Analisis Data Panel Dinamis GMM bagian 1
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth tutorial on dynamic panel data regression methods. It covers the motivation behind using dynamic panels, such as controlling for endogeneity and country-specific effects. The content explores features of dynamic panel models, including the differences between fixed and random effects. The video also delves into the Generalized Method of Moments (GMM) for estimation and compares macro and micro panels, highlighting their distinct characteristics. Additionally, the tutorial touches on error structures, the use of software tools for estimation, and various dynamic model techniques like difference GMM and system GMM, offering a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Takeaways
- 😀 Dynamic panel data models are used to address endogeneity and control for country-specific effects in regression analysis.
- 😀 GMM (Generalized Method of Moments) is an important estimation method for dynamic panel models, ensuring consistent estimates even with endogenous variables.
- 😀 The motivation behind using dynamic panel models is to account for variables that change over time, especially in dynamic processes like banking and finance.
- 😀 Data for dynamic panel models must be structured correctly, with attention to the theoretical model and whether it involves dynamic features.
- 😀 Macro panels typically involve country-level or regional data with longer time periods, while micro panels focus on individual or household-level data, often from surveys.
- 😀 Fixed effects and system GMM methods are essential techniques for estimating dynamic panel models, with differences in how they handle the error structure.
- 😀 The primary difference between static and dynamic panel models is the inclusion of lagged dependent variables in the dynamic models.
- 😀 In macro panels, the number of countries or entities (N) is often less than 100, whereas micro panels can involve thousands of individuals with more frequent data points.
- 😀 The session distinguishes between balanced and unbalanced panels, with balanced panels having data for all entities across all periods, and unbalanced ones not necessarily having full data coverage.
- 😀 Real-world examples of dynamic panel models include employment equations and economic factors such as gross capital and real GDP.
- 😀 Understanding the structure of the error term in dynamic panel models is key to applying proper estimation techniques like differenced GMM or system GMM.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture?
-The lecture focuses on dynamic panel data regression techniques, particularly on methods like GMM (Generalized Method of Moments), the use of dynamic panels, and how to interpret results from dynamic panel models.
Why is dynamic panel data used in regression analysis?
-Dynamic panel data is used to control for endogeneity, as it can help address the simultaneous correlation between the dependent variable and explanatory variables, which may not be observed with static models.
What are the key features of dynamic panel models mentioned in the lecture?
-The key features include handling endogenous explanatory variables, controlling for country-specific effects, and capturing dynamic relationships such as past period influences on current variables.
What does the term 'endogeneity' refer to in the context of dynamic panel models?
-Endogeneity refers to a situation where explanatory variables are correlated with the error term, which can lead to biased and inconsistent estimates in regression models.
What is the role of GMM (Generalized Method of Moments) in dynamic panel data models?
-GMM is used to estimate dynamic panel data models by providing consistent estimators, even when there is endogeneity or when the data contains measurement errors or omitted variables.
How do macro and micro panels differ in the context of dynamic panel models?
-Macro panels typically involve data with fewer time periods (usually related to countries or larger groups), while micro panels involve more granular data with many individual observations over a longer period of time, often from surveys.
What are the challenges associated with macro panel data mentioned in the lecture?
-Macro panel data often faces issues such as limited variability across the panel units (e.g., countries), and using instruments like fixed effects to address these challenges can require complex model adjustments.
What is the difference between 'short' and 'long' panels in dynamic panel data models?
-A 'short panel' has fewer time periods (usually less than 10), often with cross-sectional data, whereas a 'long panel' has more time periods, allowing for more dynamic analysis over time.
What is the significance of using fixed effects in dynamic panel data models?
-Fixed effects help account for individual-specific heterogeneity by controlling for unobserved variables that do not change over time, thus improving the accuracy of the model estimates.
What are the three main components of the error term in a dynamic panel model?
-The three components are the individual-specific effect (lambda), the time-invariant error, and the random error, all of which contribute to the overall error term in the model.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频
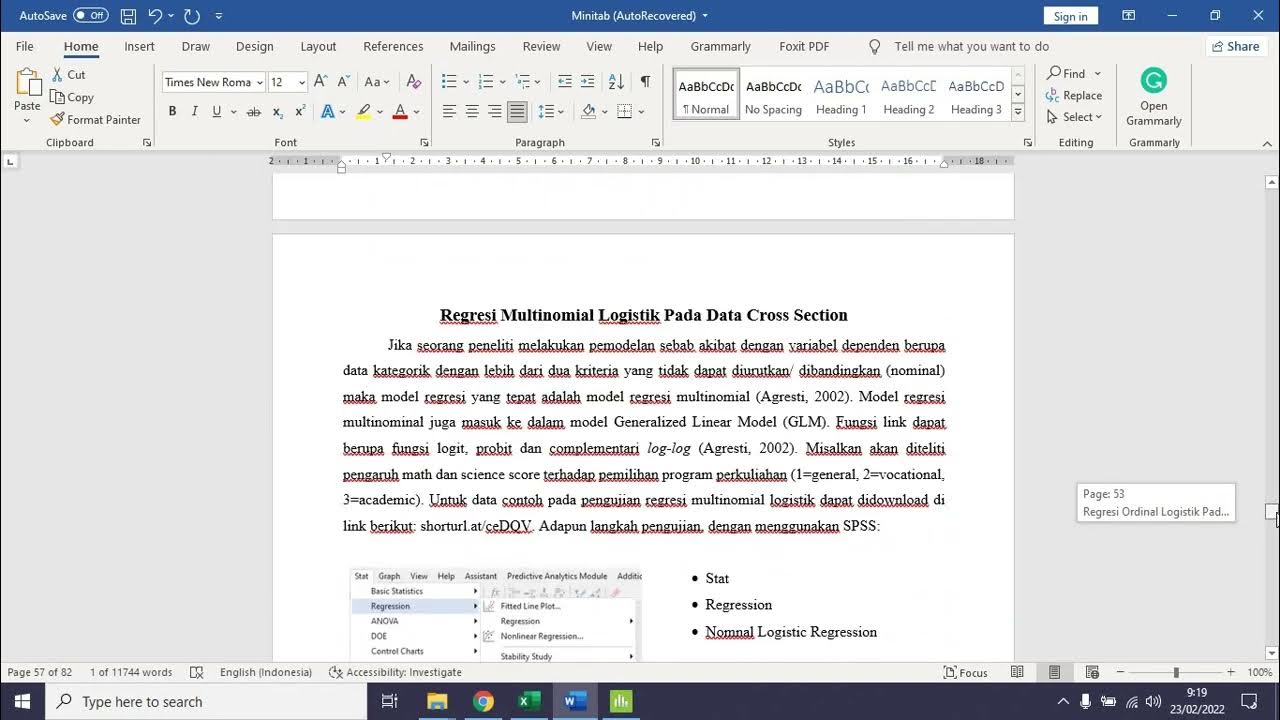
Regresi Ordinal dan Multinomial Logistik Pada Data Crosssection dengan Minitab

Regresi Data Panel Eviews 12 Lengkap dengan Penjelasannya

Part 1 - Cara Mengobati Uji Autokorelasi dengan SPSS || Durbin Two-Step Method

Statistik Terapan: Regresi Logistik penjelasan singkat

Data Mining 10 - Estimation (Linear Regression)

Memahami Perbedaan Uji Multikolinieritas, Heteroskedastisitas, Autokorelasi, dan Normalitas
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
