MASA PEMERINTAHAN GUBERNUR JENDERAL HERMAN WILLEM DAENDELS
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Yulia Noviani discusses the governance of the Dutch East Indies under Governor General Herman Willem Daendels. After the dissolution of the VOC in 1795 and the rise of the French-controlled Batavian Republic, Daendels was tasked with defending Java from British attacks. His policies included limiting royal authority, reducing feudal rights, establishing military roads and bases, forming indigenous legions, and dividing Java into administrative prefectures. He also tackled corruption and implemented economic measures like land sales, tax collection, and compulsory agricultural deliveries. His authoritarian approach led to his recall in 1811, replaced by Jan Willem Janssens, whose rule was short-lived due to British invasion and eventual Dutch surrender, marking the end of Dutch rule in the region.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script discusses the governance of the Dutch East Indies under Governor General Daendels after the dissolution of the VOC in 1795.
- 🏛️ The French took control of the Netherlands, leading to the establishment of the Batavian Republic under Louis Napoleon, while the Dutch King Willem V fled to England.
- 👑 Daendels' main task was to protect Java from British attacks, as King Willem V also sought British assistance to reclaim former VOC territories.
- 🏛️📜 Daendels' policies included limiting the power of native kings, reducing the feudal rights of government officials, and transforming Banten and Cirebon into Dutch colonial territories.
- 🗺️ Java was divided into nine prefectures, each headed by a prefect responsible to the Governor General and overseeing a bupati.
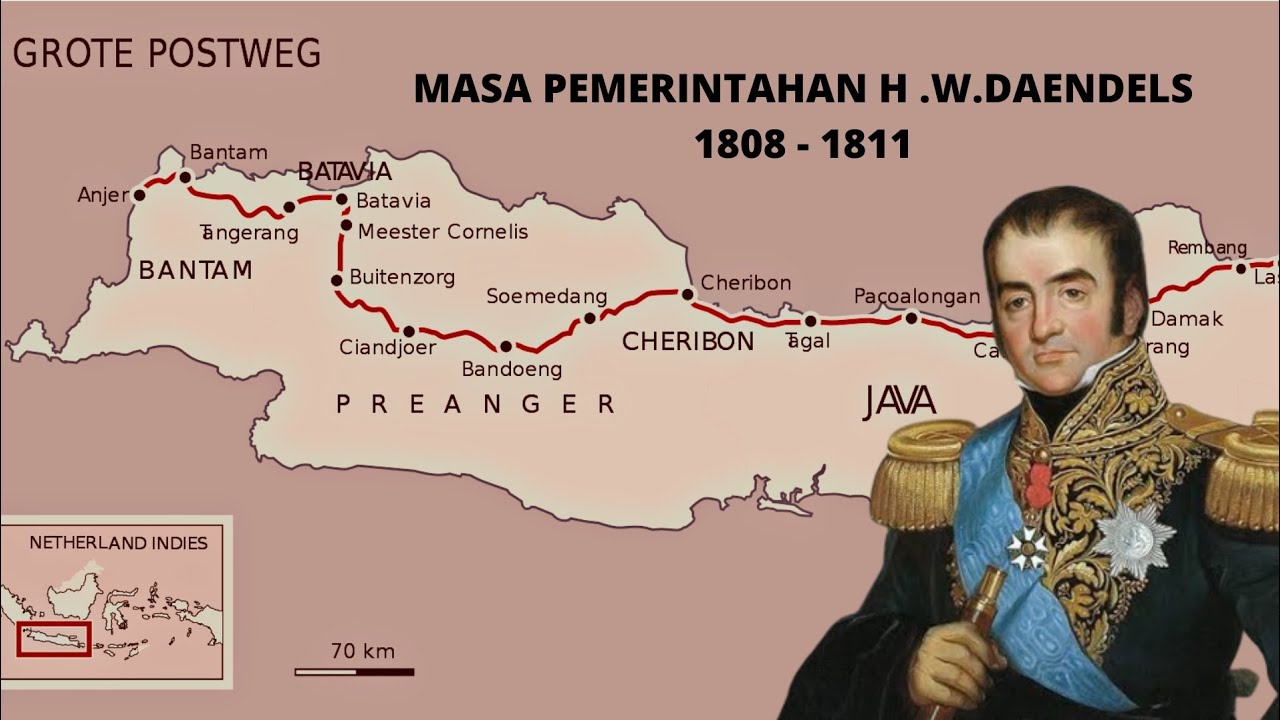
- 🛣️ In the military sphere, Daendels initiated the construction of a postal road from Anyer to Panarukan, spanning over 1100 KM, to facilitate troop mobility in Java.
- 🏠🚢 He also established naval bases in Anyer and Ujung Kulon and formed indigenous troops as part of the Dutch military, commanded by Javanese officers.
- 🏰 Daendels built various defense forts, such as Fort Ludwig in Gresik, as part of his military strategy.
- 👨⚖️ In the judicial sector, Daendels established three types of courts for Europeans, foreign Easterners, and indigenous people.
- 💼 He addressed the issue of corruption, ensuring that all corrupt individuals would be prosecuted without favoritism.
- 🌾💼 Economically, Daendels sold land parcels to private parties, levied taxes to increase government revenue, promoted agricultural production, and introduced mandatory agricultural and plantation deliveries.
- 🔚 Daendels' governance ended due to numerous reports on his autocratic approach, leading to his recall to the Netherlands in 1811 and replacement by Jan Willem Jansen.
- 🏳️ The British influence grew in Asia, eventually leading to their arrival in Batavia on August 4, 1811, and the subsequent surrender and capitulation of Jansen, marking the official British control over the Dutch East Indies.
Q & A
What was the main task assigned to Governor-General Daendels in Indonesia?
-Daendels' main task was to defend Java from British attacks, as the Dutch ruler Willem V sought British assistance to take over former VOC territories in the archipelago.
How did the French occupation of the Netherlands impact Dutch colonial rule in Indonesia?
-The French occupation led to significant changes in Dutch colonial rule, including the appointment of Herman Willem Daendels as Governor-General in Indonesia to strengthen Dutch control and protect the colony from British threats.
What were Daendels' key policies in the field of governance?
-Daendels implemented several policies in governance, including limiting the power of local rulers, reducing the feudal rights of government officials like regents, and dividing Java into nine prefectures, each headed by a prefect responsible to the Governor-General.
What measures did Daendels take to strengthen the military in Indonesia?
-Daendels' military measures included constructing the Great Post Road from Anyer to Panarukan for troop mobility, establishing naval bases in Anyer and Ujung Kulon, forming native military units like the Mangkunegaran Legion, and building various forts, such as Fort Ludwig in Gresik.
How did Daendels reform the judicial system in Indonesia?
-Daendels established three types of courts: one for Europeans, one for foreign Asians, and one for natives. He also took a strict stance against corruption, ensuring that corrupt officials were punished regardless of their status.
What were Daendels' economic policies in Indonesia?
-Daendels' economic policies included selling privately owned land to private parties, imposing taxes to increase government revenue, promoting the cultivation of cash crops, and enforcing mandatory delivery of agricultural and plantation products.
Why was Daendels recalled to the Netherlands, and who replaced him?
-Daendels was recalled to the Netherlands due to numerous reports of his authoritarian behavior. He was replaced by Jan Willem Janssens in 1811.
What happened to Dutch control in Indonesia after Daendels' departure?
-After Daendels left, Jan Willem Janssens took over but his rule was short-lived as British forces, expanding their influence in Asia, captured Batavia in August 1811, leading to Janssens' surrender and the formal transfer of Dutch territories to British control.
What role did the construction of the Great Post Road play in Daendels' military strategy?
-The Great Post Road, spanning approximately 1,100 kilometers from Anyer to Panarukan, was crucial for improving the mobility of Dutch troops across Java, enabling rapid deployment in response to British threats.
What were the long-term consequences of Daendels' policies in Indonesia?
-Daendels' policies, especially his administrative and military reforms, laid the groundwork for a more centralized and militarized colonial government, though his authoritarian methods also led to resentment and instability, ultimately weakening Dutch control and paving the way for British takeover.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Masa Pemerintahan Prancis di Indonesia [Herman Williem Daendels] Tahun 1808-1811
Masa Pemerintahan Daendels (1808 - 1811) Di Indonesia || Materi Sejarah Lengkap

KEKUASAAN REPUBLIK BATAAF DI INDONESIA | Sejarah Indonesia Kelas 11 - Video Pembelajaran

KERJA PAKSA ASLINYA DIBAYAR? Dikorupsi Pejabat Lokal? Ada Dana Untuk Pekerja! | Learning By Googling

Perebutan Hegemoni Bangsa-Bangsa Eropa di Indonesia | Sejarah Indonesia kelas XI semester 1

SEJARAH PENJAJAHAN PRANCIS DI NUSANTARA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)