Metode Penelitian Antropologi (Kualitatif)
Summary
TLDRThis lecture discusses qualitative research methods in anthropology, focusing on key differences between qualitative and quantitative approaches. It explains that qualitative research relies on data from informants, who provide rich, detailed information through interviews and observation. The lecture highlights the use of various methods, such as participant observation, interviews, and listening, to gather data. It also explores the importance of analysis methods like descriptive qualitative analysis and various theoretical approaches like structuralism and functionalism. Overall, the lecture provides an in-depth look at qualitative anthropology research, emphasizing the depth of insight it offers into human behavior.
Takeaways
- 😀 Qualitative research methods in anthropology focus on understanding human behavior through detailed, descriptive data.
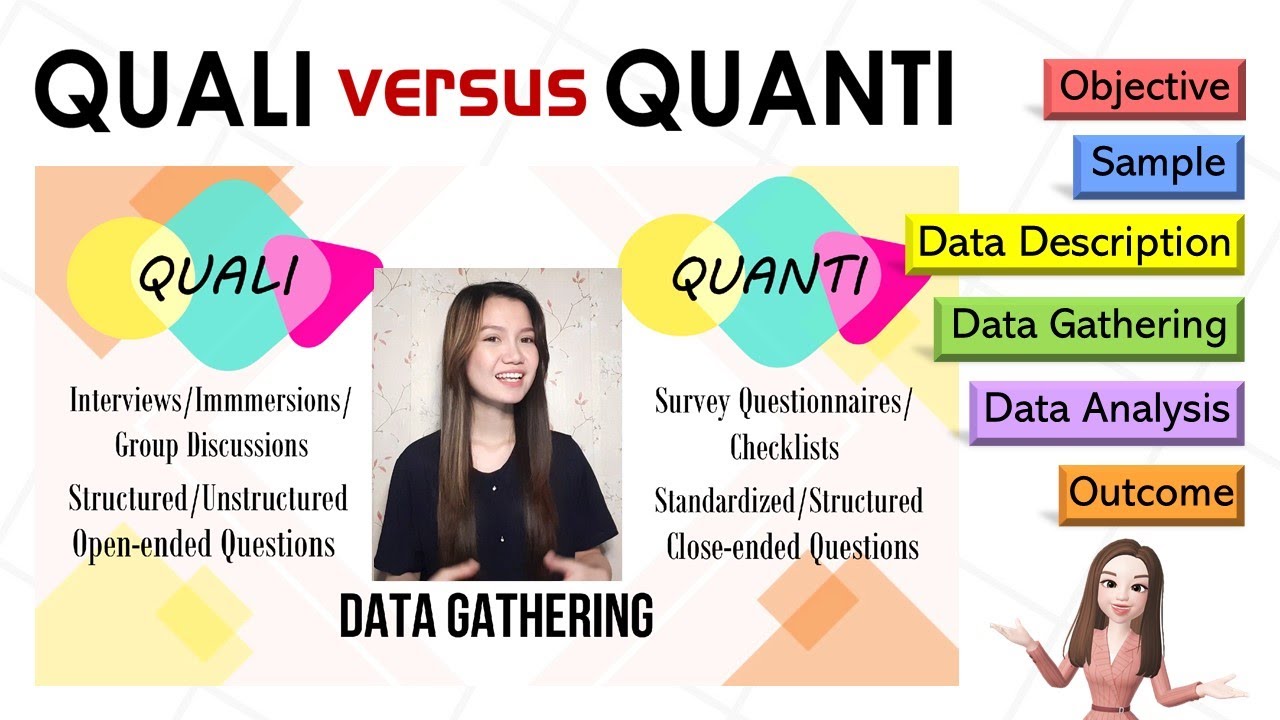
- 😀 The terms 'qualitative' and 'quantitative' refer to data types, not research methods. Qualitative research deals with narrative data, while quantitative research involves numerical data.
- 😀 Informants provide open-ended, rich information in qualitative research, whereas respondents answer predefined questions in quantitative research.
- 😀 The primary research instrument in qualitative research is an interview guide, which is a list of open-ended questions for informants.
- 😀 Improvisation is essential in qualitative interviews to elicit valuable information from informants, especially those who are talkative or reserved.
- 😀 Four primary methods for data collection in qualitative research are observation, interviews, participatory observation, and listening.
- 😀 Observational research involves watching informants’ activities relevant to the research topic to gain insights.
- 😀 Participatory observation means researchers engage directly in the informant's activities, like becoming a farmer or merchant to understand their experiences.
- 😀 Listening to informal conversations can also serve as a valuable data collection method, helping researchers capture natural interactions.
- 😀 Data analysis in qualitative research often uses descriptive methods, relying on the researcher’s theoretical approach (e.g., functionalism or structuralism) to interpret findings.
- 😀 Qualitative research methods are praised for their depth and ability to capture the complexities of human culture through immersive and flexible approaches.
Q & A
What is the focus of the lecture in this transcript?
-The focus of the lecture is on research methods in anthropology, specifically discussing qualitative research methods and how they differ from quantitative research methods.
How are qualitative and quantitative research methods different in anthropology?
-In anthropology, qualitative research is focused on gathering non-numerical data, such as interviews and observations, while quantitative research deals with numerical data, like surveys and questionnaires.
Why is 'qualitative' not considered a research method?
-'Qualitative' and 'quantitative' are not research methods, but types of data. The term 'method' refers to the process of gathering data, whereas 'qualitative' and 'quantitative' describe the nature of the data itself.
What is the difference between an informant and a respondent in qualitative and quantitative research?
-In qualitative research, the subject is called an informant, as they provide detailed, open-ended responses. In quantitative research, the subject is a respondent, who answers pre-set questions with limited response options.
What is an interview guide in anthropology research?
-An interview guide in anthropology is a list of open-ended questions designed to guide interviews with informants. It allows flexibility for the conversation to develop based on the informant’s answers.
How should a researcher handle informants who are either too talkative or too reserved?
-The researcher should use improvisation (improve) to manage the conversation, encouraging reserved informants to provide more information, while redirecting talkative informants to stay on topic.
What is 'participant observation' and why is it important in qualitative research?
-Participant observation involves the researcher actively engaging in the informant's activities to better understand their experiences. It provides deeper insights into the context of the informant’s actions and is a key technique in qualitative research.
What types of data are typically gathered in qualitative anthropology research?
-In qualitative anthropology, data typically consists of statements from informants about their experiences, behaviors, and perceptions, as well as descriptions of social phenomena.
What methods are used for data collection in qualitative anthropology research?
-Data collection methods in qualitative anthropology include observation, interviews (both in-depth and brief), participation in activities, and listening to conversations, depending on the context and the type of data needed.
How is data analyzed in qualitative anthropology research?
-Data in qualitative anthropology is usually analyzed using descriptive qualitative analysis, where the researcher interprets the data based on specific theoretical frameworks or approaches, such as functionalism or structuralism.
Outlines

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنMindmap

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنKeywords

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنHighlights

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنTranscripts

هذا القسم متوفر فقط للمشتركين. يرجى الترقية للوصول إلى هذه الميزة.
قم بالترقية الآنتصفح المزيد من مقاطع الفيديو ذات الصلة

Comparing Qualitative and Quantitative UX Research

Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Qualitative And Quantitative Research Methods | Simplilearn

Materi 7: Metode Penelitian Kualitatif #edukasi #riset #fenomenologi #etnografi #studikasus

Overview of Qualitative Research Methods

PERBEDAAN KUALITATIF DAN KUANTITATIF | MAHASISWA TINGKAT AKHIR
PRACTICAL RESEARCH 1 - Qualitative and Quantitative Research - EP.5 (Research Simplified)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
