How SNMP Works - a quick guide
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a concise introduction to SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), covering its basics to help you start monitoring devices. It explains key terms like OIDs (Object Identifiers) and MIBs (Management Information Bases), and how SNMP works in practice, including polling and notifying methods. The video also discusses the different SNMP versions, highlighting the security advantages of version 3 over versions 1 and 2c. By the end, you'll understand how to use SNMP for monitoring network devices such as switches, routers, and servers.
Takeaways
- 📘 SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol, introduced in 1988.
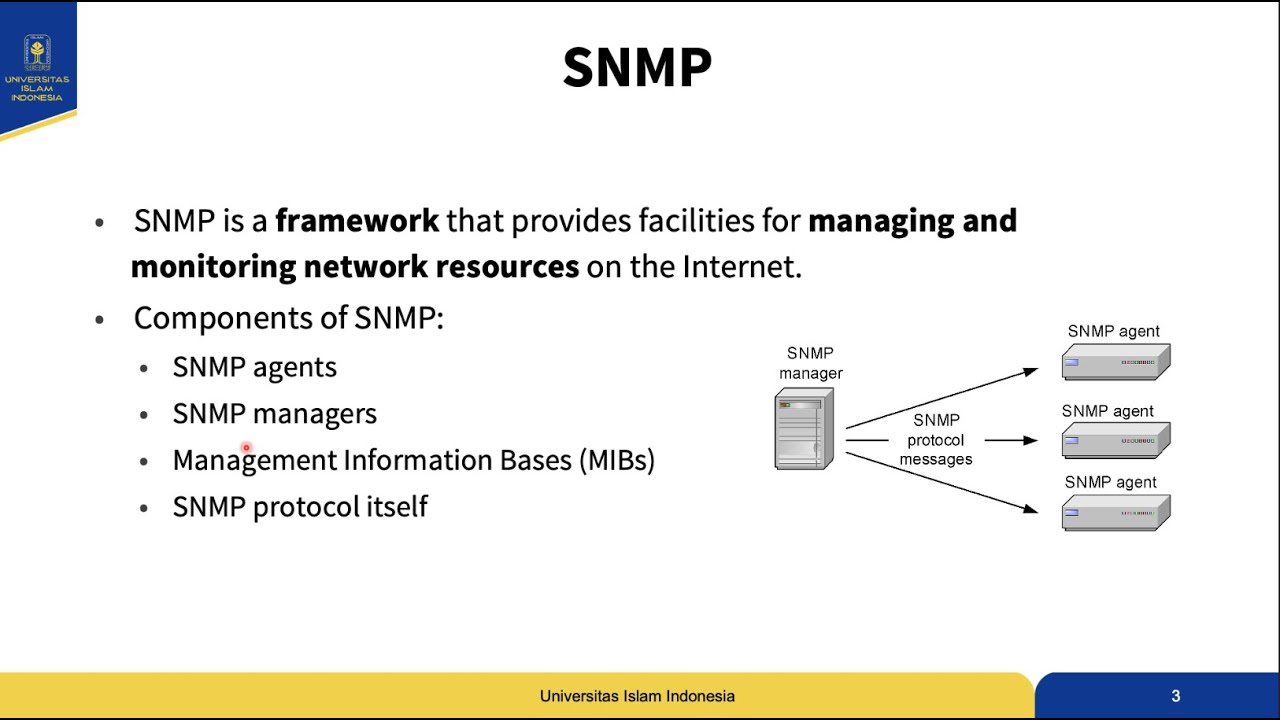
- 🔍 SNMP is used to monitor and modify settings on network equipment like switches, routers, and other devices.
- 🔑 Key terms to know: OID (Object Identifier) and MIB (Management Information Base).
- 🌡️ OIDs are unique identifiers for specific parameters on devices, such as temperature sensors.
- 📜 MIBs are text files that translate numerical OIDs into understandable names.
- 🖥️ Standard OIDs and MIBs are often built into SNMP implementations for basic monitoring.
- 🔄 SNMP can be used in two ways: polling (querying devices) and notifying (devices sending alerts).
- 🔐 There are three versions of SNMP: v1, v2c, and v3, with v3 being the most secure.
- 🛡️ Version 3 enhances security by requiring usernames, passwords, and offering encryption.
- ⚙️ Best practice is to use SNMP v3 whenever possible, although v2c is still commonly used.
Q & A
What does SNMP stand for?
-SNMP stands for Simple Network Management Protocol.
Since when has SNMP been in use?
-SNMP has been in use since 1988.
What was the initial purpose of SNMP?
-SNMP was initially developed to allow administrators to monitor networking equipment's current state and remotely modify settings and configurations on the equipment.
What are the two key terms introduced in the script related to SNMP?
-The two key terms introduced are OID (Object Identifier) and MIB (Management Information Base).
What is an OID in the context of SNMP?
-An OID is a numerical identifier used to represent anything and everything on a device that can be monitored with SNMP.
What is a MIB and why is it used?
-A MIB is a text file that allows us to translate numerical OIDs into more understandable names, making it easier to identify what is being monitored.
Why are MIBs considered helpful in SNMP monitoring?
-MIBs are helpful because they simplify the process of identifying and monitoring various parameters on a device by translating numerical OIDs into more comprehensible names.
What are the two primary methods by which SNMP can be used to monitor devices?
-The two primary methods are polling, where the network monitoring system requests information from the device, and notifying, where the device sends information to the monitoring system.
What is the main difference between SNMP versions 1 and 2c and version 3 in terms of security?
-Version 3 is more secure than versions 1 and 2c because it requires a username and password and offers encryption, whereas versions 1 and 2c only require a community string and do not offer encryption.
Why might some administrators still use SNMP version 2c despite the availability of version 3?
-Some administrators might still use SNMP version 2c because not all devices and operating systems support version 3, and it is often still considered sufficient for their needs.
What is the recommended best practice regarding the use of SNMP versions?
-The best practice is to use SNMP version 3 whenever possible due to its enhanced security features.
Where can one find information about OIDs and MIBs for specific devices?
-Information about OIDs and MIBs for specific devices can typically be found in the product manuals from the manufacturer, which are often available online.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)