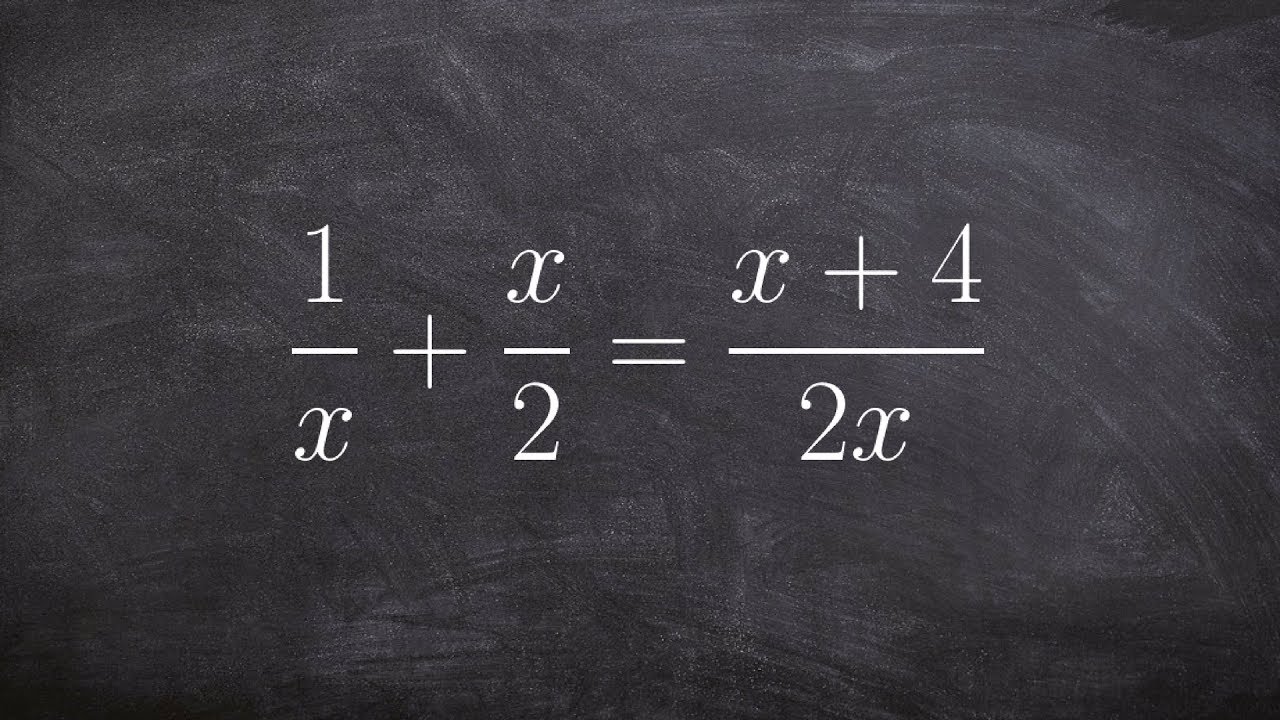Solving Rational Equations
Summary
TLDRThis lesson focuses on solving rational equations by eliminating fractions and finding the least common multiple. The instructor demonstrates step-by-step solutions for various examples, including simplifying equations, factoring, and applying cross-multiplication. Techniques for finding x values are explored, with a final example involving factoring a quadratic expression and solving for x, yielding multiple solutions.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The lesson focuses on solving rational equations by eliminating fractions to simplify the problem.
- 📚 The first example demonstrates finding the least common multiple (LCM) of 8, 5, and 10, which is 40, to clear fractions from the equation.
- 🧩 After clearing fractions, the solution involves basic arithmetic operations to solve for x, resulting in x = 1/4 for the initial example.
- 📉 In the second problem, multiplying both sides by x eliminates the denominators, leading to a quadratic equation which factors to find x = 4 and x = 2.
- ✅ The third example uses cross-multiplication to transform the equation into a linear one, solving for x = 5.
- 🤔 The fourth problem involves taking the square root of both sides after cross-multiplication, yielding two potential solutions, x = 6 and x = -6.
- 🔢 For the fifth example, cross-multiplication and simplification lead to a solution of x = 7 after combining like terms.
- 📈 The sixth example uses the LCM of 2 and 3, which is 6, to eliminate fractions and solve for x = 1.
- 📉 The seventh problem involves finding a common denominator and simplifying to form a quadratic equation, which factors to x = 2 and x = -1.
- 🔗 The last example involves factoring a difference of squares and clearing fractions to form a quadratic equation, solving for x = 13 and x = -3.
Q & A
What is the first step to solve a rational equation involving fractions?
-The first step is to find the least common multiple (LCM) of the denominators and then multiply every fraction by that LCM to eliminate the fractions.
How do you find the least common multiple (LCM) of 8, 5, and 10 from the transcript?
-You list the multiples of each number and identify the smallest number that appears in all lists. In this case, the multiples of 5 are 5, 10, 15, etc., multiples of 8 are 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, and multiples of 10 include 10, 20, 30, 40. The LCM is 40.
What is the value of x in the equation 5/8 - 3/5 = x/10?
-After clearing the fractions by multiplying by the LCM (40), you get 25 - 24 = 4x/10, which simplifies to 1 = 4x/10. Solving for x gives x = 1/4.
How do you handle the equation x + 8/x = 6?
-You multiply both sides by x to eliminate the fraction, which gives x^2 + 8 = 6x. Then, you rearrange the equation to x^2 - 6x + 8 = 0 and factor it to (x - 4)(x - 2) = 0, giving x = 4 and x = 2.
What is the process for solving the equation (x + 3)/(x - 3) = 12/3?
-You cross-multiply to get 12(x - 3) = 3(x + 3). Simplifying gives 12x - 36 = 3x + 9. Then, you combine like terms and solve for x, which results in x = 5.
How do you solve the equation 9/x = x/4?
-You cross-multiply to get 9 * 4 = x^2, which simplifies to 36 = x^2. Taking the square root of both sides gives x = ±6.
In the equation 4/(x - 3) = 9/(x + 2), what is the step after cross-multiplying?
-After cross-multiplying, you get 4(x + 2) = 9(x - 3). Expanding and simplifying leads to 4x + 8 = 9x - 27, and then you solve for x, which results in x = 7.
What is the least common multiple (LCM) of 2 and 3, and how is it used in the equation (x + 2)/3 = (x + 9)/2?
-The LCM of 2 and 3 is 6. Multiplying both sides of the equation by 6 eliminates the fractions, leading to 2x + 4 = 3x + 27/2, which simplifies to x = 1.
How do you solve the equation 4/x + 8/(x + 2) = 4?
-You multiply both sides by the common denominator x(x + 2), which gives 4(x + 2) + 8x = 4x^2 + 8x. Simplifying and solving the quadratic equation gives x = 2 and x = -1.
In the final example of the transcript, how do you simplify the equation (x + 5)/(x - 5) - 5/(x + 5) = 14/(x^2 - 25)?
-You factor x^2 - 25 as (x + 5)(x - 5) and multiply both sides by this expression to clear the fractions. Simplifying leads to x^2 - 10x - 39 = 0, which factors to (x - 13)(x + 3) = 0, giving x = 13 and x = -3.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)