Biology Basics: Gene Flow (Simplified)
Summary
TLDRThe video script delves into the concept of gene flow, crucial for maintaining genetic diversity within species. It explains how genes, the DNA segments that define individual traits, contribute to the uniqueness within a species while still preserving unity. The script uses Charles Darwin's study of finches on the Galapagos Islands to illustrate how separation by a barrier can lead to speciation, as gene flow ceases and populations diverge. The importance of gene flow is highlighted, emphasizing its role in preventing species from becoming too distinct and possibly leading to extinction, and is a reminder of the shared traits that unite all humans within the human race.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Gene Flow is the transfer of genetic material between individuals within a species, influencing their diversity and characteristics.
- 🌱 Genes are segments of DNA that determine an individual's traits, making each person and animal unique yet similar to their kin.
- 🐦 In nature, variations like feather color or size can be observed within the same species of birds, reflecting genetic diversity.
- 🐥 Even newborn birds have a unique mix of traits from their parents, illustrating the genetic individuality within a species.
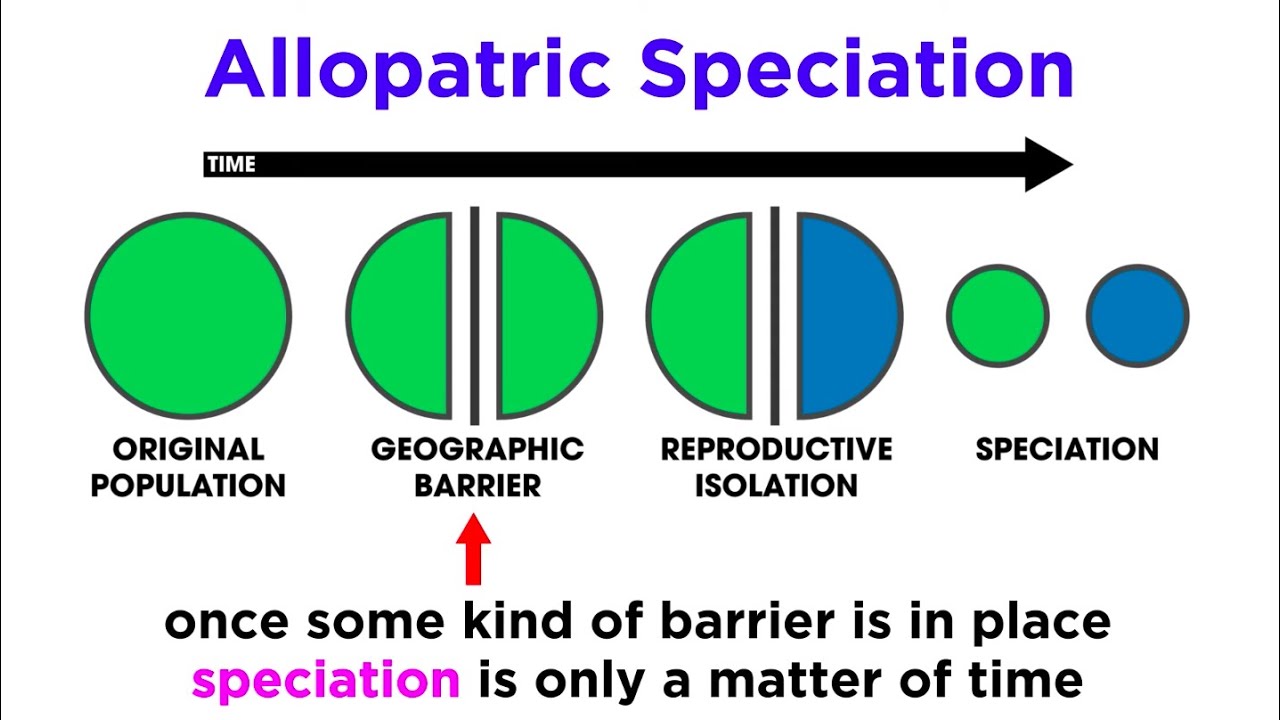
- 🌊 Charles Darwin's study of finches on the Galapagos Islands demonstrated how geographic separation can lead to speciation.
- 🌱 Finches on islands with different seed sizes evolved distinct beak sizes, showing adaptation to their environment without gene flow.
- 🏞️ The ocean acted as a natural barrier for the finch populations, preventing gene flow and leading to divergence into distinct species.
- 🔄 Gene flow is essential for maintaining genetic homogeneity within a species, as it allows for the mixing and sharing of traits.
- 🚫 Without gene flow, populations can become so genetically distinct that they may no longer be able to interbreed, potentially leading to extinction.
- 🌐 The concept of gene flow is crucial for understanding biodiversity and the evolution of species, including humans.
- 🌈 Human diversity in traits like hair and eye color is a result of gene flow, which keeps us all part of the same species.
Q & A
What is gene flow in the context of biology?
-Gene flow refers to the transfer of genetic material between different individuals within a species, which contributes to the genetic diversity of a population.
Why are genes important in determining individual traits?
-Genes are segments of DNA that carry the instructions for making proteins, which are responsible for an individual's characteristics, such as physical appearance and behavior.
How do genes contribute to the uniqueness of individuals within a species?
-Each individual has a unique combination of genes inherited from their parents, which results in a distinct set of traits that make them different from others, even within the same species.
What is the significance of gene flow in maintaining species diversity?
-Gene flow helps to mix the genetic traits within a species, preventing inbreeding and maintaining a healthy level of genetic variation, which is crucial for the species' adaptability and survival.
How did Charles Darwin's study of finches contribute to the understanding of species evolution?
-Darwin's observation of finches on the Galapagos Islands demonstrated how different environmental pressures could lead to variations in traits, such as beak size, which in turn could result in the formation of new species over time.
What is the role of a natural barrier in the process of speciation?
-A natural barrier, such as a body of water or a geographical feature, can separate populations of a species, preventing gene flow between them and leading to the development of distinct species over time.
Why did the finches on islands with different seed sizes develop different beak sizes?
-The finches adapted to the available food source on their respective islands. Those with big seeds developed larger beaks to crack the seeds, while those with small seeds had smaller beaks suitable for their diet.
What is the consequence of a lack of gene flow between separated populations?
-Without gene flow, populations can diverge genetically over time, potentially leading to the formation of new species that may no longer be able to interbreed with the original population.
How does gene flow prevent a species from becoming extinct due to lack of genetic diversity?
-Gene flow ensures that new genetic variations are introduced into a population, which can help the species adapt to changing environments and resist diseases, thus reducing the risk of extinction.
What would be the outcome if gene flow were to cease in a human population?
-If gene flow were to stop, human populations could become genetically isolated, leading to a decrease in genetic diversity and potentially resulting in health issues and a lack of adaptability to environmental changes.
Why is gene flow considered a unifying process for the human species?
-Gene flow allows for the mixing of genetic traits among different human populations, ensuring that despite variations in physical appearance, all humans belong to the same species with the ability to interbreed.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)