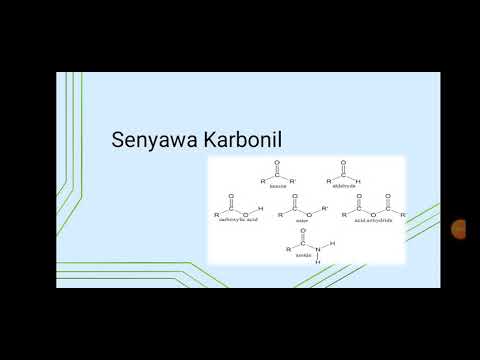
Senyawa Karbonil : Struktur, Sifat Fisika dan Reaksi Umum
Summary
TLDRThis organic chemistry lecture covers the fundamentals of carbonyl compounds, highlighting their importance in everyday life and their diverse applications. The video explains the basic structure and various types of carbonyl compounds, such as aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylates, along with their physical properties like boiling points and solubility. It also delves into key chemical reactions, including nucleophilic addition, substitution, and condensation, as well as alpha substitution reactions. The lecture aims to provide a thorough understanding of carbonyl compounds and their behavior in chemical reactions, essential for organic chemistry studies.
Takeaways
- 😀 Carbonyl compounds are present in everyday substances like citric acid (in lemon), acetaminophen (a painkiller), and polyester (used in clothing).
- 😀 The carbonyl group (C=O) is the functional group that defines carbonyl compounds and influences their properties and reactivity.
- 😀 Variations in the atoms or groups attached to the carbonyl carbon give rise to different types of carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and esters.
- 😀 The physical properties of carbonyl compounds, such as boiling points and solubility, vary depending on the structure and size of the molecule.
- 😀 Amides have the highest boiling points among carbonyl compounds due to strong dipole-dipole interactions, whereas alcohols form hydrogen bonds that contribute to high boiling points.
- 😀 Carbonyl compounds with fewer than four carbon atoms are generally soluble in water, while larger ones dissolve in organic solvents.
- 😀 Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions, where a nucleophile attacks the carbonyl carbon, forming a tetrahedral intermediate.
- 😀 Carboxylic acids and their derivatives undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions, where a leaving group is replaced by a nucleophile.
- 😀 The alpha substitution reaction occurs when a hydrogen atom adjacent to the carbonyl group is substituted by an electrophile.
- 😀 Carbonyl condensation reactions involve the combination of two carbonyl compounds, often resulting in a larger molecule, as seen in aldol condensation.
Q & A
What is the significance of carbonyl compounds in daily life?
-Carbonyl compounds are important in everyday life as they are present in various substances such as citric acid in fruits, acetaminophen (paracetamol) as a common medicine, and polyester used in clothing.
What is the basic structure of a carbonyl compound?
-The basic structure of a carbonyl compound consists of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom (C=O). The groups attached to the carbonyl carbon can vary, influencing the compound's reactivity.
How are carbonyl compounds classified based on their structure?
-Carbonyl compounds are classified into two main groups: Group 1 includes aldehydes and ketones, which have no leaving group; Group 2 includes carboxylates and derivatives such as esters, amides, and halides, where the carbonyl group has a leaving group and can undergo nucleophilic substitution.
Why do amides have higher boiling points than other carbonyl compounds?
-Amides have higher boiling points due to strong dipole-dipole interactions between molecules, which are stronger than the interactions seen in other carbonyl compounds like esters or ketones.
What factors influence the solubility of carbonyl compounds?
-The solubility of carbonyl compounds depends on their size and polarity. Compounds with fewer than four carbon atoms are soluble in water, while larger compounds are soluble in organic solvents like ethers and hydrocarbons.
How does the electronegativity of oxygen affect the reactivity of the carbonyl group?
-The high electronegativity of oxygen in the carbonyl group creates a partial positive charge on the carbon and a partial negative charge on the oxygen, making the carbonyl carbon electrophilic and susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
What happens during a nucleophilic addition reaction with carbonyl compounds?
-In a nucleophilic addition reaction, a nucleophile attacks the electrophilic carbonyl carbon, resulting in the formation of a tetrahedral intermediate. This reaction typically leads to the formation of alcohols.
What is the difference between nucleophilic addition and nucleophilic substitution reactions?
-In nucleophilic addition, the nucleophile adds to the carbonyl carbon, while in nucleophilic substitution, a leaving group is replaced by a nucleophile. Nucleophilic substitution occurs in carboxylic acid derivatives, which have a leaving group attached to the carbonyl carbon.
What is alpha substitution in carbonyl compounds, and how does it occur?
-Alpha substitution occurs when a nucleophile attacks the carbon atom adjacent to the carbonyl group (alpha position). This reaction typically requires the formation of an enol intermediate before proceeding to substitution.
What is carbonyl condensation, and how does it differ from other carbonyl reactions?
-Carbonyl condensation involves two carbonyl compounds reacting to form a larger molecule, often through a process like aldol condensation. This reaction can proceed via nucleophilic addition or substitution, depending on the type of carbonyl compound involved.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)