TOYOTA Production System;Kanban Production
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into two production systems: the Kanban system, which emphasizes 'Just-in-Time' production, and the Push system, based on demand forecasts. Kanban uses a card system to control production, ensuring materials are produced and procured only as needed, minimizing waste and inventory. In contrast, the Push system plans production in advance and maintains stock to prevent stockouts, but can lead to overproduction if demand forecasts are inaccurate. The script highlights the importance of balancing production speed with sales speed to manage inventory effectively.
Takeaways
- 📈 Just-in-Time (JIT) Production: The script introduces the JIT production style, which focuses on producing only the exact amount of products needed based on received orders, minimizing waste and inventory costs.
- 🔄 Kanban System: The JIT production is controlled by a tool called 'Kanban,' which carries production and logistics information and acts as a pull signal for the next process in the production line.
- 🔄 Backward Scheduling: The Kanban system works by moving backward through the production process, starting with the shipping of finished products and pulling required parts from previous processes based on Kanban instructions.
- 🚫 No Production Without Orders: The script highlights that in the Kanban system, production only occurs when there are orders, which helps in aligning production with actual demand and reducing overproduction.
- 📉 Inventory Control: The main goal of production control in the JIT system is to keep inventory at a minimum by matching production speed with sales speed, which is influenced by external factors like customer demand and competition.
- 🔄 Sales Speed Dependency: The script points out that sales speed is not controllable by the manufacturer and can fluctuate widely, necessitating adjustments in production speed to manage inventory effectively.
- 🛡 Safety Stock Concept: The concept of safety stock is introduced as a buffer to handle fluctuations in sales speed, ensuring that production can continue even when sales temporarily exceed production capacity.
- 🔮 Demand Forecasting: The script discusses the importance of demand forecasting in a general production style, which is crucial for planning production amounts and maintaining an optimal level of inventory.
- 🚀 Push System Production: The push system is contrasted with the JIT/Kanban system, where production is based on demand forecasts and maintains a certain level of inventory, shipping products from stock upon receiving orders.
- 📉 Overproduction Risk: The push system is highlighted as potentially leading to overproduction and excess inventory if the demand forecast is inaccurate or if actual demand falls below the forecasted levels.
- 🔄 Flexibility in Production: The script concludes by emphasizing the need for a flexible production style that can adapt to demand fluctuations, aligning production speed with sales speed to minimize inventory and stockouts.
Q & A
What is the main principle behind the pole system production style?
-The pole system production style, also known as just-in-time (JIT), is based on producing the right material at the right time, at the right place, and in the exact amount as per the orders received, thus minimizing waste and inventory.
What tool is used in the pole system production to control production?
-A tool called 'Kanban' is used in pole system production to control the production process, carrying all necessary information for production and logistics.
How does the Kanban system ensure the production of the right amount of material?
-The Kanban system ensures the production of the right amount of material by signaling the production line to process parts using materials to fulfill the instructions indicated on the Kanban, which represents the product that has been shipped or parts used.
What is the purpose of passing the Kanban from one process to another in the pole system production?
-The purpose of passing the Kanban from one process to another is to ensure that materials required for processing are picked up from storage and processed according to the instructions on the Kanban, thus maintaining a smooth flow of production.
How does the pole system production respond to fluctuations in sales speed?
-The pole system production responds to fluctuations in sales speed by adjusting the production speed to match the sales speed, using accumulated inventory when sales exceed production, and replenishing inventory when sales drop.
What is the main target of production control in the pole system?
-The main target of production control in the pole system is to keep inventory at its minimum by controlling the sales speed and production speed without causing stockouts.
What is the push system production and how does it differ from the pole system?
-The push system production is a style based on demand forecasts and production schedules, maintaining a certain amount of inventory and shipping products from stock upon receiving orders. It differs from the pole system by focusing on the manufacturer's logic, ordering materials in large lots, and maintaining a large production lot size for efficiency.
How does the push system production plan its production schedule?
-The push system production plans its production schedule based on demand forecasts and internal information from customers, making plans for materials, production facilities, personnel, and production steps accordingly.
What are the potential problems of the push system production?
-The potential problems of the push system production include inaccuracies in demand forecasts leading to stockouts or excess inventory, and the difficulty in adapting quickly to market fluctuations due to its reliance on large lot sizes and set production schedules.
How can a company minimize stock or stockouts in the push system production?
-A company can minimize stock or stockouts in the push system production by not solely relying on demand forecasts but also implementing a flexible style that adjusts production speed according to actual demand trends, thus reducing the difference between production and sales speeds.
What is the significance of safety stock in production control within the push system?
-Safety stock is significant in production control within the push system as it serves as a buffer to prevent stockouts. It is considered standard stock and is used to control production to ensure that it is always maintained, even when there are fluctuations in demand.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

Make-to-stock vs. Make-to-order (Push vs. Pull)
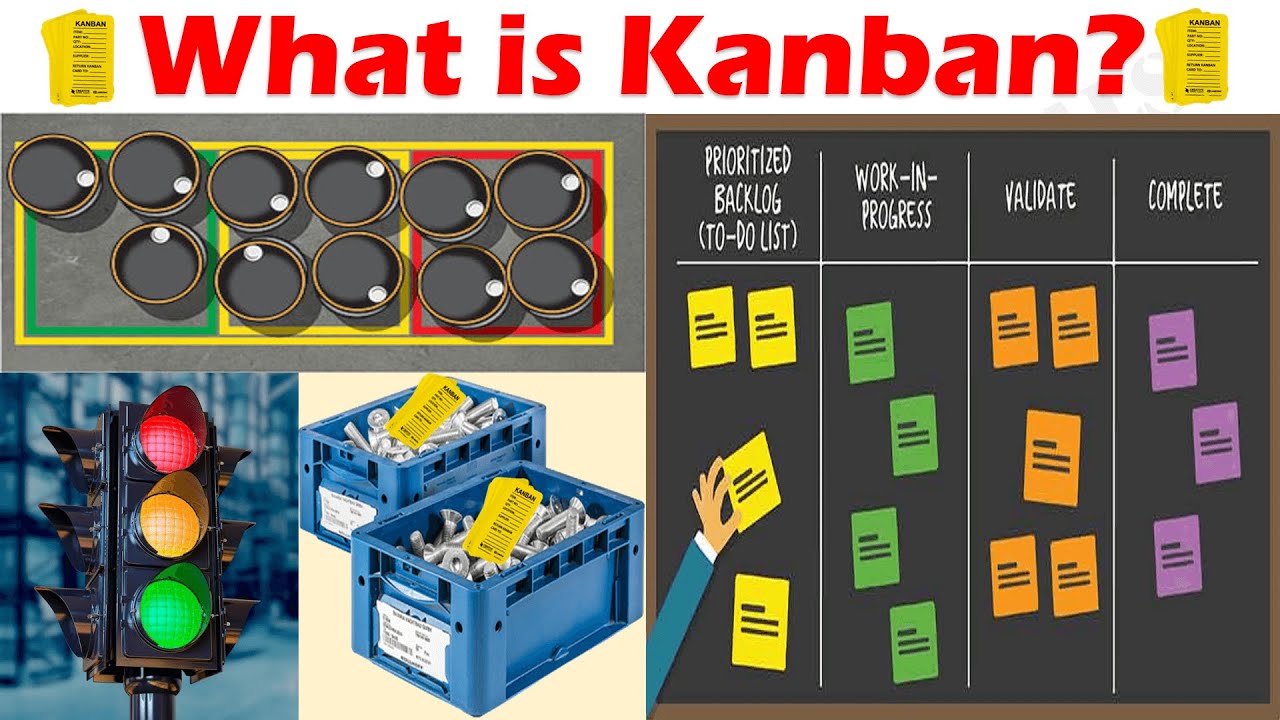
What is Kanban? Kanban Visual Systems Explained in 4 stages Easily.

Learn How Kanban Systems are Used in a Lean Manufacturing Environment

Just In Time JIT Definition Investopedia

English for Business Studies Track 17 Inventory, Kanban and MRP
How Toyota Changed The Way We Make Things
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
