Language Assessment Principles
Summary
TLDRThis video discusses key principles of language assessment, including practicality, reliability, validity, authenticity, and washback. It emphasizes the importance of ensuring assessments are feasible, consistent, and accurate in measuring what they intend to measure. Validity is broken down into types such as content-related, criterion-related, and construct validity. The video also explores the role of authenticity in assessments, ensuring they mirror real-world language use, and highlights the need for beneficial washback, where both students and teachers can learn and improve from the results. The session aims to guide educators in designing and choosing effective language assessment tools.
Takeaways
- 😀 Practicality in language assessment refers to the feasibility of the test in terms of cost, time, and resources.
- 😀 A test's practicality includes ensuring it's affordable for students, easy to administer, and can be corrected promptly.
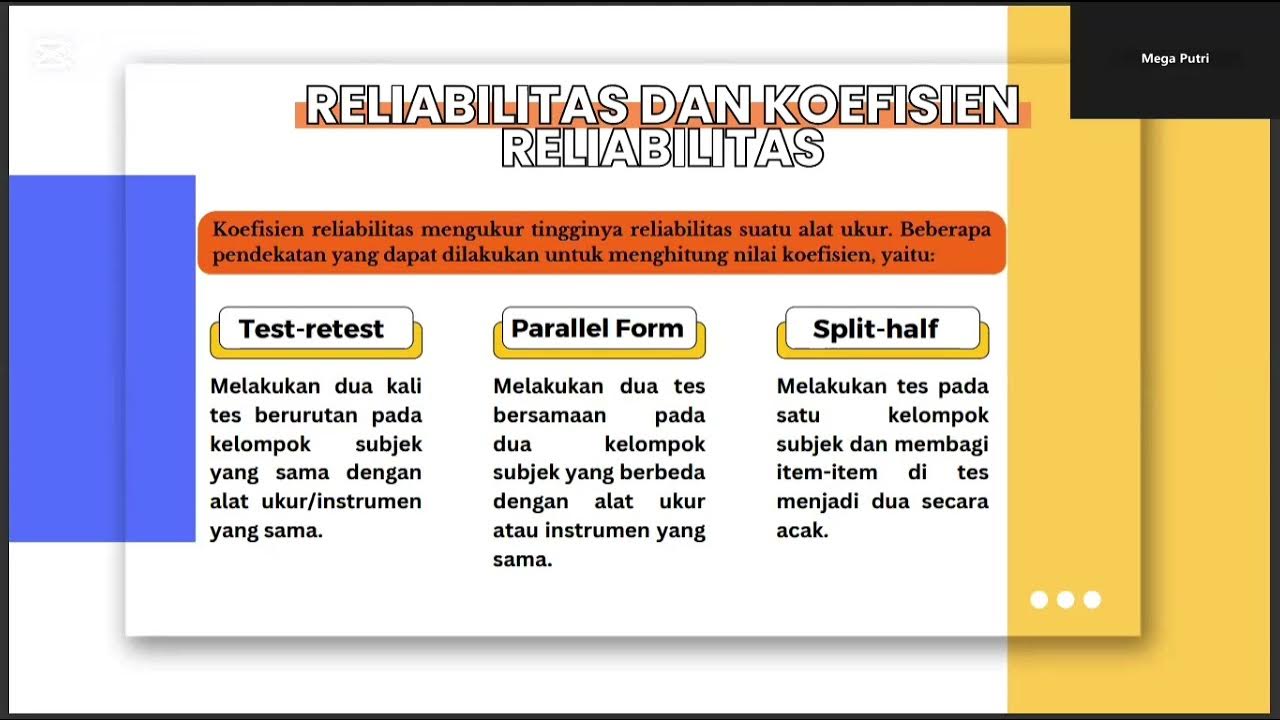
- 😀 Reliability involves ensuring a test consistently yields the same results when administered to the same group over time.
- 😀 There are multiple types of reliability, including test components, student variability, rater reliability, and test administration reliability.
- 😀 Validity assesses whether a test measures what it is intended to measure, with types like content validity, criterion-related validity, and construct validity.
- 😀 Content validity ensures the test accurately measures the intended subject (e.g., grammar vs. vocabulary).
- 😀 Construct validity checks if the test is based on sound theoretical foundations and actually measures what it claims to measure.
- 😀 Authenticity in assessments refers to the use of real-world tasks and natural language to ensure the test reflects actual language use.
- 😀 Washback describes the impact of the test on both teaching and learning, with positive washback helping students and teachers improve.
- 😀 Tests with good washback provide valuable feedback, helping students identify strengths and weaknesses and teachers improve their teaching methods.
Q & A
What is the concept of practicality in language assessment?
-Practicality in language assessment refers to the feasibility of implementing a test. This includes considerations such as the cost of the test, whether it is affordable for students or schools, the clarity of instructions, the time it takes to administer, and the time needed to return results.
How does reliability affect language assessment?
-Reliability in language assessment concerns the consistency of test results. A reliable test will yield the same results when administered to the same group of people under similar conditions. Factors affecting reliability include test components, student conditions, and rater consistency.
What is the relationship between validity and test scores in language assessment?
-Validity is about ensuring that a test accurately measures what it claims to measure. It involves using empirical evidence and theoretical rationales to support decisions based on test scores. For instance, a grammar test should assess grammar knowledge, not vocabulary understanding.
What are the different types of validity mentioned in the transcript?
-The transcript highlights several types of validity: content validity (measuring what the test is supposed to measure), criterion-related validity (achieving the test's objectives), construct validity (based on sound theoretical foundations), consequential validity (considering the impact of the test), and face validity (how well the test appears to measure the intended skills).
What is the importance of authenticity in language assessments?
-Authenticity in language assessment means ensuring the test reflects real-world language use. This includes using natural language, presenting linguistic items in context, and designing tasks that replicate real-life situations, making the test more relevant and effective.
How can poor test design lead to negative washback?
-Poor test design can create negative washback by discouraging students and teachers. If the test does not provide useful feedback or is perceived as irrelevant, it can lead to decreased motivation and hinder learning.
What does the term 'washback' refer to in the context of language assessments?
-Washback refers to the impact of a test on both learners and teachers. Positive washback occurs when feedback from a test helps improve learning and teaching, while negative washback happens when the test leads to discouragement or confusion.
Why is inter-rater reliability important in language assessment?
-Inter-rater reliability is crucial because it ensures that multiple raters assess the same test in a consistent manner. This consistency helps guarantee that the test results are fair and accurate, avoiding subjective bias from individual raters.
What role does content validity play in the design of a language test?
-Content validity ensures that a test accurately measures the specific skill or knowledge it is intended to assess. For example, if a test is meant to assess grammar knowledge, it should not include questions that test vocabulary or other unrelated skills.
How can a test be made more practical according to the script?
-A test can be made more practical by considering factors such as affordability, clarity of instructions, the time required for both administering and evaluating the test, and ensuring it provides timely results. Offering practice tests or preparation materials can also make a test more practical for students.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)