How Cement Is Made In Factories?
Summary
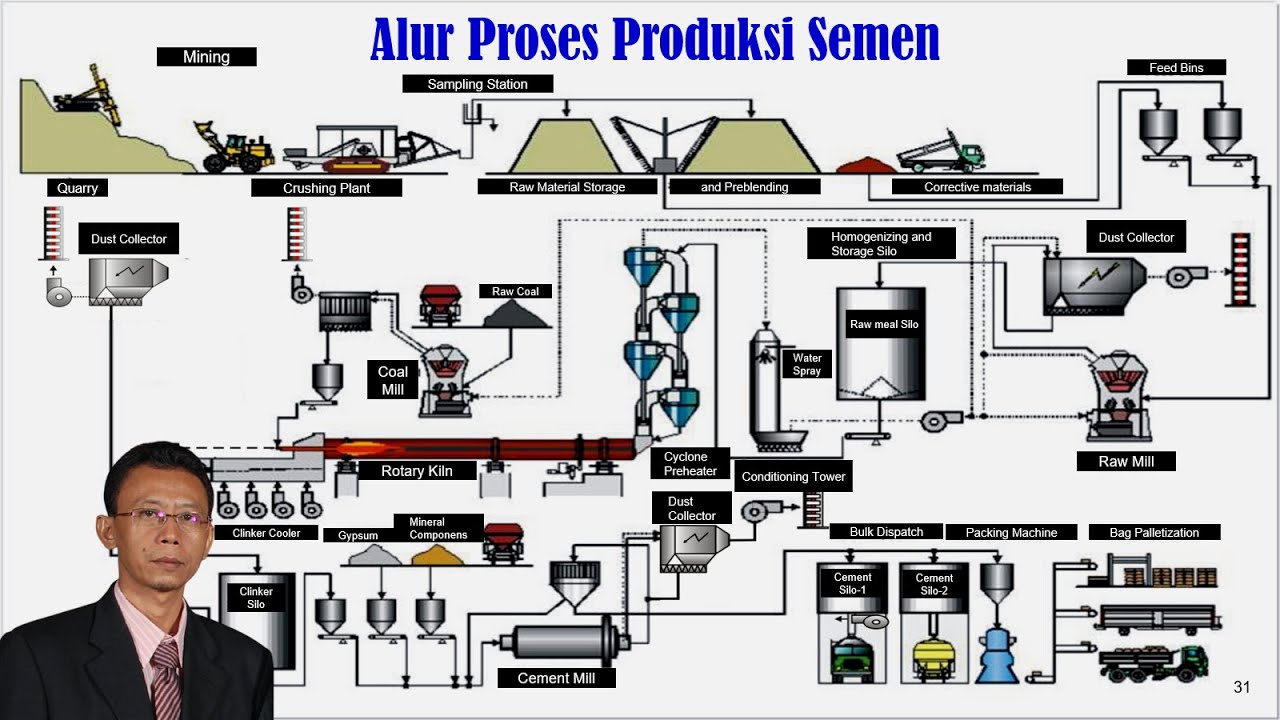
TLDRThis video takes viewers on aGenerate summary script fascinating journey through the entire cement manufacturing process, from raw material extraction to the final product. It explains how limestone, shale, marl, and additives like gypsum and iron ore are quarried, crushed, mixed, and ground into a fine powder. The raw mix is preheated, burned in a rotary kiln to produce clinker, and then cooled, stored, and combined with gypsum and limestone before final milling. The video also highlights quality control measures, energy-efficient techniques, and the packaging and dispatch of cement, providing a clear, step-by-step overview of how cement is produced with precision and care.
Takeaways
- 🪨 Cement production begins with the extraction of raw materials such as limestone, shale, and marl from quarries, along with iron ore and gypsum from mines.
- 🚛 Raw materials are transported using 60-ton haul trucks to crushers and ground to a rough gravel-like consistency.
- ⚙️ Crushed materials are mixed in a large mixing bay to create a homogeneous blend, with corrective additives added if chemical proportions are off.
- 🌡️ The homogenized mixture is ground into fine powder (raw mix) in roller mills, which are more energy-efficient than traditional ball mills.
- 🔥 The raw mix is preheated and then burned in a 54-meter-long rotary kiln at temperatures exceeding 1450°C to produce clinker.
- ❄️ Clinker is cooled using air in a grate cooler and stored in large silos with a capacity of 55,000 tons.
- ⚗️ Additives such as gypsum and high-grade limestone are added to clinker before it is milled in cement mills to produce final cement products.
- 🧪 Quality control is maintained through a fully equipped lab that tests over 140 samples per day across 11 sampling stations.
- 📦 Cement is packaged in 50 kg bags on pallets or transported in bulk by road, rail, or sea for distribution.
- 🖥️ The entire cement manufacturing process is continuously monitored and controlled from a central control room to ensure consistent, high-quality output.
- 🌱 Using limestone extension in cement reduces the carbon footprint of the final products.
- 📊 The process ensures continuous availability of cement products with precise storage capacities for raw mix, clinker, and finished cement.
Q & A
What are the primary raw materials used in cement production?
-The primary raw materials are limestone, shale, and marl, which are extracted from quarries.
Which additional materials are added to the cement mixture besides the primary raw materials?
-Iron ore and gypsum are added, and sometimes high-grade limestone is used as an additive to reduce the carbon footprint.
What is the purpose of the crusher in the cement production process?
-The crusher reduces the raw materials to the consistency of rough gravel, preparing them for further processing.
How is the raw mixture homogenized before milling?
-Crushed limestone, shale, and marl are conveyed to the mixing bay, where they are blended to form a homogeneous mixture, and corrective materials are added if needed.
What advantages do roller mills have over traditional ball mills in cement production?
-Roller mills save about 30% of electrical power compared to traditional ball mills while grinding the raw mix into a fine powder.
Describe the process and conditions in the rotary kiln.
-The rotary kiln, 54 meters long, burns the raw mix at temperatures exceeding 1450°C to produce clinker, with a daily production capacity of 2,100 tons.
How is clinker cooled and stored before cement milling?
-Clinker is cooled using air quenching in a grate cooler and then stored in a clinker silo with a capacity of 55,000 tons.
What is the purpose of adding gypsum and high-grade limestone to clinker before milling?
-Gypsum controls the setting time of cement, while high-grade limestone extends the mixture and reduces the carbon footprint of the final product.
How is quality controlled throughout the cement production process?
-A chemical and physical laboratory takes samples at various stages, with 11 sampling stations handling over 140 samples per day, ensuring consistent, world-class product quality.
In what forms is cement dispatched, and how is it packaged for protection?
-Cement is dispatched as bulk or in 50 kg bags, with bags arranged on pallets (40 per pallet) and shrink-wrapped for protection against weather conditions.
What role does the control room play in cement manufacturing?
-The control room continuously monitors the entire production process, allowing personnel to make immediate adjustments to maintain the highest quality standards.
What is the overall sequence of the cement production process from raw material to finished product?
-The sequence is: Quarry extraction → crushing → mixing to homogeneous material → addition of additives → raw milling → preheating → rotary kiln burning to clinker → cooling → clinker storage → addition of gypsum and limestone → cement milling → storage in silos → bagging or bulk dispatch.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

How Cement is Made? Cement Production Process 🪨

Kimia Industri - Diagram Alir Proses Pembuatan Semen

Process de fabrication du ciment - Ciments Calcia
Alur Proses Produksi Semen (Tahapan Proses Produksi Semen)_Indonesia

Sunflower Oil Production Process – How Sunflower Seeds Become Pure Cooking Oil

Cement Manufacturing
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)