Episode 42: The Lorentz Transformation - The Mechanical Universe
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the historical and theoretical foundations of the theory of relativity, highlighting the contributions of physicists like Lorentz, Fitzgerald, and Einstein. It discusses the Michelson-Morley experiment, which failed to detect the luminiferous aether, leading to the development of the Lorentz transformation equations. The script delves into the concept of the constancy of the speed of light and how it challenges traditional notions of time and space. It also touches on the personal influences and the significance of Einstein's approach to relativity, which redefined our understanding of the universe.
Takeaways
- 🌌 The conventional history of relativity starts with the Ether theory, which was disproven by the Michelson-Morley experiment, leading to Einstein's theory of relativity.
- 🔍 The real story of relativity involves the Lorentz transformation, which includes the constant speed of light derived from Maxwell's equations.
- 🚂 At the end of the 19th century, the speed of trains was the fastest human experience, with the Earth's rotation around the Sun being faster but unnoticed by inhabitants.
- 🌟 The Michelson-Morley experiment aimed to detect motion through the Ether by measuring the speed of light, but found that the speed of light is constant regardless of the observer's motion.
- 🤔 GF Fitzgerald and Hendrik Lorentz proposed that motion through the Ether causes a contraction in the direction of motion, which was a key insight for the theory of relativity.
- 🕰 Lorentz's work suggested that time, as well as distance, is affected by motion, leading to the idea that time dilation occurs in moving frames of reference.
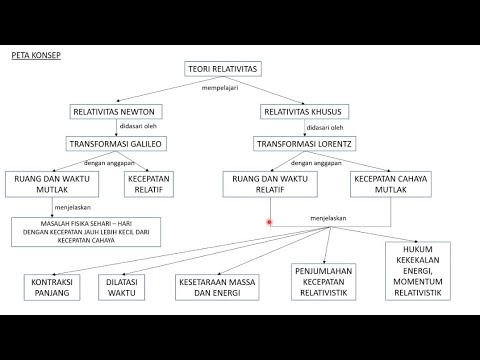
- 📏 The Lorentz transformation equations express how time slows and distances contract in a moving frame, and they join time and space into a single continuum.
- 🌐 Einstein's special theory of relativity was based on two postulates: the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames, and the speed of light is constant for all observers.
- 🚀 Einstein's theory provided a deeper understanding of the Lorentz transformation, viewing the constant speed of light as a fundamental principle rather than an appearance.
- 📚 There are two independent histories of the theory of relativity: one through the Ether theory and Lorentz's work, and the other through Einstein's independent development of the same theory with a different perspective.
Q & A
What was the conventional history of relativity mentioned in the script?
-The conventional history of relativity mentioned in the script includes the theory of the Ether, the Michelson-Morley experiment which showed the Ether theory was wrong, and then Albert Einstein's formulation of the theory of relativity.
What is the Lorentz transformation and why is it significant?
-The Lorentz transformation is a set of equations that describe how space and time coordinates transform from one inertial frame of reference to another moving relative to the first. It is significant because it incorporates the constant speed of light and introduces the concepts of length contraction and time dilation, which are fundamental to the theory of special relativity.
What was the Michelson-Morley experiment aiming to prove?
-The Michelson-Morley experiment aimed to detect the motion of the Earth through the luminiferous Ether by measuring the effects of the Ether on the speed of light.
What was the unexpected result of the Michelson-Morley experiment?
-The unexpected result of the Michelson-Morley experiment was that the speed of light was found to be the same regardless of the motion of the observer, which contradicted the expectation that the speed of light would vary depending on the observer's motion through the Ether.
Who were Albert A. Michelson and Edward Morley, and what was their contribution to the development of the theory of relativity?
-Albert A. Michelson and Edward Morley were American physicists who conducted the Michelson-Morley experiment. Their experiment, which failed to detect the luminiferous Ether, contributed to the development of the theory of relativity by challenging the classical understanding of space and time.
What was Hendrik Lorentz's contribution to the understanding of the Michelson-Morley experiment results?
-Hendrik Lorentz contributed to the understanding of the Michelson-Morley experiment results by proposing the concept of length contraction, suggesting that objects contract in the direction of motion relative to the Ether, which could explain why the speed of light appeared constant to all observers.
What is the significance of the speed of light in the theory of relativity?
-In the theory of relativity, the significance of the speed of light is that it is constant for all observers, regardless of their relative motion. This constancy leads to the concepts of time dilation and length contraction, which are fundamental to understanding the behavior of objects at speeds close to the speed of light.
What is the principle of relativity as mentioned in the script?
-The principle of relativity, as mentioned in the script, states that the laws of physical phenomena should be the same for an observer at rest and for an observer in uniform motion. This principle is a cornerstone of the theory of special relativity.
How did Albert Einstein's approach to the theory of relativity differ from Hendrik Lorentz's?
-Albert Einstein's approach to the theory of relativity differed from Hendrik Lorentz's in that Einstein based his theory on two postulates: the principle of relativity and the constancy of the speed of light for all observers. Einstein's approach was more fundamental and universal, while Lorentz was focused on explaining specific experimental results like those from the Michelson-Morley experiment.
What is the Lorentz factor (gamma) and how does it relate to time dilation and length contraction?
-The Lorentz factor, denoted by gamma (γ), is a mathematical factor that relates the time and space measurements of an object in motion to those in a stationary frame of reference. It is given by the equation γ = 1 / √(1 - v²/c²), where v is the relative velocity and c is the speed of light. The Lorentz factor is used to calculate time dilation (moving clocks run slower) and length contraction (objects in motion contract in the direction of motion).
Outlines

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Mindmap

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Keywords

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Highlights

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级Transcripts

此内容仅限付费用户访问。 请升级后访问。
立即升级5.0 / 5 (0 votes)