Apa sih Perhutanan Sosial itu??
Summary
TLDRThe social forestry program in Indonesia is a sustainable forest management initiative that empowers local and customary law communities to manage state and customary forests. Aimed at improving community welfare and forest conservation, it was formalized under Law No. 41 of 1999 and further defined in Regulation No. 9 of 2021. With a target of 12.7 million hectares by 2030, the program seeks to balance social and environmental benefits. Progress has been made, but the government acknowledges the need for accelerated efforts, such as through the 2023 Presidential Regulation, to address conflicts and streamline forest management processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Social Forestry (SOP) is a sustainable forest management system implemented by local communities in Indonesia's state, rights, or customary forests to improve welfare, environmental balance, and socio-cultural dynamics.
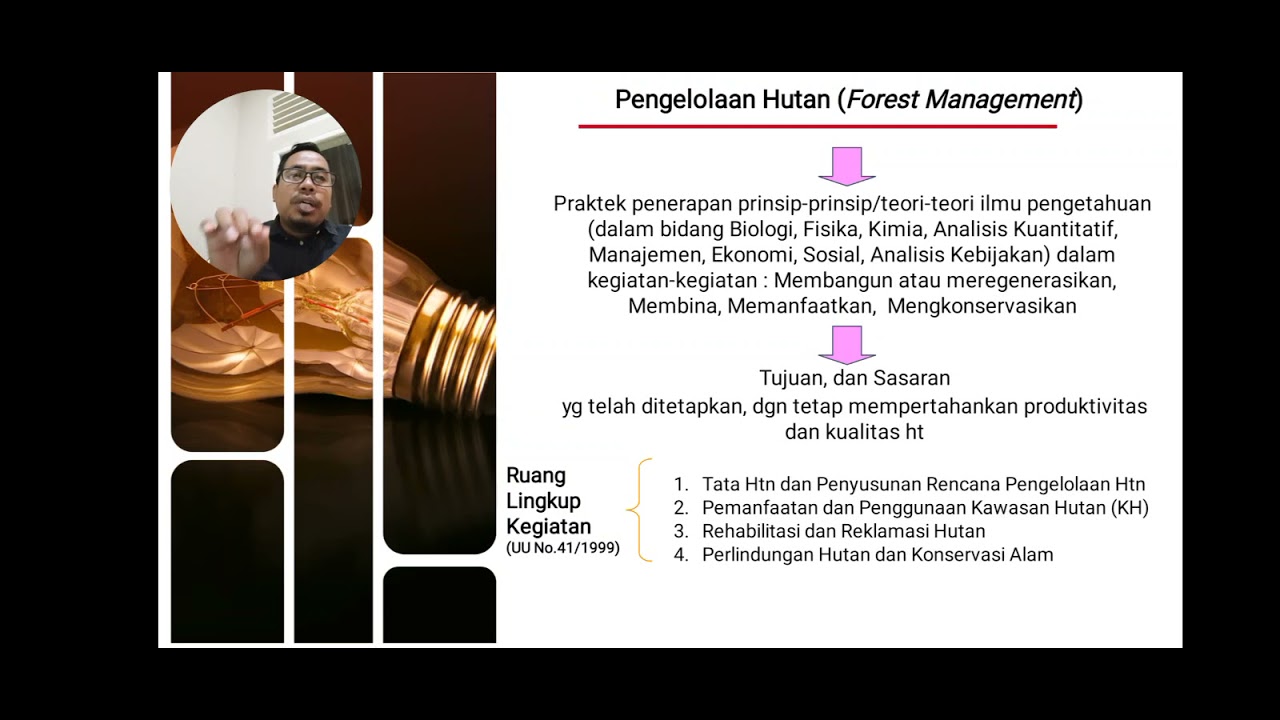
- 😀 The social forestry program began with the enactment of Law Number 41 of 1999 on Forestry, with significant developments following the Indonesian reform era.
- 😀 Since 2017, over 239,000 families have been granted legal access to manage the nation's forest areas, while more than 2,460 groups have been socialized and facilitated by the program.
- 😀 To participate in social forestry, communities must prove their identity as Indonesian citizens living around or within state forest areas, with a history of forest cultivation and dependence on the forest ecosystem.
- 😀 The program’s main agendas are improving the welfare of surrounding communities and creating an effective forest resolution model.
- 😀 Social forestry is implemented through various schemes, including village forests, community forests, community plantation forests, customary forests, and forestry partnerships.
- 😀 The government has set a target of 12.7 million hectares for social forestry by 2030, aiming to accelerate forest area management.
- 😀 As of October 2022, 5.1 million hectares of the target have been achieved, indicating that there's still significant progress to be made.
- 😀 The Indonesian government has introduced Presidential Regulation No. 28/2023 to accelerate the achievement of the 12 million hectare target by focusing on priority scales, legal access, land conflict resolutions, and strengthening forest management mechanisms.
- 😀 Public participation and feedback are encouraged, with calls to share opinions about the effectiveness of current social forestry management practices.
Q & A
What is social forestry, as defined by the regulation in Indonesia?
-Social forestry, according to the Minister of Environment and Forestry Regulation Number 9 of 2021, is a sustainable forest management system carried out by local communities or customary law communities in state forest areas, rights forests, or customary forests. The aim is to improve welfare, balance the environment, and support socio-cultural dynamics.
When did the social forestry program first start in Indonesia?
-The social forestry program in Indonesia began after the enactment of Law Number 41 of 1999 concerning forestry. The program gained momentum following the reform period and continued to develop through 2017.
How many families and groups have been involved in the social forestry program by 2017?
-By 2017, as per the Ministry of Environment and Forestry, 239,341 families were granted legal access to manage forest areas, and 2,460 groups were socially assisted and facilitated by the program.
Who can apply for social forestry, and what are the basic requirements?
-Social forestry can be proposed by Indonesian citizens who live around forest areas, or within state forest areas. Applicants must prove their identity with an ID card and demonstrate a history of forest area cultivation and dependency on the forest ecosystem.
What are the primary goals of the social forestry program?
-The two main goals of the social forestry program are to improve the welfare of communities living around forests and to create an effective model for forest resolution and management.
What schemes are included in Indonesia's social forestry program?
-The social forestry program includes several schemes such as village forests, community forests, community plantation forests, customary forests, and forestry partnerships.
What is the government's target for social forestry in terms of land area?
-The Indonesian government has targeted the allocation of 12.7 million hectares of forest area for social forestry management.
What is the current progress of the social forestry program as of October 2022?
-As of October 1, 2022, the social forestry program has successfully reached 5.1 million hectares of forest area, which is less than half of the government’s target.
What steps has the government taken to accelerate the social forestry program?
-To accelerate the program, the government issued Presidential Regulation Number 28 of 2023. This regulation aims to integrate planning for social forestry and improve the management process, including resolving land tenure conflicts, strengthening mechanisms, and speeding up the granting of forest management approvals.
What are some of the challenges faced in the social forestry program?
-Despite the government's efforts, the social forestry program faces challenges such as slow progress in achieving the target area, unresolved land tenure conflicts, and the need for more efficient implementation of forest management approval processes.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Hutan Kemasyarakatan di Papua - Community Forestry in Papua (english sub)

Kearifan Lokal Masyarakat Kenegerian Rumbio | Bingkai Sumatera

Advokasi Pengakuan Hutan Adat MHA Benuaq Madjaun dan Benuaq Telimuk

Pertemuan Ke 11

Terobosan Penting! Agroforestry Tebu Mandiri dalam Rangka Dukung Program Ketahanan Pangan
kebijakan Kehutanan Part 5
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
