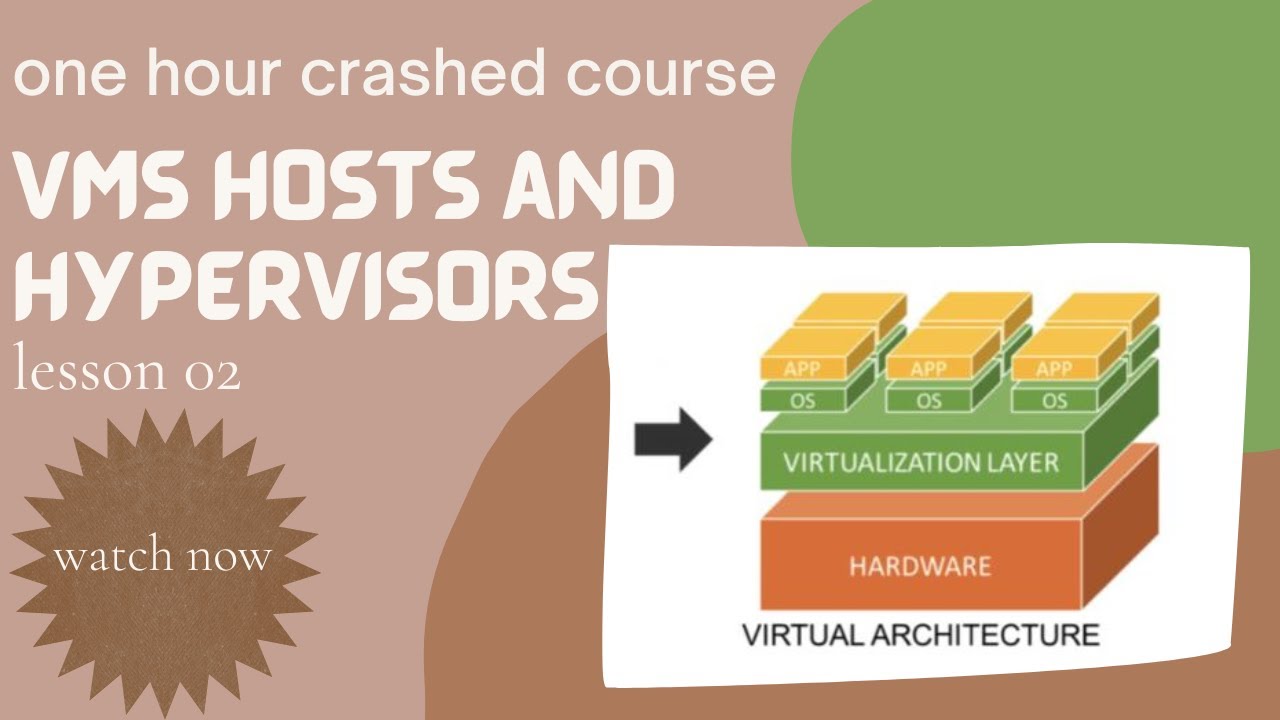
Virtual machines
Summary
TLDRVirtualization technology allows multiple systems, known as Virtual Machines (VMs), to run on the same hardware, optimizing resource utilization. Google Cloud's Compute Engine enables users to create and manage VMs, offering flexibility in configuration and cost-effective options like preemptable and spot VMs. Billing is based on usage, with discounts for sustained use and committed use.
Takeaways
- 💻 Virtualization technology allows multiple systems (Virtual Machines or VMs) to run on the same hardware, optimizing resource utilization.
- 🌐 Google Cloud's Compute Engine is an infrastructure-as-a-service product that enables users to create and manage VMs on Google's infrastructure.
- 💼 There are no upfront investments required for using Compute Engine, making it a flexible and cost-effective solution for running VMs.
- 🚀 Compute Engine supports thousands of virtual CPUs on a system designed for speed and consistent performance.
- 🖥️ Each VM in Compute Engine has the capabilities of a full-fledged operating system, allowing for extensive configuration options.
- 🛠️ VM instances can be created through the Google Cloud Console, Google Cloud CLI, or through infrastructure automation tools like Terraform or the Compute Engine API.
- 🔌 APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are crucial for enabling communication between different software programs, and they play a significant role in managing VMs.
- ⏱️ Compute Engine bills by the second with a one-minute minimum, and sustained use discounts automatically apply for VMs running over 25% of a month.
- 💰 Committed use discounts are available for users who commit to using resources for one or three years, offering savings over on-demand prices.
- 🏃♂️ Preemptable and spot VMs can significantly reduce costs for workloads that do not require immediate completion, such as batch jobs.
- 🔄 Spot VMs offer more flexibility than preemptable VMs, with no maximum run time, although they can still be terminated if resources are needed elsewhere.
Q & A
What problem did virtualization technology solve for organizations?
-Virtualization technology relieved the pressures of tightly binding specific computing hardware resources to specific applications, allowing multiple systems to run on the same hardware.
What are Virtual Machines (VMs)?
-Virtual Machines (VMs) are systems that share the same pool of processing, storage, and networking resources, enabling organizations to run multiple applications simultaneously on a server efficiently and manageably.
What is Google Cloud's Compute Engine?
-Compute Engine is Google Cloud's infrastructure as a service (IaaS) product that lets users create and run virtual machines on Google's infrastructure without upfront investments, offering fast and consistent performance.
How can a virtual machine be configured?
-A virtual machine can be configured much like a physical server by specifying the amount of CPU power, memory, storage, and the operating system needed.
What tools can be used to create a virtual machine instance on Google Cloud?
-A virtual machine instance can be created through the Google Cloud Console, the Google Cloud CLI command line interface, or using infrastructure automation tools such as Terraform or the Compute Engine API.
How does Compute Engine's billing work for virtual machines?
-Compute Engine bills by the second with a one-minute minimum. Sustained use discounts start to apply automatically to virtual machines that run for more than 25% of a month, and additional discounts are applied for each incremental hour of use.
What are committed use discounts in Compute Engine?
-Committed use discounts offer reduced prices when users commit to using resources for either a one-year or three-year period.
What are preemptable and spot VMs, and how do they differ from regular VMs?
-Preemptable and spot VMs are types of virtual machines that can be terminated by Compute Engine if their resources are needed elsewhere. They offer cost savings but need to ensure jobs can be stopped and restarted without impact. Spot VMs offer more features than preemptable VMs, such as no maximum run time.
What is a key difference between preemptable and spot VMs?
-A key difference is that preemptable VMs can only run for up to 24 hours at a time, whereas spot VMs do not have a maximum run time.
How can users choose the machine properties of their virtual machine instances on Compute Engine?
-Users can choose the machine properties of their instances by selecting from predefined machine types or by creating custom machine types, specifying the number of virtual CPUs, operating system, and amount of memory.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)