Tutorial atau Cara Uji Korelasi Spearman Hitung Manual dan SPSS
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker, an ASN (civil servant) and aspiring YouTuber, explains Spearman's rank correlation. Using a real-world example of motivation and performance data from 10 respondents, the video demonstrates how to calculate Spearman's correlation coefficient. The speaker also highlights when to use Spearman's correlation versus Pearson's, and offers insights into hypothesis testing. Additionally, SPSS is briefly used to verify calculations. The video encourages learning through practical application and invites viewers to engage and share feedback on potential errors. Overall, it serves as a tutorial on statistical correlation analysis.
Takeaways
- 😀 The speaker introduces themselves as a civil servant (ASN) and a YouTuber sharing educational content in statistics.
- 😀 The main topic of the video is Spearman's rank correlation, a statistical method used to assess relationships between two ordinal variables.
- 😀 Spearman's rank correlation is appropriate for ordinal data, where values are ranked but not necessarily equidistant, such as responses on a Likert scale.
- 😀 The video uses an example with 10 employees who rated their motivation and performance, demonstrating how Spearman's correlation is applied.
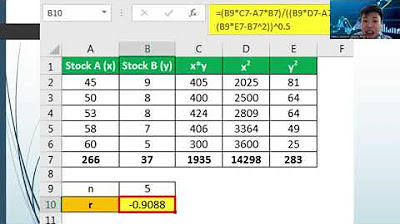
- 😀 The formula for Spearman's rank correlation is presented as: ρ = 1 - (6 Σ d²) / (n(n² - 1)), where 'd' is the rank difference and 'n' is the number of data points.
- 😀 The process of calculating Spearman’s correlation involves ranking the data, calculating the rank differences, and then applying the formula to compute the correlation coefficient.
- 😀 The hypothesis being tested is whether there is a significant relationship between motivation and performance. The null hypothesis (H0) states no relationship, while the alternative hypothesis (H1) posits there is a relationship.
- 😀 After calculating the Spearman’s correlation coefficient, the result is compared with a critical value from a correlation table to determine whether H0 should be rejected.
- 😀 If the calculated value of the correlation coefficient is greater than the critical value, H0 is rejected, meaning a significant relationship exists between the variables.
- 😀 The speaker demonstrates how the calculation is also verified using SPSS software, which gives the same result as the manual calculation.
- 😀 The speaker encourages viewers to engage and help improve the content, emphasizing the video as a place for collaborative learning in statistics.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic is Spearman's Rank Correlation, which is used to find the relationship or test the hypothesis of associations between two ordinal variables.
Why did the speaker wear a Korpri uniform for this video?
-The speaker wore the Korpri uniform because he had attended a civil servant (PNS) inauguration earlier in the day, which was unplanned for the recording.
What is Spearman's Rank Correlation used for?
-Spearman's Rank Correlation is used to measure the strength and direction of association between two ranked (ordinal) variables, particularly when the data involves Likert scales.
What are the differences between Pearson's correlation and Spearman's correlation?
-Pearson's correlation is used for continuous variables that are linearly related, while Spearman's correlation is used for ordinal variables or when the data doesn't meet the assumptions of Pearson's correlation.
What is the significance of the formula for Spearman's Rank Correlation?
-The formula for Spearman's Rank Correlation calculates the correlation coefficient by comparing the differences between the ranks of paired data points and providing a value that indicates the strength of their relationship.
How is the 'D' value calculated in Spearman's Rank Correlation?
-The 'D' value is the difference between the ranks of each pair of observations. After finding the differences, you square them, sum them up, and then apply the formula to calculate the correlation coefficient.
What does the null hypothesis (H0) represent in this analysis?
-The null hypothesis (H0) states that there is no relationship between the two variables being studied, meaning that any observed correlation is due to chance.
What is the critical value used to reject the null hypothesis in this case?
-The critical value for the Spearman correlation is 0.64 for a significance level of 5% with 10 data points. If the calculated correlation coefficient exceeds this value, the null hypothesis is rejected.
How did the speaker use SPSS to validate the results?
-The speaker used SPSS to perform the Spearman Rank Correlation analysis, which produced a correlation coefficient of 0.957, confirming the results obtained manually.
What conclusion did the speaker draw from the analysis?
-The speaker concluded that there is a significant relationship between motivation and achievement, as the calculated correlation coefficient was higher than the critical value, leading to the rejection of the null hypothesis and acceptance of the alternative hypothesis.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Spearman Rank Correlation [Simply explained]

Spearmen's Rank Correlation || Gnani The Knowledge ||

Week 5-Lecture 33 : Spearman’s Rank Correlation.
Statistics Lecture 5 Test of Relationship

Korelasi Spearman - Matematika Wajib SMA Kelas XI Kurikulum Merdeka

Lesson 3 Pemberian Gaji dan TPP / pengelolaan keuangan daerah part 3
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
