2.6 Introduction to Bonding
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging video, the instructors explain the basics of chemical bonding, focusing on the three main types: ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. They highlight how atoms bond based on their electron interactions, using humor and relatable analogies like 'opposites attract' to make complex ideas more understandable. The video also touches on electronegativity, the ability of atoms to attract electrons, and compares atomic strength to well-known figures like The Rock. Overall, the lesson offers a light-hearted yet informative introduction to chemical bonding concepts.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chemical bonding involves the connections between atoms, often driven by the attraction between positively charged nuclei and negatively charged electrons.
- 🧑🔬 Atoms bond to achieve a full outer shell of eight electrons, known as the octet rule, which is key to chemical stability.
- ⚡ The three main types of chemical bonds are ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds, each involving different types of atoms.
- 🔗 Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a non-metal, where electrons are transferred from one atom to another.
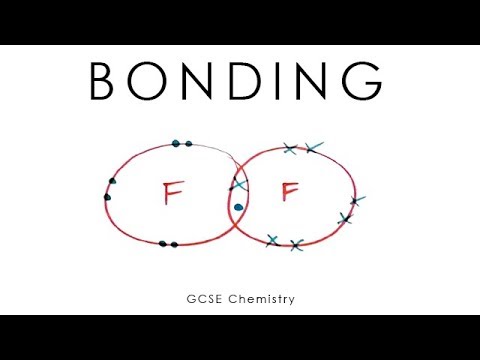
- 🤝 Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals, where atoms share electrons to satisfy the octet rule.
- 🔨 Metallic bonds occur between metals, where atoms share a pool of electrons, often described as a 'sea of electrons.'
- 📈 The strength of an atom's ability to attract electrons is called electronegativity, and this property plays a crucial role in determining bond type.
- 💪 In ionic bonding, one atom loses electrons (becoming positively charged), while the other gains electrons (becoming negatively charged).
- 🪙 In covalent bonding, both atoms share electrons equally or unequally, depending on their electronegativities.
- 🧲 The concept of electronegativity can be likened to strength—strong atoms like fluorine attract electrons easily, while weak atoms like francium do not.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is chemical bonding, specifically focusing on the three types of bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic.
What is a chemical bond?
-A chemical bond is a connection between atoms that occurs due to the attraction between their electrons and nuclei. It involves the outermost electrons, known as valence electrons.
Why are valence electrons important in bonding?
-Valence electrons are important because they are involved in the interactions between atoms. These electrons either transfer or share between atoms to help them achieve a full outer shell, typically containing eight electrons, which leads to stability.
What are the three major types of chemical bonds?
-The three major types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds.
What is an ionic bond, and between which types of elements does it occur?
-An ionic bond occurs between a metal and a non-metal. It involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another, where the metal loses electrons and becomes positively charged, while the non-metal gains electrons and becomes negatively charged.
What is a covalent bond, and which elements form it?
-A covalent bond is formed between two non-metal atoms. In this type of bond, the atoms share electrons instead of transferring them, allowing each atom to achieve a full outer electron shell.
What is a metallic bond, and how does it work?
-A metallic bond occurs between metal atoms. In this bond, the metal atoms share a 'sea' of delocalized electrons, which move freely between atoms, giving metals their properties such as conductivity and malleability.
How does electronegativity affect chemical bonding?
-Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a bond. Atoms with higher electronegativity, like fluorine, attract electrons more strongly, while those with lower electronegativity, like francium, attract electrons less strongly. The difference in electronegativity between atoms determines the type of bond they form.
What is the 'toddler principle of ownership' in the context of covalent bonds?
-The 'toddler principle of ownership' is a humorous analogy used to explain covalent bonding. It refers to the idea that in a covalent bond, two atoms share electrons, similar to how toddlers might both claim ownership of the same toy.
Why do atoms form chemical bonds?
-Atoms form chemical bonds to achieve a more stable electron configuration, typically a full outer shell of electrons, which makes them more energetically stable.
How are ionic bonds different from covalent bonds?
-Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between a metal and a non-metal, resulting in charged ions. Covalent bonds, on the other hand, involve the sharing of electrons between two non-metals without forming ions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Chemical Bonding | Chemistry

Chemical Bonding Explained | Ionic, Covalent and Metallic | GCSE Chemistry

Seri Kimia Dasar - Ikatan Kimia - perbedaan antara ikatan ionik, ikatan kovalen, dan ikatan logam

Types of Bonding (Ionic, Covalent, Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry Revision
Bonding (Ionic, Covalent & Metallic) - GCSE Chemistry - long version

enlace covalente 1a parte
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)