Grade 10 Chemical Bonding: Introduction
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Miss Martins gives a concise introduction to chemical bonding. She explains that chemical bonds form when atoms of different elements come together, resulting in a chemical change and new compounds. The video covers types of bonds, including covalent (sharing electrons) and ionic (transfer of electrons), using examples like water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Miss Martins also discusses the importance of valence electrons in bonding and highlights the difference between compounds and molecules. Future videos will explore Lewis Dot diagrams and deeper concepts in bonding.
Takeaways
- 🔬 Chemical bonding involves a chemical change, where atoms of different elements bond to form a compound.
- 💧 An example of chemical bonding is the formation of water (H2O) from hydrogen and oxygen gases.
- 🧪 Atoms of different elements chemically bond to form compounds, while atoms of the same element bond to form molecules.
- 🧠 Atoms bond to achieve a noble gas structure, seeking stability by filling their outer energy levels.
- ⚛️ Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a non-metal, involving the transfer of electrons from one atom to another.
- 🔗 Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between two non-metals, forming a molecule or compound.
- 👩🏫 The periodic table helps identify metals and non-metals, where metals are generally on the left and non-metals on the right.
- ⚙️ Valence electrons (electrons in the outer energy levels) play a crucial role in bonding, whether they are shared (covalent) or transferred (ionic).
- 🔄 Ionic bonds form positive ions (cations) and negative ions (anions) due to electron transfer, leading to attraction between opposites.
- 📝 Understanding Lewis Dot diagrams is important to visualize how electrons are shared or transferred in covalent and ionic bonds.
Q & A
What is chemical bonding?
-Chemical bonding occurs when atoms of different elements come together and undergo a chemical change, forming a new product with different properties compared to the starting reactants.
Can you give an example of chemical bonding?
-An example of chemical bonding is the combination of hydrogen (H2) and oxygen (O2) to form water (H2O), a compound with different properties from the individual gases.
What is the difference between a compound and a molecule?
-A compound is formed when atoms of two or more different elements bond chemically, such as H2O or CO2. A molecule, on the other hand, is formed when two or more atoms of the same element bond, such as O2 or N2.
What is a diatomic molecule, and can you provide an example?
-A diatomic molecule consists of two atoms of the same element bonded together. Examples include oxygen gas (O2), nitrogen gas (N2), and hydrogen gas (H2).
Why do atoms bond with each other?
-Atoms bond with each other to achieve a noble gas structure, which makes them stable. They tend to bond in ways that fill their outer energy levels or orbitals, leading to greater stability.
What is ionic bonding?
-Ionic bonding occurs when electrons are transferred from one atom (usually a metal) to another atom (usually a non-metal), resulting in the formation of oppositely charged ions that attract each other, such as sodium (Na+) and chloride (Cl-).
What is covalent bonding?
-Covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms, typically between non-metals. This type of bonding results in the formation of molecules or compounds, such as H2O or HCl.
What is the purpose of Lewis Dot Diagrams?
-Lewis Dot Diagrams are visual representations that show how atoms bond by illustrating the sharing or transferring of valence electrons in covalent and ionic bonds.
How do you differentiate between metals and non-metals on the periodic table?
-Metals are found on the left side of the periodic table, while non-metals, along with hydrogen, are located on the right side. Hydrogen, although on the left, is a non-metal.
What are valence electrons, and why are they important in bonding?
-Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. They are crucial in bonding because they are the electrons that are either shared in covalent bonds or transferred in ionic bonds.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen
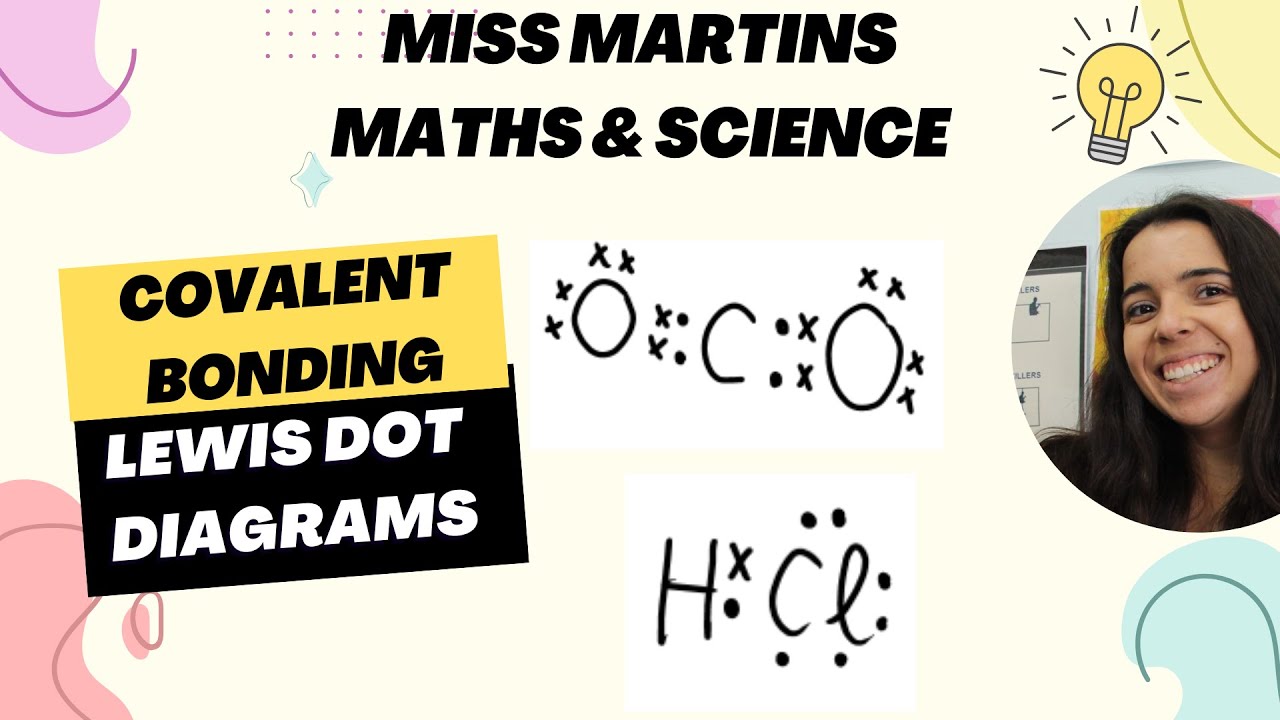
Chemical Bonding: Covalent Bonding Lewis Dot Diagrams
Grade 10 Physics Transverse waves Period and Frequency

Kinetic Molecular Theory grade 10 Introduction

BAB 5: UNSUR, SENYAWA DAN CAMPURAN | Part 1: UNSUR | IPA SMP Kelas 8 Kurikulum Merdeka

2.6 Introduction to Bonding

Ikatan Kimia • Part 1: Kestabilan Unsur, Lambang Lewis, dan Ikatan Ion
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
