GEOGRAFI KELAS 10 DINAMIKA LITHOSFER DAN DAMPAKNYA TERHADAP KEHIDUPAN (1) - ROHANA RETNO FEBRIYANI
Summary
TLDRThe video presents an introductory geography lesson on lithosphere dynamics for high school students. It begins with greetings, attendance reminders, and an opening prayer before outlining the semester’s focus on the lithosphere and its impact on life. The teacher explains the definition of the lithosphere, Earth’s internal structure, and the rock cycle, emphasizing how rocks transform through processes such as cooling, weathering, erosion, sedimentation, pressure, heat, and melting. The lesson details classifications of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, including their formation processes, characteristics, and examples. The session concludes with an assignment requiring students to identify rock examples and their uses, followed by motivational encouragement.
Takeaways
- 📚 The lesson introduces the topic of lithosphere dynamics and their impacts on life, beginning the second semester’s geography material.
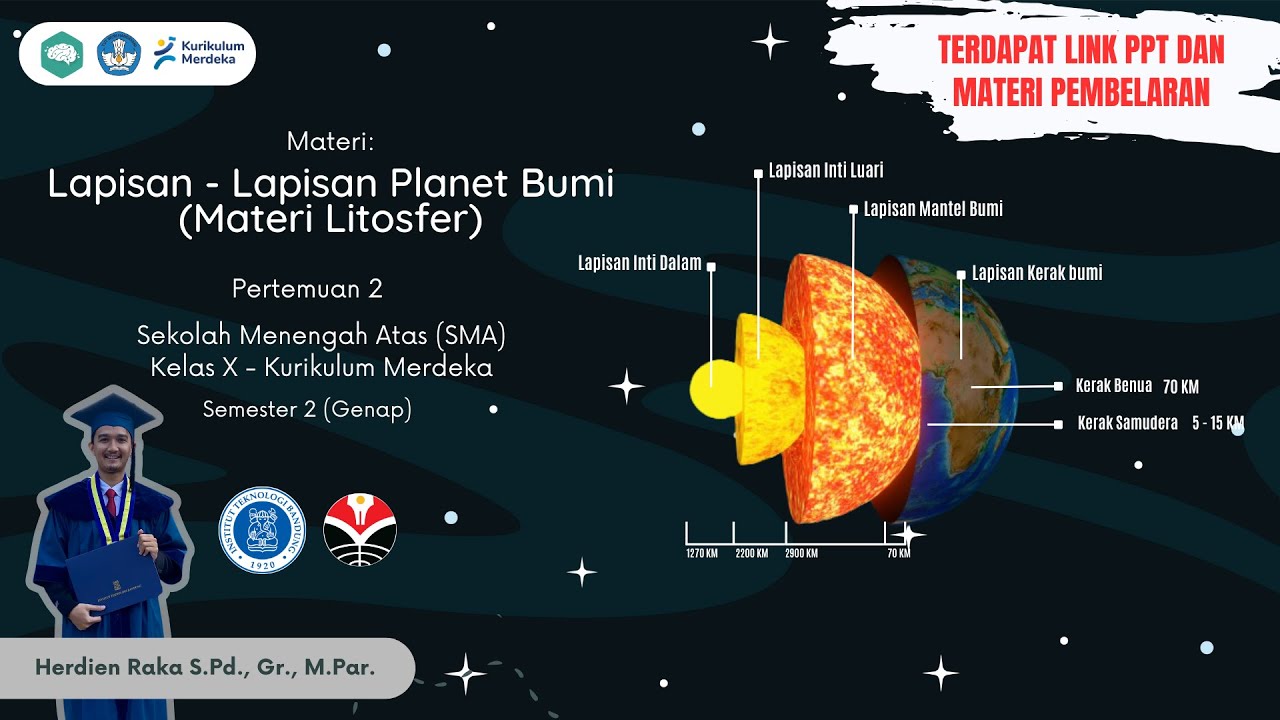
- 🌍 The lithosphere is defined as the Earth’s outermost layer, including the crust and the upper part of the mantle.
- 🧱 Students are expected to understand Earth’s internal structure, including the crust, mantle, and core, as part of lithosphere study.
- 🔄 The rock cycle explains how magma cools into igneous rock, which can weather into sediment, become sedimentary rock, transform into metamorphic rock, and melt back into magma.
- 🌋 Endogenic forces (internal forces) shaping Earth include tectonic activity, volcanism, and earthquakes.
- 🌧️ Exogenic forces (external forces) include weathering, erosion, and deposition that reshape Earth’s surface.
- 🪨 Rocks are classified into three main types: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks.
- 🔥 Igneous rocks form from cooling magma and are categorized into intrusive (deep), intermediate, and extrusive (surface) types based on where cooling occurs.
- 🏞️ Sedimentary rocks form from accumulated and compacted materials from weathered rocks and can be clastic, chemical, or organic in origin.
- ضغط Metamorphic rocks form when existing rocks are altered by high temperature, high pressure, or both, producing rocks like marble and slate.
- 🧪 The order of the rock cycle is not always fixed; rocks can transform between types depending on environmental conditions and geological processes.
- 📝 Students are assigned to find examples of each rock type and explain their uses in daily life, submitting written and photographed work through Google Classroom.
- 💡 The teacher encourages optimism and perseverance, emphasizing that challenges can be overcome with determination.
Q & A
What is the main topic of this lesson?
-The main topic of this lesson is the 'Lithosphere' and its dynamics, including the formation of Earth's surface and the different types of rocks.
What is the lithosphere?
-The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth, which includes the Earth's crust and the upper part of the mantle.
What are the key areas of focus in studying the lithosphere?
-The key areas of focus are the structure of Earth's layers, the rock cycle, the classification of rocks, and the forces that shape the Earth's surface.
What are the two types of forces that influence the Earth's surface?
-The two types of forces are endogenic (internal forces like tectonic activity and volcanic activity) and exogenic (external forces like weathering, erosion, and sedimentation).
What is the rock cycle, and how does it work?
-The rock cycle is the process through which rocks transform from one type to another over time. It begins with magma cooling to form igneous rocks, which can then be weathered and eroded to form sedimentary rocks, or undergo heat and pressure to become metamorphic rocks. These can later melt to form magma again, continuing the cycle.
What are the three main types of rocks?
-The three main types of rocks are igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and metamorphic rocks.
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
-Weathering refers to the breakdown of rocks into smaller particles, while erosion involves the movement of these particles by natural forces like wind, water, or ice.
Can rocks go through the rock cycle in different orders?
-Yes, rocks may go through different processes in different orders depending on geological conditions. For example, sedimentary rocks can sometimes transform directly into igneous rocks without first becoming metamorphic rocks.
What are the characteristics of igneous rocks formed inside the Earth?
-Igneous rocks formed inside the Earth (intrusive rocks) cool slowly and have a coarse texture, such as granite, because the cooling process allows larger crystals to form.
What is the role of sedimentary rocks in the rock cycle?
-Sedimentary rocks form from the accumulation of materials like sand, mud, or organic matter, and they play an important role in preserving historical records of Earth's surface conditions, including fossils.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)