DNA, Chromosomes & Genes
Summary
TLDRDNA, the genetic code present in every cell, is organized into chromosomes, which are like neatly wound yarn balls. Humans have 46 chromosomes, inherited in 23 pairs from parents, with one from each. Genes, specific segments of DNA, dictate traits like eye color and insulin production, located on particular chromosomes. Each cell uses different genes, making us unique, as the combination of inherited chromosomes and genes shapes our characteristics.
Takeaways
- 🧬 DNA is the genetic code found in every cell of the body, acting as an instruction manual for all characteristics of a species.
- 🌀 DNA is organized into structures known as chromosomes, which are like neatly organized yarn balls compared to the messy stringy yarn of DNA.
- 🔢 Different species have varying numbers of chromosomes; humans have 46 chromosomes organized into 23 pairs.
- 🧵 Chromosomes are inherited from both parents, with one chromosome of each pair coming from the mother (egg) and one from the father (sperm).
- 🤝 During sexual reproduction, the chromosomes from the sperm and egg pair up to form a new DNA code in the offspring.
- 🧬 Genes are specific segments of DNA that code for particular traits, and they are located in specific places on specific chromosomes.
- 👁️ Scientists have mapped the exact locations of many human genes, such as the eye color gene on chromosome 15 and the insulin gene on chromosome 2.
- 🧪 All cells in the body contain a full copy of DNA, but different cells use different parts of the DNA to code for different structures and functions.
- 🌟 The unique combination of inherited chromosomes and genes determines the traits that make each individual unique.
- 🔑 DNA is highly organized, with specific genes located in precise positions on chromosomes, contributing to the complexity of genetic inheritance.
Q & A
What is DNA and where is it located in the human body?
-DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the genetic code found in every single cell of the human body. It is located inside a structure called the nucleus.
How is DNA organized within a cell?
-DNA is organized into structures called chromosomes. It is like a long, stringy yarn, while chromosomes are neatly organized yarn balls.
How many chromosomes do humans have?
-Humans have 46 chromosomes, which are organized into 23 pairs.
What is the significance of the number of chromosomes in different species?
-Different species have different numbers of chromosomes, which means their DNA is organized in different ways, contributing to their unique characteristics.
How are chromosomes inherited from parents to offspring?
-During sexual reproduction, the egg and sperm each carry single copies of chromosomes. When they unite, the chromosomes pair up, and a new DNA code is formed.
What is a gene and how is it related to DNA?
-A gene is a specific segment of DNA that codes for a particular trait. It is located in a specific place on a specific chromosome.
How are genes and chromosomes connected?
-Each chromosome contains many genes. Genes are the segments of DNA that have instructions to code for specific traits in the body.
What determines the traits that make each person unique?
-Inherited chromosomes and genes determine the traits that make each person unique. These traits are influenced by the combination of genes received from both parents.
Can you provide an example of a gene and its location on a chromosome?
-One example is the gene that controls eye color, which is located in a specific region on chromosome 15.
How does the body use the information in DNA?
-Different types of cells use different parts of the DNA to code for different structures. This means that while all cells carry a full copy of DNA, they use different genes to perform their specific functions.
What is the role of DNA in the process of reproduction?
-DNA is passed on from parents to offspring in the form of chromosomes. This genetic information is crucial for the development and characteristics of the offspring.
Outlines

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenMindmap

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenKeywords

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenHighlights

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenTranscripts

Dieser Bereich ist nur für Premium-Benutzer verfügbar. Bitte führen Sie ein Upgrade durch, um auf diesen Abschnitt zuzugreifen.
Upgrade durchführenWeitere ähnliche Videos ansehen

DNA: The book of you - Joe Hanson

GCSE Biology - DNA Part 1 - Genes and the Genome #63

BIOLOGIA - Lezione 5 - Il Nucleo e il DNA

Genetics Basics | Chromosomes, Genes, DNA and Traits | Infinity Learn
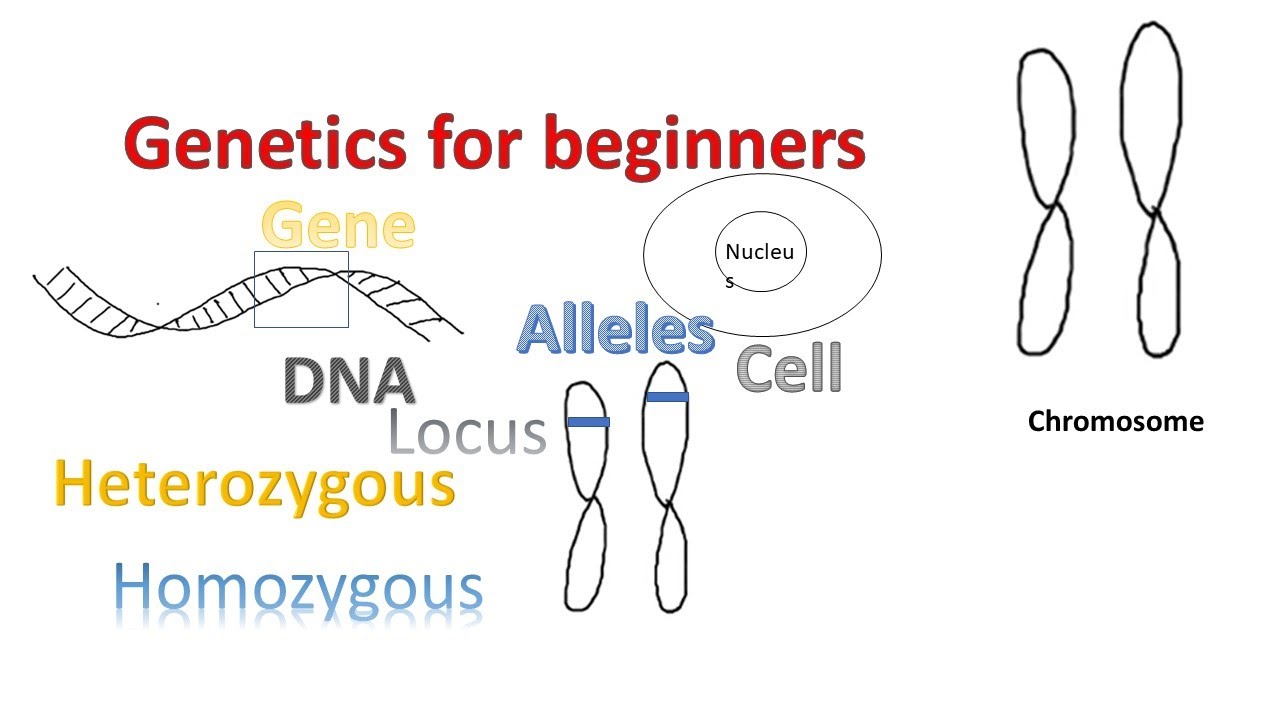
Genetics for beginners | Genes Alleles Loci on Chromosomes |

Comparing mitosis and meiosis | Cells | MCAT | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
