MÉDIA, MODA E MEDIANA | MEDIDAS DE TENDÊNCIA CENTRAL \Prof. Gis/
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the instructor explains how to calculate the mean, mode, and median using real-life examples of student grades and ages. Mode refers to the most frequent value, median is the middle value in an ordered sequence, and mean is the arithmetic average of all values. The script takes viewers through the steps of determining these statistics for two different datasets, emphasizing how to handle odd and even numbers of elements. The instructor also demonstrates rounding techniques for decimal results and provides helpful insights for mastering these foundational concepts in statistics.
Takeaways
- 😀 The arithmetic mean is calculated by adding all the values in a dataset and dividing by the total number of values.
- 😀 The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a dataset. If there are multiple values with the same highest frequency, the dataset is called bimodal or multimodal.
- 😀 The median is the middle value in a dataset when the numbers are arranged in order. For odd-numbered datasets, it's the single middle value, while for even-numbered datasets, it's the average of the two middle values.
- 😀 To calculate the mode, arrange the data in ascending order and identify the most frequent value.
- 😀 The mode can be unimodal (one mode), bimodal (two modes), or multimodal (multiple modes). If no number repeats, the dataset is called amodal.
- 😀 For odd-numbered datasets, the median is the middle value after arranging the data in order.
- 😀 For even-numbered datasets, the median is the average of the two central values.
- 😀 In the case of the grades dataset (5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10), the mode is 6, the median is 7, and the mean is 7.28 (rounded to 7.3).
- 😀 In the case of the ages dataset (11, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16), the mode is 11, the median is 13, and the mean is 13.2 (rounded).
- 😀 When calculating the mean, make sure to add all elements together and divide by the total number of elements. Always round the result as necessary for clarity and precision.
Q & A
What is the mean, and how is it calculated?
-The mean is the arithmetic average of a set of numbers. To calculate it, you sum all the values in the dataset and divide the total by the number of values. For example, in the set [5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], the sum is 51, and dividing by 7 gives a mean of 7.28, which rounds to 7.3.
What does the mode represent in a dataset?
-The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a dataset. If no value repeats, the dataset is said to have no mode. If two or more values appear most frequently, the dataset is bimodal or multimodal, respectively.
How do you determine the mode in a sequence of numbers?
-To find the mode, first arrange the numbers in order. Then, identify the value that appears the most. In the example [5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], the mode is 6 because it appears twice, more than any other number.
What happens when a dataset has no mode?
-When a dataset has no mode, it is called 'amodal.' This occurs when all values in the dataset appear with the same frequency, or no value repeats.
How do you calculate the median in a dataset with an odd number of terms?
-For a dataset with an odd number of terms, the median is the middle value when the data is arranged in ascending or descending order. In the example [5, 6, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10], the median is 7 because it is the central value in the sorted list.
How do you find the median when there is an even number of terms?
-For an even number of terms, there are two middle values. To find the median, you calculate the average of these two values. For example, in the set [11, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16], the middle values are 12 and 14, and their average (12 + 14) / 2 = 13 is the median.
What does it mean for a dataset to be bimodal or multimodal?
-A dataset is bimodal if it has exactly two modes, i.e., two values that appear most frequently. It is multimodal if there are more than two modes. These terms describe datasets with multiple frequent values.
What is the significance of rounding when calculating the mean or median?
-Rounding is important when the result of a calculation is a decimal and a precise value is unnecessary. It makes the result easier to interpret and compare. For example, the mean of [11, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16] is 13.1666... and is rounded to 13.2 for clarity.
Why is it necessary to put numbers in ascending or descending order when calculating the median?
-Sorting the numbers ensures that you can accurately identify the middle value(s). The median is defined as the central value in an ordered list, so sorting is a necessary step in finding it.
How is the arithmetic mean different from the median and mode?
-The arithmetic mean is the average of all values in a dataset, whereas the median is the middle value and the mode is the most frequent value. The mean is sensitive to all values, while the median and mode focus on the central and most frequent values, respectively.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

MÉDIA, MODA e MEDIANA | RÁPIDO E FÁCIL

ESTATÍSTICA ENEM I MÉDIA, MODA e MEDIANA
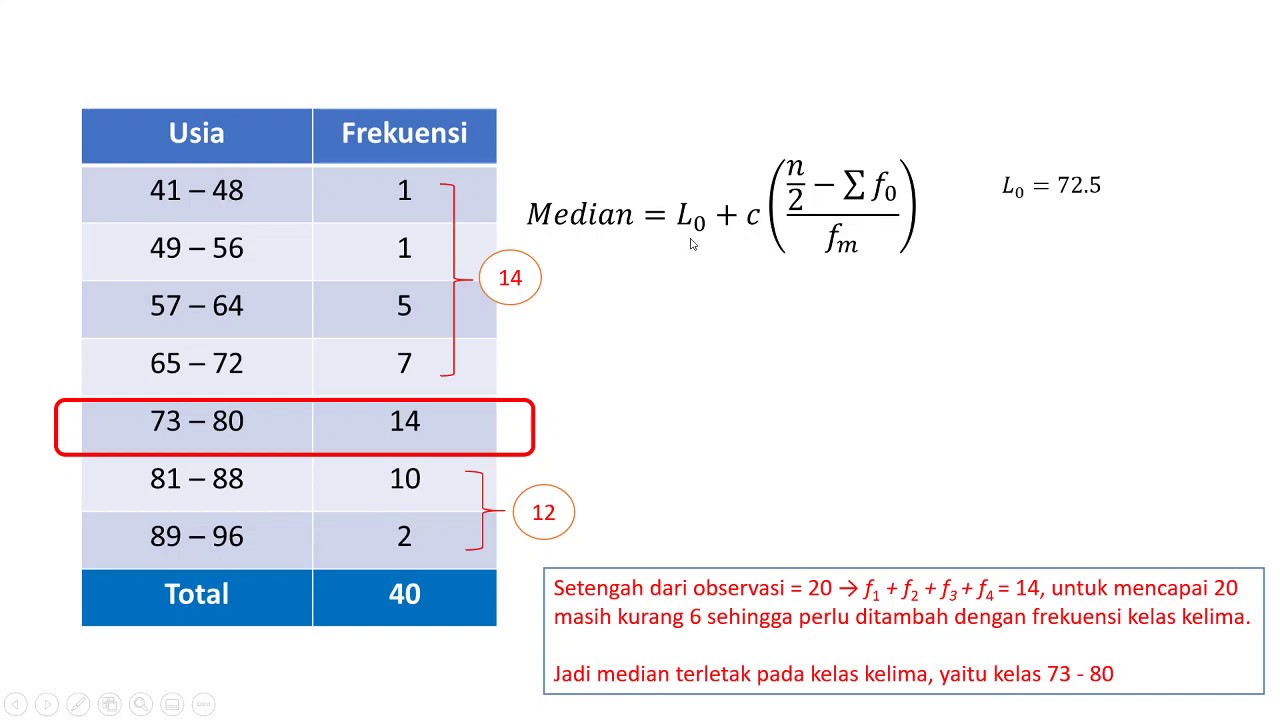
UKURAN PEMUSATAN DATA BERKELOMPOK | Rataan Median Modus Kuartil Desil Persentil

Data Processing Material (Mean, mode, median

Statistika - Ukuran Pemusatan Data (Mean, Median, Modus)

Statistika - Ukuran Pemusatan Data Tunggal (Mean, Median, Modus)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
