KIAT CEPAT MEMILIH METODE RISET
Summary
TLDRThis video provides guidance on how to choose the appropriate research methodology based on factors like academic level, advisor support, and research interests. It explores different research paradigms, including deductive vs. inductive, qualitative vs. quantitative, and positivistic vs. phenomenological approaches. The speaker emphasizes the importance of aligning research objectives with the chosen methodology, taking into consideration time constraints, available resources, and personal skills. The video helps viewers understand how to select the best research method that fits their specific needs and context, ensuring a successful and efficient research process.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understanding different research paradigms is crucial when choosing a methodology. It depends on your academic level and the focus of your study.
- 😀 The method you choose should align with your academic program (S1, S2, or S3) and your supervisor's guidance.
- 😀 Deductive research is about confirming existing theories through real-world cases and is often used in quantitative studies.
- 😀 Inductive research builds theories from real-world data and is common in qualitative research.
- 😀 Quantitative research uses numerical data and statistical methods to confirm hypotheses, while qualitative research focuses on in-depth exploration and understanding of phenomena.
- 😀 If your research is focused on confirming or predicting outcomes, quantitative methods are best; if it’s exploratory, qualitative methods should be used.
- 😀 For quantitative research, use large sample sizes, standardized tools, and statistical analysis like SPSS.
- 😀 Qualitative research requires smaller sample sizes, in-depth interviews, and observational methods for data collection.
- 😀 Consider your research timeline: quantitative methods are faster to execute, while qualitative research takes longer to collect and analyze data.
- 😀 Your personal skills and strengths in communication and analysis should influence your choice between qualitative and quantitative methods.
- 😀 Be mindful of the context in which you're working: if the reality is complex and difficult to measure numerically, qualitative methods may be more suitable.
Q & A
What is the importance of understanding paradigms in research methodology?
-Understanding paradigms is essential in research methodology as it helps in defining the approach and perspective from which the researcher will view the research problem. Paradigms guide the researcher's understanding of reality and how to approach data collection and analysis, ensuring the research process is coherent and methodologically sound.
How do the research paradigms differ across undergraduate (S1), master’s (S2), and doctoral (S3) students?
-Undergraduate students (S1) tend to follow the research paradigm set by their supervisors, focusing more on confirming or testing existing theories. In contrast, master’s and doctoral students (S2 and S3) are encouraged to adopt more complex and abstract paradigms, often inductively developing theories from real-world cases and linking them to broader academic frameworks.
What is the difference between deductive and inductive research?
-Deductive research starts with a theory or hypothesis and tests it using empirical data, moving from general principles to specific cases. Inductive research, on the other hand, begins with observations or data and builds theories or generalizations from these specific cases.
What factors should a researcher consider when choosing between quantitative and qualitative research methods?
-Researchers should consider the research's objective (whether it is to explain or explore a phenomenon), the type of data (numerical vs. descriptive), and the available resources (such as time and expertise). Quantitative research is suitable for confirming theories and testing hypotheses, while qualitative research is more appropriate for exploring complex, context-dependent phenomena.
When is it appropriate to use a qualitative research approach?
-Qualitative research is suitable when the researcher aims to explore, interpret, and understand complex phenomena, especially when the data is subjective, contextual, and rich in detail. It is used to explore experiences, meanings, and relationships rather than to test or predict.
What are the characteristics of deductive and inductive reasoning in research?
-Deductive reasoning is characterized by a top-down approach, where a researcher starts with a theory and then tests its validity through observations. Inductive reasoning follows a bottom-up approach, where researchers gather data and then develop a theory based on that data.
How does the choice of research method relate to the researcher's ability to work with data?
-The choice between quantitative and qualitative methods depends largely on the researcher's ability to manage data. Quantitative research often requires skills in statistical analysis and handling large datasets, while qualitative research demands strong abilities in data interpretation, communication, and contextual analysis.
What role does the supervisor play in helping students choose the appropriate research method?
-The supervisor plays a crucial role in guiding students to choose the most suitable research method by considering the student’s research interests, academic level, and the nature of the research topic. The supervisor ensures that the chosen method aligns with the student's strengths and the project's objectives.
How do the researcher's epistemology and the choice of methodology relate to each other?
-A researcher’s epistemology, or their theory of knowledge, influences their choice of methodology. For example, a researcher who believes in objective, measurable truths will likely choose a positivist approach with quantitative methods. In contrast, a researcher who values subjective, contextual knowledge might prefer qualitative methods like phenomenology.
What are the key differences between positivism, rationalism, and phenomenology in research methodology?
-Positivism focuses on objective, quantifiable data and generalizable results, often using deductive reasoning. Rationalism emphasizes the role of logic and reason in understanding the world and may use both deductive and inductive methods. Phenomenology, however, seeks to understand lived experiences and focuses on subjective, context-specific data, using inductive methods to explore these experiences deeply.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Como surgem as ideias de pesquisa científica?
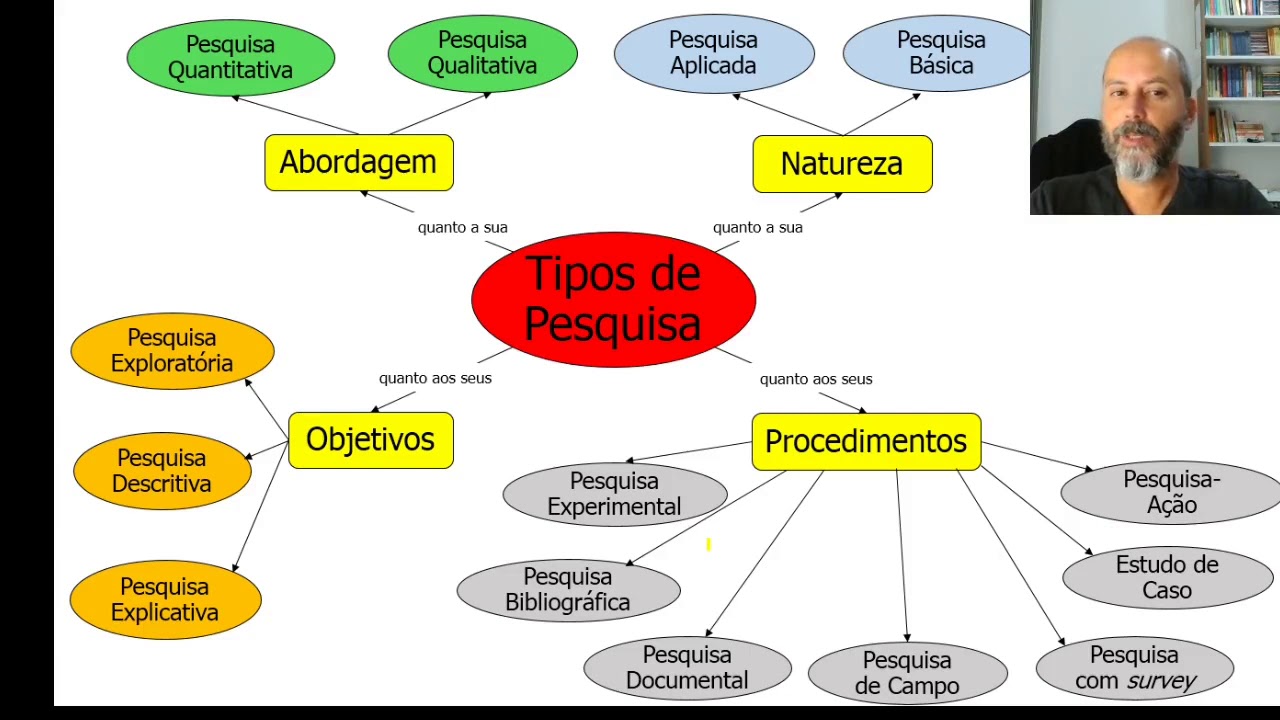
Tipos de Pesquisa

Jenis-Jenis Teknik Sampling & Kapan Menggunakannya? (Wajib Tahu Peneliti Kuantitatif & Kualitatif)

What Is Research Philosophy? Ontology, Epistemology, Deduction, Induction + More!

Cara Memilih Topik Penelitian Skripsi: Materi Kuliah Seminar MSDM

JUDUL SKRIPSI ANTI REVISI | LANGSUNG DI ACC LHO!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
