Introduction to a Closed Loop Control System
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the function of a closed-loop system in maintaining a variable at a setpoint in a manufacturing process, using a heat exchanger as an example. It details the components of the system, including the controlled variable (water temperature), measurement device (thermal sensor), set point, error detector, controller, and actuator (flow valve). The script also discusses how disturbances affect the process and the role of closed-loop control in ensuring precise control within manufacturing.
Takeaways
- 🔧 The function of a closed-loop system is to monitor and maintain a variable at a desired setpoint in a manufacturing process.
- 🔄 An example given is a heat exchanger in a food processing operation, where heated water is supplied.
- 💧 Cold water enters the heat exchanger, warms up through steam-heated coils, and exits at the top.
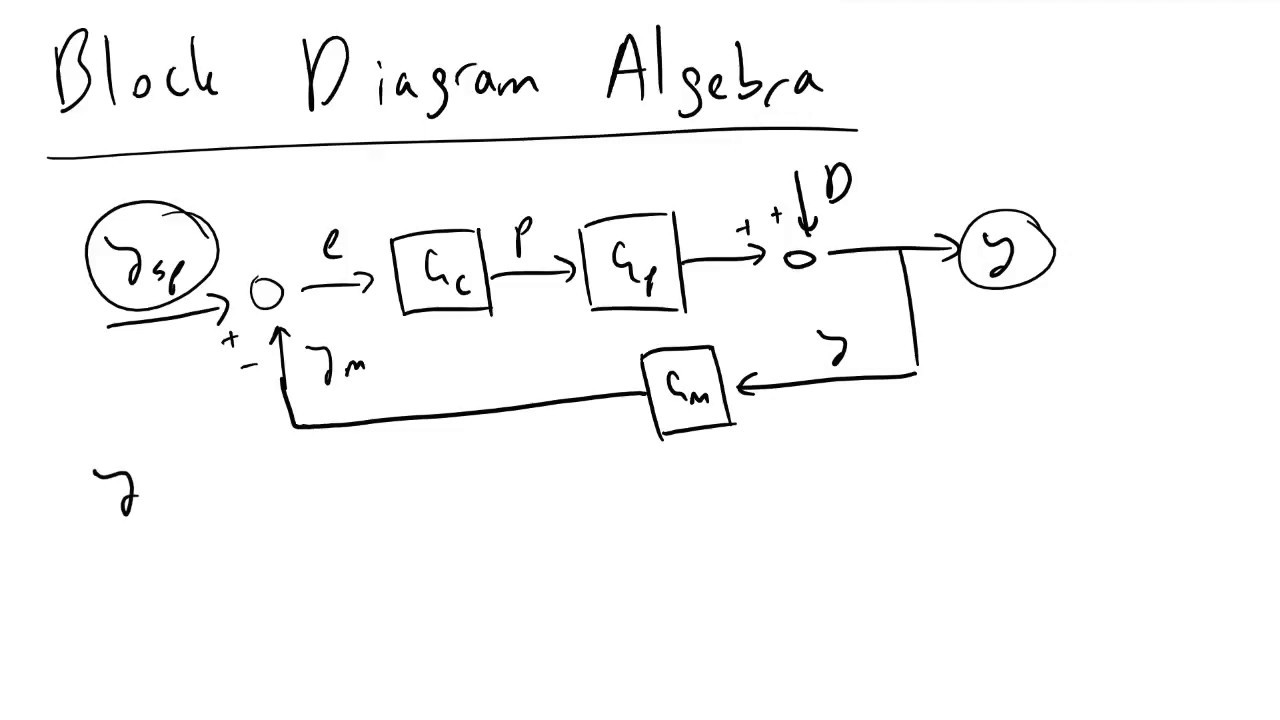
- 📊 A block diagram is used to illustrate the operation, with blocks representing functions and lines indicating process flow.
- 🌡 The controlled variable is the water temperature leaving the tank, which is maintained at a set level.
- 📏 The measured variable is the actual water temperature, sensed by a thermal sensor to provide a feedback signal.
- 🎯 The set point is a predetermined desired condition for the control variable, like the water temperature.
- ⚖️ The error detector compares the set point with the feedback signal, producing an error signal if they differ.
- 🤖 The controller is the system's brain, receiving the error signal and adjusting the final control element to match the set point.
- 🚰 The actuator, such as a flow valve, controls the steam flow to adjust the manipulated variable, which is the amount of energy or steam.
- 🔍 Disturbances are changes in the process that affect the control variable, like sudden changes in water temperature or flow.
- 📚 Closed-loop control is essential in manufacturing systems where precise control of physical variables is required.
Q & A
What is the primary function of a closed-loop system in manufacturing?
-The primary function of a closed-loop system is to monitor and automatically maintain a variable at a desired setpoint in a manufacturing process.
Can you provide an example of a closed-loop system in operation?
-An example of a closed-loop system is a heat exchanger in a food processing operation, which supplies heated water and maintains water temperature at a set point.
What is the role of the controlled variable in a closed-loop system?
-The controlled variable is the actual variable maintained in the process, such as the temperature of the water leaving the tank in the heat exchanger example.
What is the measured variable in the heat exchanger example?
-In the heat exchanger example, the measured variable is the water temperature, which is monitored to ensure it matches the set point.
How does a measurement device contribute to a closed-loop system?
-A measurement device, such as a thermal sensor in the heat exchanger, senses the measured variable and produces an output signal that represents the status of the controlled variable.
What is the purpose of the feedback signal in a closed-loop system?
-The feedback signal from the sensor provides an electrical signal to the controller, indicating the current status of the controlled variable for comparison with the set point.
What is the significance of the set point in a closed-loop system?
-The set point is the predetermined value of the desired condition of the control variable, such as the programmed water temperature leaving the tank in the heat exchanger.
What does an error detector do in a closed-loop system?
-An error detector compares the set point to the feedback signal and produces an output proportional to the difference between them, known as the error signal.
What is the role of the controller in a closed-loop system?
-The controller is the brain of the system; it receives the error signal as input and provides an output signal to the final control element or actuator to adjust the controlled variable to match the set point.
Can you explain the function of an actuator in a closed-loop system?
-An actuator, such as a flow valve in the heat exchanger example, is the final control element that adjusts the manipulated variable, like steam flow, to control the process variable and achieve the set point.
What is a disturbance in the context of a closed-loop system?
-A disturbance is a change in the manufacturing process that results in a change in the control variable, such as a sudden change or stop in water flow affecting the water temperature.
Why are closed-loop controls important in manufacturing systems?
-Closed-loop controls are important in manufacturing systems where precise control is required to maintain process variables at set points, ensuring consistent product quality and efficiency.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)