The Crown Court
Summary
TLDRThis video script outlines the trial process in a Crown Court, focusing on the roles of key participants: the judge, prosecution and defense barristers, jury, and the defendant. It describes how the judge guides the jury on legal matters, while the prosecution and defense present their cases, questioning witnesses through examination and cross-examination. The jury is responsible for determining the defendant's guilt based on evidence. The script also highlights the procedures for delivering a verdict, sentencing, and the judge's role in summing up the case and issuing a final decision.
Takeaways
- 👩⚖️ The judge's role is to interpret and uphold the law during a trial.
- 👨⚖️ The jury is responsible for deciding the defendant's guilt based on evidence, not law.
- ⚖️ The prosecution barrister outlines the case, presents evidence, and questions witnesses.
- 🕵️♂️ The defense barrister can cross-examine witnesses after the prosecution's examination.
- 🔍 After all evidence is presented, both barristers give closing speeches to persuade the jury.
- 📜 The prosecution must prove the defendant's guilt beyond reasonable doubt.
- 🚪 If the defense barrister argues that there is no case to answer and the judge agrees, the defendant is acquitted.
- 👩💼 The judge sums up the case for the jury and directs them on legal matters.
- 🗳️ The foreperson of the jury announces the verdict, either guilty or not guilty.
- 👨⚖️ If found guilty, the judge may sentence immediately or postpone if other factors need consideration.
Q & A
What is the role of the judge in the trial?
-The judge's role is to interpret and uphold the law, direct the jury on legal issues, and, if necessary, sentence the defendant after the verdict.
Who are the key participants in a Crown Court trial?
-The key participants are the judge, the prosecution barrister, the defense barrister, the solicitors, the jury, and the defendant.
What is the jury's responsibility during the trial?
-The jury's responsibility is to consider the evidence presented and determine if it proves the defendant's guilt, without interpreting the law, as the judge provides guidance on legal matters.
What is the prosecution’s task when addressing the jury?
-The prosecution outlines the case, explains the offenses, presents the evidence, and must prove beyond any reasonable doubt that the defendant is guilty.
What happens during 'examination in chief'?
-During 'examination in chief,' the prosecution asks a series of questions to a witness based on their police statement to support the case.
What is the purpose of 'cross-examination'?
-Cross-examination allows the defense to question the prosecution’s witness to challenge or clarify their testimony.
What is an application of 'no case to answer'?
-An application of 'no case to answer' is made by the defense when they believe the prosecution has not provided sufficient evidence to prove the defendant’s guilt. If accepted, the defendant is acquitted.
What happens after all prosecution witnesses have testified?
-Once all prosecution witnesses have testified, the prosecution closes its case, and the defense may begin presenting its own witnesses.
What is the purpose of the closing speeches from both the prosecution and defense?
-The closing speeches aim to persuade the jury by summarizing each side's case, with the prosecution seeking to prove guilt and the defense aiming to raise doubt about the prosecution's claims.
What factors may influence the judge’s decision to postpone sentencing?
-The judge may postpone sentencing if there are contentious issues or if the defendant's background may significantly impact the sentence.
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级浏览更多相关视频

Crown Court - Preparing to come to court
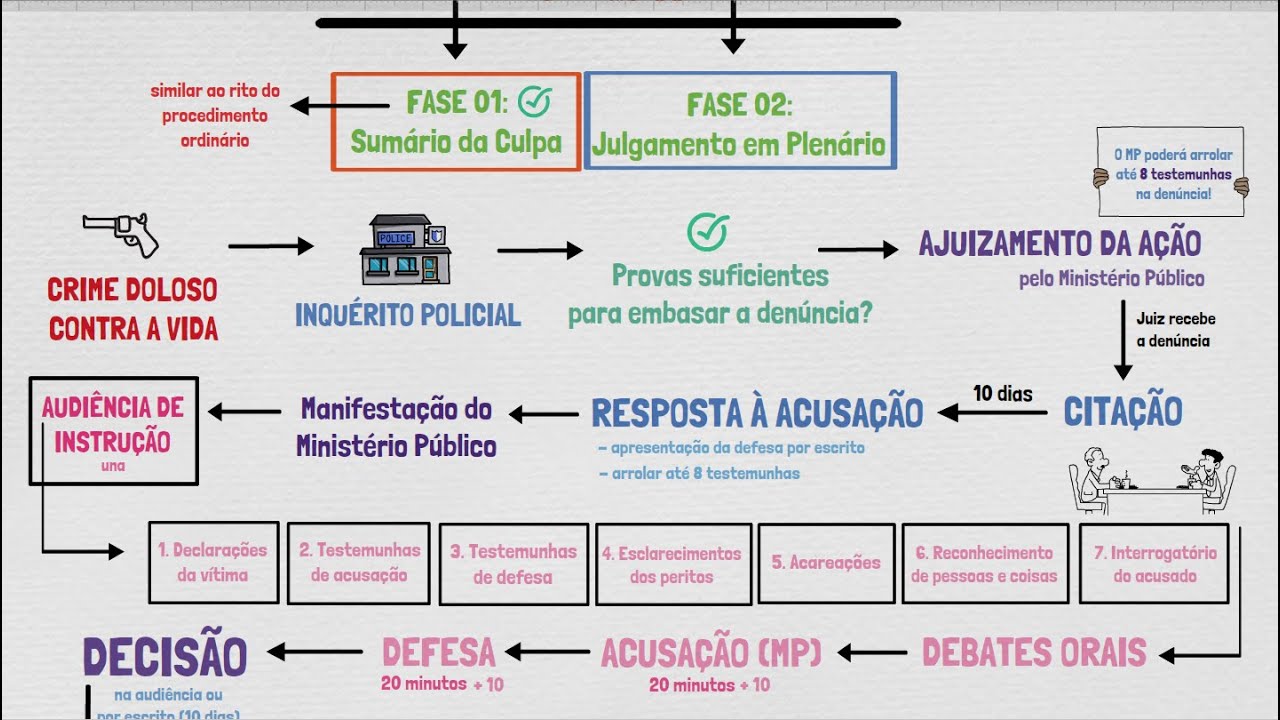
TRIBUNAL DO JÚRI: Como funciona? | Aula 02 | Sumário da Culpa - PROCESSO PENAL

VCE Legal Studies: Criminal case scenario (part 2)

We the Jury - a short film about jury service in Victoria

Tugas PPKN Kelompok 2 12 IPA 6 [Simulasi Sidang Pengadilan Negeri]

CONTOH PERSIDANGAN KASUS KORUPSI
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
