Physical Layer and Media (Part 2)
Summary
TLDRThis educational session delves into the fundamentals of the physical layer of communication, focusing on analog and digital signals. It explains the nature of these signals, using examples like room temperature variation to illustrate signal representation. The session further explores various physical media, including copper cables, fiber optics, and wireless transmission, detailing their components and signaling methods. By comparing these media, learners gain insights into the differences and applications of each, enhancing their understanding of signal transmission in modern communication systems.
Takeaways
- 📶 The session aims to teach learners about analog and digital signals, different physical layer media, and how to compare them.
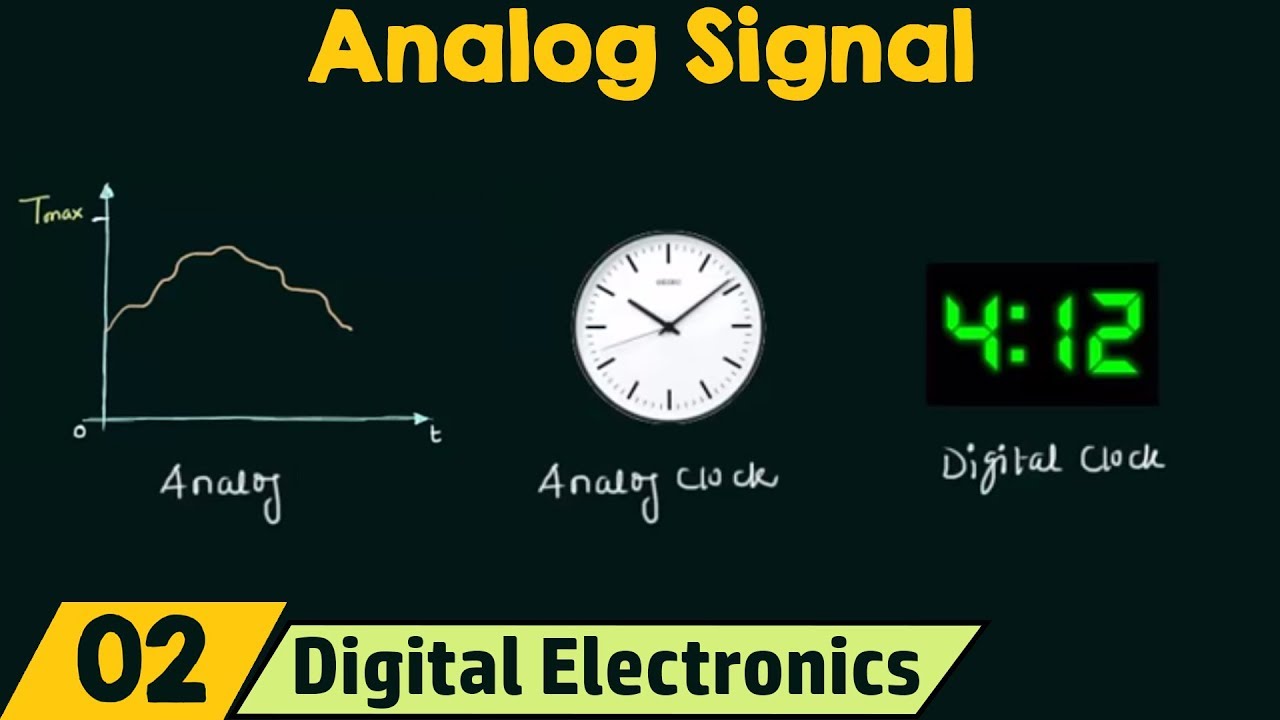
- 📉 A signal represents the variation of a physical quantity over time, such as the change in room temperature throughout a day.
- 🔁 Analog signals can take any value within a defined range and are continuous, representing real-life phenomena like colors, temperature, and sound.
- 🔢 Digital signals are discrete, taking on a finite number of values at any given time, and are used in systems that require time and magnitude discretization.
- 📈 The physical layer media can be categorized into wired and wireless, with each focusing on the transmission of signals.
- 🛰 Wired media includes copper cables, which can be either Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) or Shielded Twisted Pair (STP), and are used for electrical signal transmission.
- 🌐 Fiber optic cables are another type of wired media that transmit light signals, using either single mode or multimode fibers, and require specific components like lasers or LEDs.
- 🔌 Connectors such as RJ45 for UTP and specific NICs are essential physical components for establishing connections in wired networks.
- 📡 Wireless media relies on access points for devices like mobile phones to connect to networks via Wi-Fi, using radio waves for signaling.
- 📳 Wireless NICs in devices convert data into radio waves for transmission, requiring components like radios and antennas for communication.
- 🔄 The comparison of physical media highlights the differences in signaling methods, with copper using electromagnetic signals and fiber optics using light pulses, while wireless uses radio waves.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the session on the physical layer and media?
-The session focuses on understanding analog and digital signals, knowing various physical layer media, and comparing different physical media.
What is a signal in the context of the physical layer?
-A signal is a function that represents the variation of a physical quantity with respect to time, such as the change in room temperature over a 24-hour period.
What are the two kinds of signals discussed in the session?
-The two kinds of signals discussed are analog signals and digital signals.
How is an analog signal defined in the session?
-An analog signal is defined as a signal that can take any value in the defined range and is continuous in nature, representing real-life phenomena like colors, temperature, and sounds.
What is the key difference between an analog and a digital signal?
-The key difference is that an analog signal can take any value within a range and is continuous, while a digital signal can only take on a finite number of values at a given time, discretizing both time and magnitude.
What are the physical components involved in copper cable communication?
-The physical components in copper cable communication include Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP), Shielded Twisted Pair (STP), coaxial cables, connectors like RJ45, and Network Interface Cards (NICs).
What are the types of fiber optic cables mentioned in the session?
-The types of fiber optic cables mentioned are single mode fiber, which produces a single straight path for light, and multimode fiber, which allows multiple paths and can result in dispersion.
What is the main physical component required for fiber optic communication?
-The main physical components required for fiber optic communication are lasers or light-emitting diodes to generate light signals.
What is the role of an access point in wireless media?
-An access point in wireless media serves as a connection point for devices like mobile phones, allowing them to connect to a network via Wi-Fi.
How do wired and wireless media differ in terms of the signals they use?
-Wired media, such as copper cables, use electromagnetic signals, while wireless media use radio waves to transmit information.
What is the purpose of a Network Interface Card (NIC) in wireless communication?
-In wireless communication, a NIC converts the physical data into radio waves, allowing the transmission of data through the air via antennas.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)