonstrates how traders can target low resistance liquidity for entries, using high resistance liquidity for stop loss placement. Various real-life chart examples are provided to illustrate these concepts and help traders refine their strategies by understanding market structure shifts.
Takeaways
- 😀 A failure swing occurs when there is a swing high followed by a lower high, or a swing low followed by a higher low, indicating a reversal.
- 😀 Low resistance liquidity refers to a failure swing where liquidity is resting above previous highs and lows, which gets swept as the market moves.
- 😀 High resistance liquidity is when liquidity above highs and lows gets swept before a market reversal, resulting in higher resistance before further price movement.
- 😀 To use low and high resistance liquidity effectively, target low resistance liquidity for entries and use high resistance liquidity for stop loss placements.
- 😀 Market structure shift or a change in the state of delivery is crucial for identifying the right entry points using liquidity dynamics.
- 😀 A valid entry often comes after sweeping previous lows or highs, confirming the shift in market sentiment and direction.
- 😀 On the daily chart, identifying failure swings and high resistance liquidity can help frame a bias for potential trades.
- 😀 High resistance liquidity can be found after price sweeps highs or lows, typically marking areas of reversal or consolidation before further price movements.
- 😀 Order blocks, especially those formed after liquidity sweeps, can act as crucial levels for predicting future price movements.
- 😀 The mean threshold of an order block should be respected in trades, acting as a level where price could react before continuing its direction.
Q & A
What is the concept of a 'failure swing' as described in the video?
-A failure swing occurs when there is a swing high followed by a lower high, or a swing low followed by a higher low, without the previous high or low being swept before the reversal.
What differentiates low resistance liquidity from high resistance liquidity?
-Low resistance liquidity is created by failure swings, where liquidity builds above previous highs and lows. High resistance liquidity occurs when these highs and lows are swept before a reversal, wiping out the liquidity resting at those points.
How does liquidity change as the market moves away from highs and lows?
-As the market moves away from highs and lows, more highs and lows are generated, creating additional liquidity resting above and below those levels.
What is the purpose of targeting low resistance liquidity in trading?
-Targeting low resistance liquidity is helpful because it indicates a price level where a reversal might occur, allowing traders to take advantage of market structure shifts.
How does high resistance liquidity impact stop-loss placement?
-High resistance liquidity acts as a stop-loss zone or a level that can be used to define the risk in a trade. It provides a boundary beyond which a trader might exit if the price moves against the position.
Why is it important to analyze failure swings on different timeframes?
-Analyzing failure swings across different timeframes helps identify where liquidity might build and shift, providing insight into potential market reversals and trend changes.
How can traders use both high and low resistance liquidity in conjunction?
-Traders can use high resistance liquidity for their stop-loss placement and low resistance liquidity as a target. The idea is to trade in the direction of low resistance liquidity, while using high resistance liquidity to manage risk.
What does a 'state of delivery' change refer to in the context of market structure?
-A 'state of delivery' change refers to a shift in market structure, such as a reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend or vice versa, which is often indicated by a sweep of liquidity.
What is the significance of order blocks and mean thresholds in this approach?
-Order blocks and their mean thresholds are important for identifying potential entry points. The mean threshold represents the level within an order block where price action might reverse, and closing above this threshold validates the order block for entry.
How does understanding low resistance liquidity on a daily chart help in decision-making?
-By observing low resistance liquidity on a daily chart, traders can spot failure swings and high resistance liquidity zones, which inform their bias for trading long or short setups.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How I Formed My Trading Strategy Using LRLR

MMXM Mentorship Episode 3: Failure Swings

Low Resistance Liquidity Run - ICT Concepts
Episode 2: Low Resistance vs. High Resistance Liquidity - ICT Concepts

HIGH VS LOW RESISTANCE LIQUIDITY RUNS l ICT CONCEPTS

Liquidity Tells You Everything (Beat Stop Loss Hunts)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)