How To Write Chemical Equations From Word Descriptions
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial guides viewers on how to write and balance chemical equations from word descriptions. It covers various reactions involving solid elemental phosphorus, calcium metal, sulfur, and pentane, explaining the importance of recognizing diatomic molecules and the use of the crisscross method for ionic compounds. The tutorial emphasizes understanding solubility rules, predicting products of reactions, and balancing equations effectively. With step-by-step examples, viewers learn to convert descriptions into balanced equations while grasping essential concepts in chemistry. This engaging lesson is perfect for those looking to enhance their skills in writing and balancing chemical equations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chemical equations can be derived from word descriptions, requiring knowledge of chemical symbols and states of matter.
- 😀 Diatomic molecules include nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and hydrogen, which must be noted in chemical equations.
- 😀 Phosphorus pentafluoride is formed when solid phosphorus (P4) reacts with fluorine gas (F2), resulting in the balanced equation: 4P4 + 10F2 → 4PF5.
- 😀 When balancing equations, ensure the number of atoms for each element is equal on both sides.
- 😀 Ionic compounds are formed using the crisscross method for balancing charges, as demonstrated with calcium nitride (Ca3N2).
- 😀 Knowledge of the solubility of compounds is essential; most ionic compounds are solids, while some are soluble in water.
- 😀 Understanding the difference between covalent and ionic compounds helps in predicting products of reactions, like in the case of sulfur trioxide (SO3).
- 😀 For double replacement reactions, it is crucial to predict products and balance the reaction, as shown with hydrochloric acid and barium hydroxide.
- 😀 Single replacement reactions require knowledge of the activity series to determine if a reaction will occur, such as zinc displacing hydrogen in hydrobromic acid.
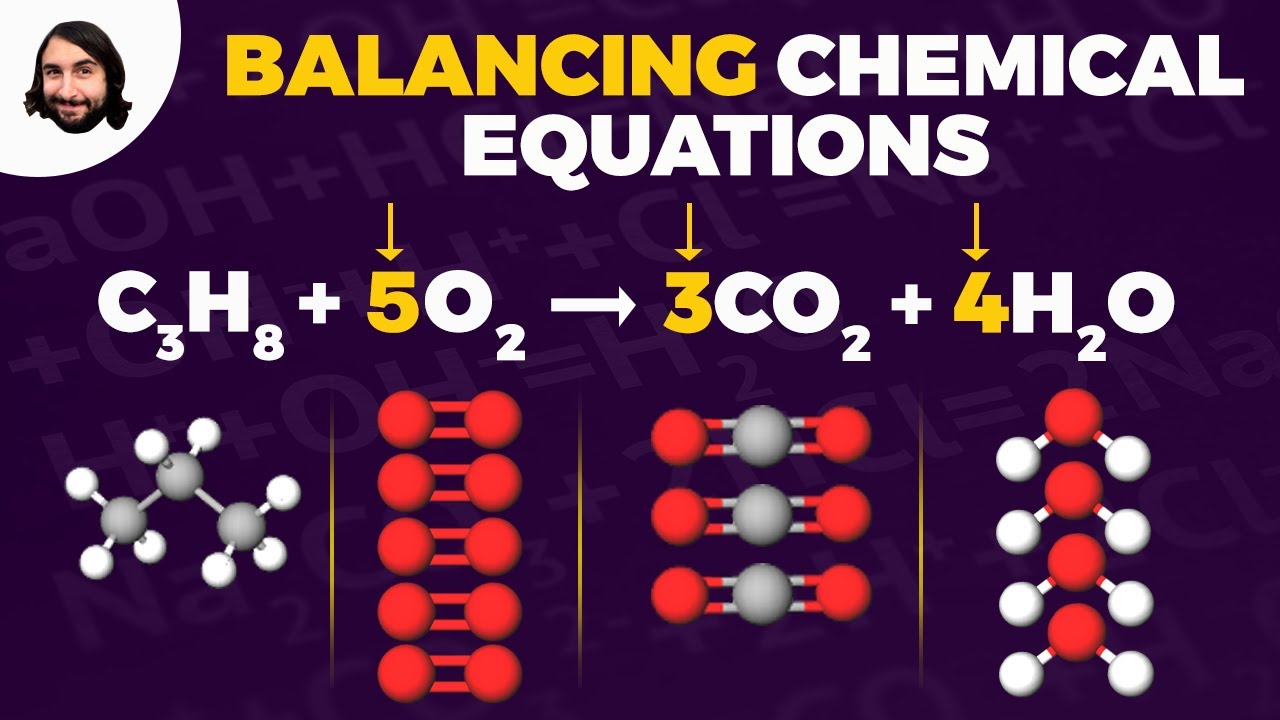
- 😀 Combustion reactions produce carbon dioxide and water, requiring balancing of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms systematically.
Q & A
What is the process for converting word descriptions into chemical equations?
-The process involves identifying the reactants and products from the word description, writing their chemical formulas, and then balancing the equation to ensure that the number of atoms for each element is equal on both sides.
What are the seven diatomic elements mentioned in the video?
-The seven diatomic elements are nitrogen (N2), oxygen (O2), fluorine (F2), chlorine (Cl2), bromine (Br2), iodine (I2), and hydrogen (H2).
How do you balance the equation for the reaction of phosphorus and fluorine?
-To balance the equation, you first identify the number of phosphorus and fluorine atoms on each side. You place a coefficient of 4 in front of PF5 to balance phosphorus, leading to 20 fluorine atoms, which requires a coefficient of 10 in front of F2 to balance fluorine.
What is the significance of using the crisscross method when writing chemical formulas?
-The crisscross method helps to determine the correct ratios of ions in ionic compounds by using the charges of the ions to find the subscripts needed for the formula, ensuring charge neutrality.
Why is calcium nitride considered an ionic compound?
-Calcium nitride is considered an ionic compound because it consists of a metal (calcium) and a nonmetal (nitrogen), and it forms through the transfer of electrons, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions.
How can you determine the state of a compound if it is not specified in the word description?
-If the state of a compound is not specified, you can often determine it based on the type of compound: ionic compounds are typically solids, while many molecular compounds are gases or liquids. You can also look up the compound online to find its state.
What is a double replacement reaction, and how do you predict the products?
-A double replacement reaction involves the exchange of ions between two compounds. To predict the products, you must identify the possible new pairs of ions formed and ensure that the products formed are stable and follow solubility rules.
What is the importance of knowing solubility rules in chemistry?
-Solubility rules help predict whether a compound will dissolve in water, which is essential for determining the phase (aqueous or solid) of compounds in a chemical reaction and understanding the reaction's outcome.
In a combustion reaction, what are the typical products formed?
-The typical products of a combustion reaction are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), formed when a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen.
How do you balance a combustion reaction like the burning of pentane?
-To balance a combustion reaction, start by balancing the carbon atoms first, followed by the hydrogen atoms, and finally balance the oxygen atoms last, adjusting coefficients as necessary to ensure that the number of atoms is equal on both sides.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
Balancing Chemical Equations

CBSE Class 10 Science - 1 | Chemical Reactions and Equations | Full Chapter | NCERT Animation

Penyetaraan Persamaan Reaksi Kimia dengan Cepat- Kimia Kelas 10

REACCIONES ORGANICAS DE COMBUSTIÓN | Ejercicios con Alcanos

GCSE Chemistry Revision "Balancing Chemical Equations"

Physical Science : 5 EASY STEPS in BALANCING EQUATIONS (TAGALOG) with Explanation and Full Examples
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
