Sistema de Informação Geográfica (SIG)
Summary
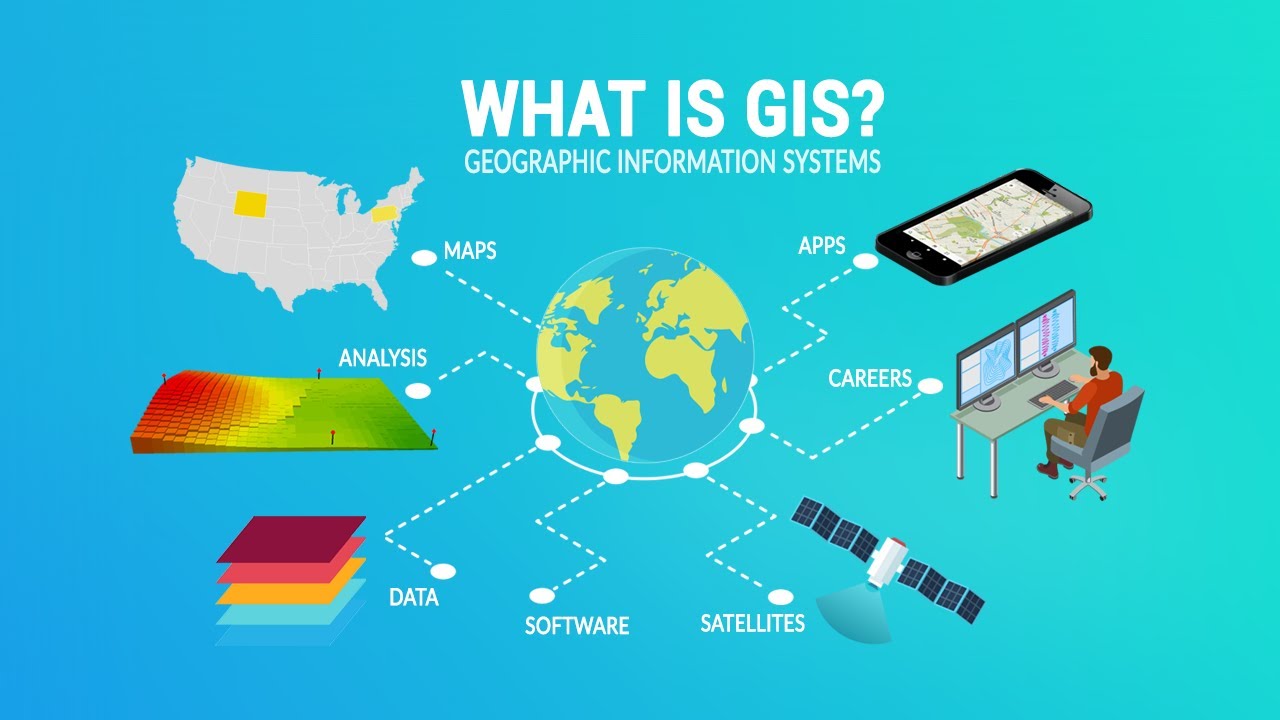
TLDRThis lecture provides a comprehensive overview of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and geoprocessing, exploring how GIS integrates geographic and descriptive data for analysis and decision-making. It covers essential concepts such as data structures (vector and matrix), spatial referencing, and methodologies used in geospatial analysis. The speaker explains the role of different software and hardware tools in processing and visualizing spatial data, highlighting the importance of accurate data collection methods, including satellite imagery and GPS. The lecture also differentiates between three key user groups: geomatics specialists, thematic users, and general users, each contributing uniquely to GIS applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 GIS (Geographic Information Systems) link geographic data with descriptive information, enabling decision-making and spatial analysis.
- 😀 GIS processes geospatial data collected through various methods, such as satellites, drones, and GPS, into usable information for different applications.
- 😀 Vector and raster (matrix) data structures are key in geospatial processing, with vector data represented as points, lines, and polygons, and raster data as images or grid cells.
- 😀 GIS operates using layers, allowing different types of information (e.g., land use, terrain slope) to be analyzed separately or together for a more comprehensive understanding.
- 😀 Good hardware is essential for efficient GIS analysis, enabling quick processing and reliable results.
- 😀 Different methods of data collection in GIS include satellite imagery, drone technology, GPS, and topographic surveys, all of which provide georeferenced data.
- 😀 GIS is used by three main groups: geomatics (focused on developing GIS tools and technologies), thematic users (who apply GIS for specific tasks like land use planning), and general users (who may lack technical GIS knowledge).
- 😀 Methodologies for GIS analysis vary based on the project's goals, such as studying land use, monitoring deforestation, or making agricultural recommendations.
- 😀 GIS software includes both paid (e.g., ArcGIS) and free (e.g., QGIS) options, with each offering unique features and functionalities for processing spatial data.
- 😀 The power of GIS lies in its ability to integrate spatially referenced geographic data with descriptive information, providing actionable insights for decision-making.
Q & A
What is the main goal of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)?
-The main goal of GIS is to integrate geographic data with descriptive information to support decision-making processes, particularly in areas like land management, urban planning, and environmental monitoring.
How is georeferencing important in GIS?
-Georeferencing ensures that spatial data is linked to real-world locations accurately, which is crucial for mapping and analyzing geographic features.
What are the key components of GIS?
-The key components of GIS include data, hardware, software, and human resources. Data refers to spatially referenced information, hardware is needed to process and store the data, software facilitates spatial analysis, and human resources consist of specialists, users, and analysts.
What types of data does GIS use?
-GIS uses both vector data (points, lines, and polygons) and matrix data (raster images such as satellite imagery) to represent geographic features and phenomena.
Which software tools are commonly used in GIS?
-Common GIS software tools include ArcGIS (paid), QGIS (open-source), and Spring (used for image processing), along with other tools like ERDAS Imagine or ENVI for digital image processing.
What are the roles of the different human resource groups in GIS?
-In GIS, geomatics groups develop new GIS tools and technologies, thematic users apply GIS to specific fields like agriculture or land management, and general users utilize GIS for basic tasks or data analysis.
How is satellite imagery used in GIS?
-Satellite imagery provides valuable spatial data that can be used to monitor land use, track deforestation, urbanization, and other environmental changes. It is often free and widely accessible for analysis.
What methodologies are commonly used in GIS for spatial analysis?
-Common GIS methodologies include overlaying data layers, performing buffer analyses, and executing spatial queries such as clipping or zoning to extract meaningful patterns and insights from geographic data.
How does QGIS compare to other GIS software like ArcGIS?
-QGIS is a free and open-source alternative to ArcGIS, which is paid software. While QGIS is widely used for general GIS tasks and is highly customizable, ArcGIS offers more comprehensive features and support for advanced users, particularly in professional and enterprise environments.
Why is it important to have different levels of GIS expertise in a project?
-Different levels of expertise ensure that GIS projects are approached with the appropriate knowledge. Geomatics experts develop tools and analyze complex data, thematic users apply GIS to specific disciplines, and general users can operate the software for more straightforward tasks.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)