Fractions Basic Introduction - Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying & Dividing Fractions
Summary
TLDRThis lesson focuses on adding, subtracting, multiplying, and dividing fractions. It explains step-by-step methods to find common denominators, add or subtract fractions, and simplify the results. The lesson also covers how to handle multiple fractions, find the least common denominator, and provides useful tricks to break down large numbers for easier calculations. Additionally, the 'keep-change-flip' technique is introduced for dividing fractions. Through various examples, the lesson demonstrates efficient methods to solve fraction problems, both with simple and complex numbers, without needing a calculator.
Takeaways
- 🔢 The process of adding fractions involves finding a common denominator by multiplying the denominators.
- ✖️ To add fractions like 3/5 and 4/7, multiply the denominators (5 and 7) to get a common denominator of 35, then adjust the numerators accordingly.
- ➖ When subtracting fractions like 7/8 - 2/9, the same principle applies: find a common denominator, subtract the adjusted numerators, and simplify if possible.
- 🔄 The least common denominator (LCD) is essential when adding or subtracting multiple fractions, and it can be found by listing multiples or multiplying denominators together.
- 📉 When combining three fractions, first find the least common denominator by listing multiples or multiplying the denominators (e.g., for 3/4 + 5/3 - 7/2, the LCD is 12).
- ➕ Once a common denominator is found, combine the numerators and adjust for any negative signs if subtracting fractions.
- 📝 In more complex fraction operations, like adding three fractions, you can use a larger common denominator if needed and simplify at the end.
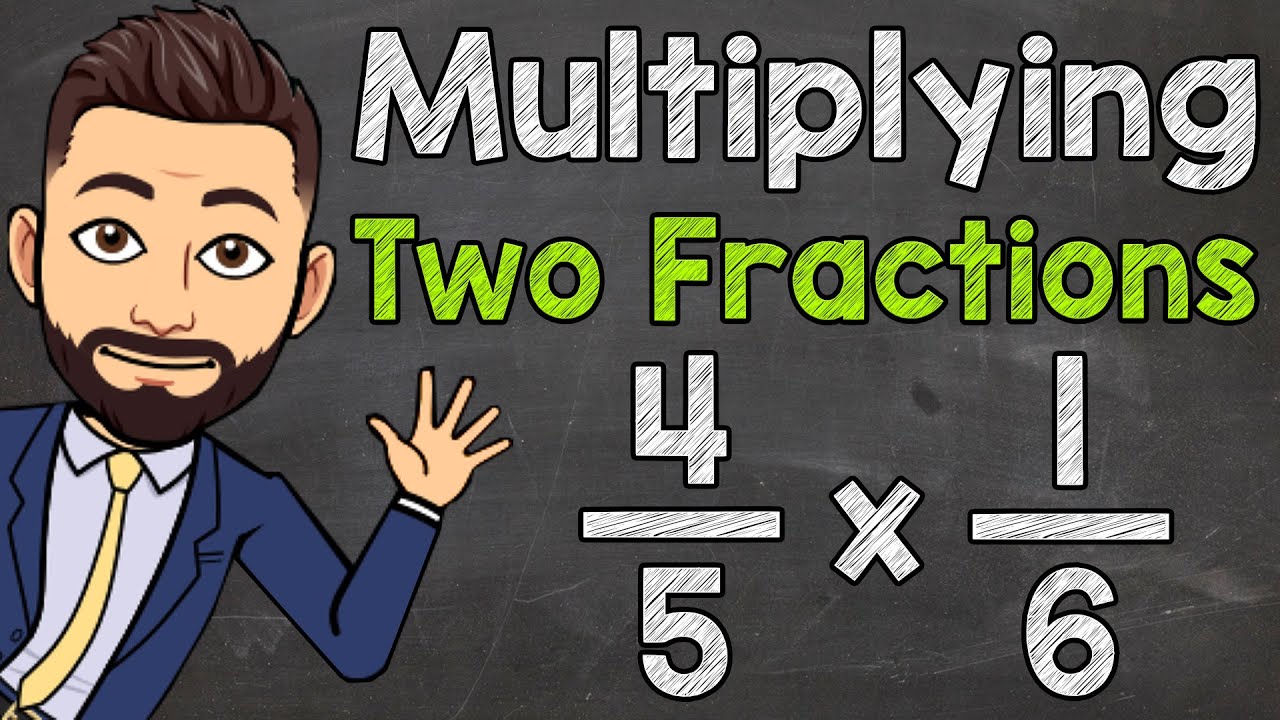
- 💡 Multiplying fractions involves multiplying the numerators and denominators directly, but you can simplify by breaking down larger numbers to avoid large products.
- 🧮 Simplifying before multiplying helps reduce the numbers, as shown when breaking 24/45 into smaller factors and canceling common terms.
- 🔄 Dividing fractions involves using the 'keep, change, flip' method: keep the first fraction, change the division to multiplication, and flip the second fraction before multiplying.
Q & A
What is the first step in adding or subtracting fractions?
-The first step is to find a common denominator by multiplying the denominators of the fractions.
How do you add fractions like 3/5 + 4/7?
-First, multiply the denominators (5 and 7) to get 35. Then, multiply 3 by 7 (21) and 5 by 4 (20). Finally, add the numerators to get 41, resulting in the fraction 41/35.
What should you do when subtracting fractions like 7/8 - 2/9?
-Multiply the denominators (8 and 9) to get 72. Multiply 7 by 9 (63) and 8 by 2 (16), then subtract the numerators to get 47/72.
How can you find the least common denominator (LCD) when adding or subtracting fractions?
-List the multiples of the denominators and find the smallest multiple they have in common. For example, the LCD of 2, 3, and 4 is 12.
What happens if you use a common denominator that is not the least common denominator?
-You can still get the correct answer, but you will need to simplify the final result at the end.
In the example 3/4 + 5/3 - 7/2, why is 12 chosen as the common denominator?
-12 is the least common denominator (LCD) because it is the smallest multiple common to 2, 3, and 4.
How do you add or subtract fractions with the same denominator?
-Once the denominators are the same, combine the numerators. For example, in 9/12 + 20/12 - 42/12, add 9 and 20, then subtract 42 to get -13/12.
What is the process for multiplying two fractions?
-Multiply the numerators and the denominators across the fractions. For example, 3/5 * 7/2 = 21/10.
Why is it helpful to break down large numbers when multiplying fractions?
-Breaking down large numbers allows you to simplify the multiplication by canceling common factors, making the process easier and reducing the need for a calculator.
How do you divide fractions using the 'keep, change, flip' method?
-Keep the first fraction, change the division to multiplication, and flip the second fraction. Then, multiply the fractions across.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)