Ethernet frame format in data link layer | IEEE 802.3
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the Ethernet frame format, also known as IEEE 802.3, detailing its structure and function within the MAC sublayer of the data link layer. It explains the protocol's design for 10 Mbps operation, various cable types and their characteristics, advantages, and the frame's minimum and maximum lengths. The script also breaks down the Ethernet frame into its components, including the preamble, start delimiter, destination and source addresses, data length, data field, pad, and frame check sequence, emphasizing error detection and the importance of adhering to the standard's specified frame lengths.
Takeaways
- 📚 The Ethernet frame format is governed by the IEEE 802.3 standard, which is developed by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
- 🚀 Ethernet protocol was initially designed to operate at a speed of 10 megabits per second.
- 🔌 Different types of cables can be used with Ethernet, including thick coaxial, thin coaxial, twisted pair, and optical fiber, each with varying maximum segment lengths and topologies.
- 🔶 The maximum segment length for Ethernet cables ranges from 100 meters for twisted pair to 2 kilometers for optical fiber.
- 🌐 Topologies for Ethernet include bus for coaxial cables and star for twisted pair and optical fiber.
- 🔑 Advantages of Ethernet include cost-effectiveness for thin coaxial cables, the use of hubs with twisted pair cables, and noise immunity for optical fibers.
- 🔄 Ethernet uses the 1-persistent CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) method for channel access in LANs.
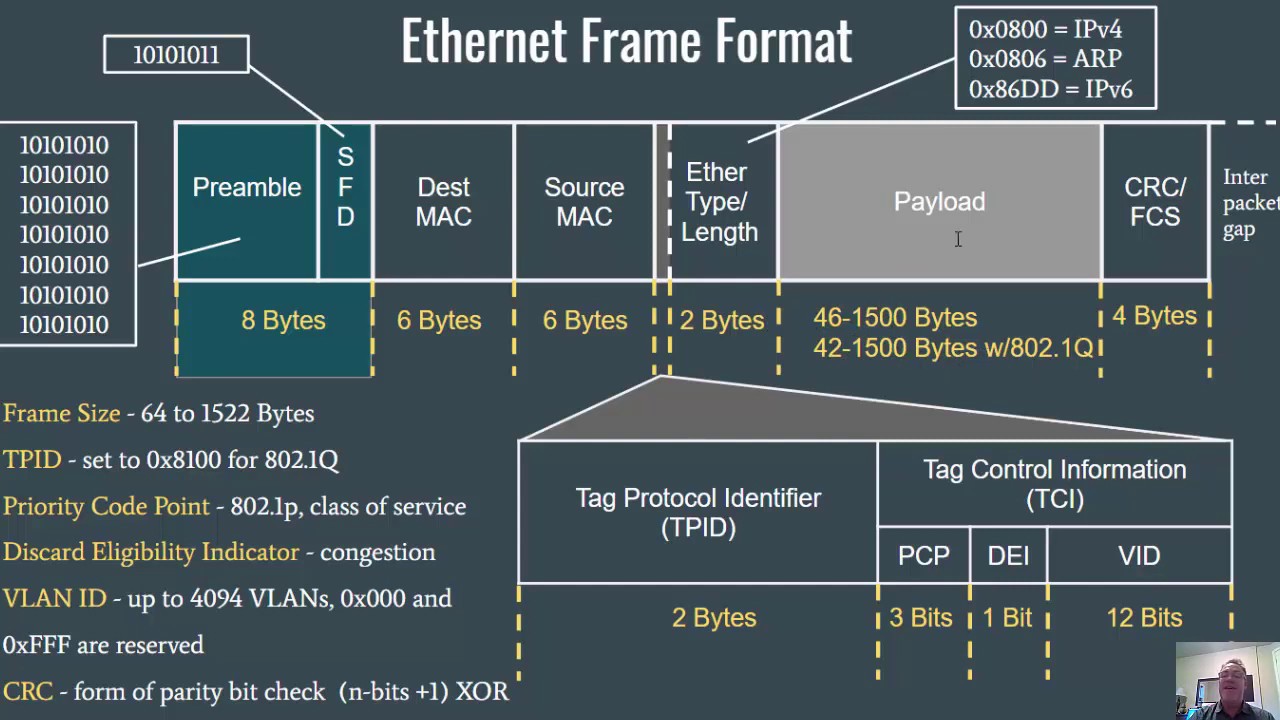
- 📈 The Ethernet frame structure includes fields for preamble, start delimiter, destination address, source address, length/data field, pad, and frame check sequence (FCS).
- 🔢 The preamble is 7 bytes long and helps the receiver synchronize and identify the beginning of a frame.
- 🏷️ The destination and source addresses are each 6 bytes long, containing the physical addresses of the receiver and sender, respectively.
- 📦 The data field of an Ethernet frame can range from a minimum of 46 bytes to a maximum of 1500 bytes, with padding used if data is less than 46 bytes.
- 🛡️ The frame check sequence (FCS) is used for error detection in the transmitted data, ensuring data integrity.
Q & A
What is the IEEE 802.3 standard?
-The IEEE 802.3 standard is the set of rules that define the Ethernet frame format, also known as the Ethernet protocol, which operates at the Data Link Layer of the OSI model.
What is the original speed at which the Ethernet protocol was designed to operate?
-The Ethernet protocol was originally designed to operate at 10 megabits per second.
What are the different types of cabling that can be used with Ethernet?
-Ethernet can use various types of cabling including thick coaxial cable (10Base5), thin coaxial cable (10Base2), twisted pair (10BaseT), and optical fiber (10BaseF).
What is the maximum length for each type of Ethernet cable segment?
-For 10Base5, the maximum segment length is 500 meters; for 10Base2, it's 185 meters; for 10BaseT, it's 100 meters; and for 10BaseF, it's 2 kilometers.
What are the topologies used for different types of Ethernet cables?
-10Base5 and 10Base2 use a bus topology, while 10BaseT and 10BaseF use a star topology.
What are the advantages of using optical fiber (10BaseF) for Ethernet?
-Optical fiber offers advantages such as good noise immunity and is less susceptible to interference, providing clearer signal transmission.
How does the Ethernet protocol access the channel in a LAN?
-Ethernet uses the 1-persistent CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection) method to access the channel in a LAN.
What is the purpose of the preamble in an Ethernet frame?
-The preamble is a 7-byte field consisting of a pattern of alternating ones and zeros that helps the receiver synchronize and identify the beginning of a frame.
What is the function of the start delimiter in an Ethernet frame?
-The start delimiter, also known as SD, is a 1-byte field that follows the preamble and indicates the beginning of the frame, ensuring the receiver knows to expect the destination address next.
What is the minimum and maximum length of an Ethernet frame?
-The minimum length of an Ethernet frame is 64 bytes, and the maximum length is 1518 bytes, excluding the preamble and start delimiter.
What is the purpose of the frame check sequence (FCS) in an Ethernet frame?
-The FCS is a 4-byte field used for error detection in the transmitted data. It helps identify any changes or errors in the bits during transmission.
Why is there a minimum length requirement for Ethernet frames?
-The minimum length requirement ensures that the entire frame is not transmitted before the first bit is received by the receiver, which is necessary for the proper operation of the CSMA/CD protocol and to reduce the likelihood of data frame collisions.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)