Einstein's Theory Of Relativity | The Curvature of Spacetime | General Relativity | Dr. Binocs Show
Summary
TLDRThis video explores gravity, starting with Newton's description of it as a force pulling objects toward each other and progressing to Einstein's revolutionary theory of general relativity. It explains how massive objects bend the fabric of space-time, causing what we perceive as gravitational attraction, illustrated with a trampoline analogy. The video highlights real-world confirmations of Einstein's theory, including black holes and GPS satellite adjustments. It emphasizes the transformative impact of general relativity on our understanding of the universe and includes a fun trivia fact about Einstein's academic struggles, making complex physics accessible and engaging for viewers.
Takeaways
- 🌍 Gravity is the invisible force that pulls objects toward each other and keeps planets in orbit around stars.
- 📚 Isaac Newton described gravity as a force, with its strength depending on mass and distance between objects.
- 💡 Newton's theory explained gravity well but treated it as a magical force acting instantly across any distance.
- 🕰️ Albert Einstein showed that space and time are connected, forming a fabric called spacetime.
- ⚡ Einstein discovered that the speed of light is constant, which led to his insights into relativity.
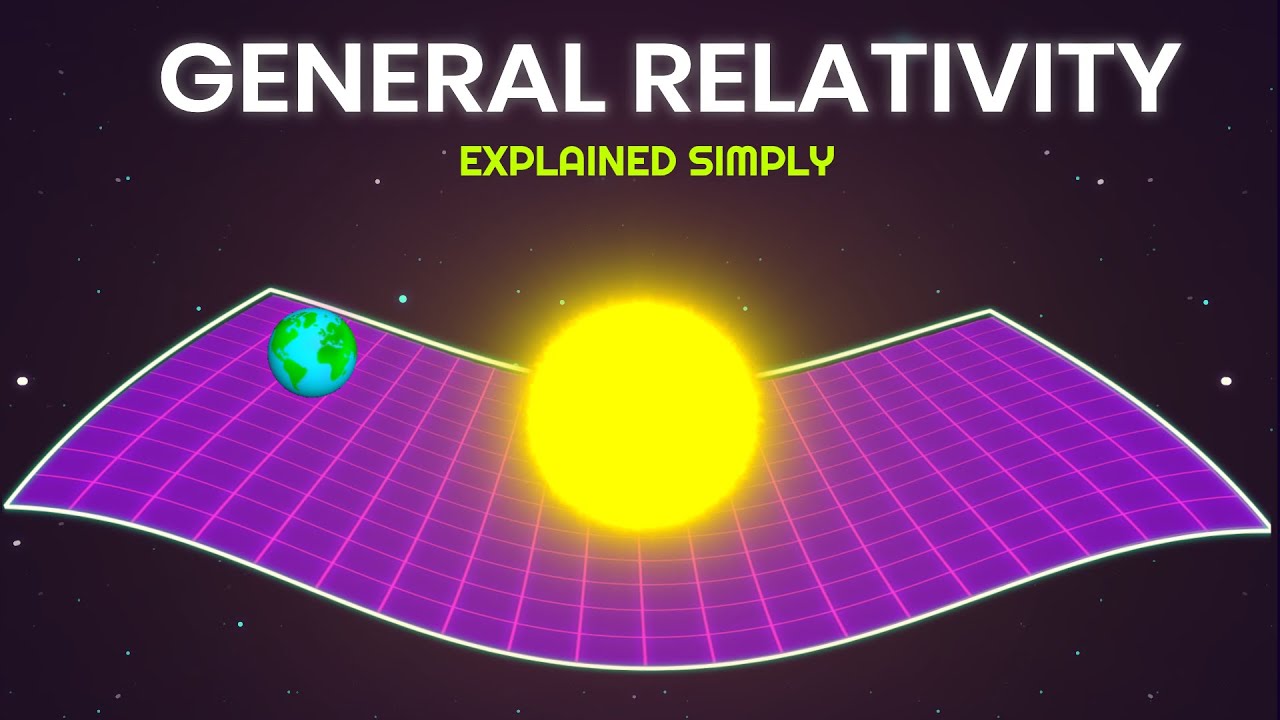
- 🌀 Massive objects bend spacetime, and gravity is the result of this curvature, not a mysterious force.
- 🎳 The trampoline analogy illustrates general relativity: heavy objects create curves in spacetime, guiding smaller objects along these curves.
- ☀️ The Sun bends spacetime, and planets follow these curves, explaining orbital motion without invoking a pull.
- 🛰️ Technologies like GPS rely on general relativity because Earth's gravity affects the passage of time.
- 🕳️ Observations of black holes support Einstein's theory, showing extreme warping of spacetime.
- 🧠 Einstein revolutionized our understanding of the universe by explaining gravity through spacetime curvature.
- 🎨 Trivia: Einstein passed science and math exams but failed other subjects like history and languages.
Q & A
What is the basic concept of gravity according to Sir Isaac Newton?
-According to Sir Isaac Newton, gravity is a force that pulls objects toward each other. The strength of gravity depends on the mass of the objects and the distance between them. Larger objects exert a stronger gravitational pull.
How did Newton describe gravity in his book 'The Principia'?
-In 'The Principia,' Newton described gravity as an invisible force that acts instantly across any distance, pulling objects toward one another based on their masses and the space between them.
What was the limitation of Newton's view on gravity?
-Newton thought of gravity as a magical force that acted instantly across any distance. However, this explanation didn't account for all observations, particularly in extreme conditions like those near black holes or at very high speeds.
How did Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity change the understanding of gravity?
-Einstein's theory of general relativity revolutionized the concept of gravity. Instead of being a force, gravity was understood as the result of massive objects bending the fabric of space-time, causing other objects to follow these curves.
What is the connection between space and time in Einstein's theory?
-Einstein discovered that space and time are interconnected into a single entity called 'space-time.' His theory of special relativity showed that space and time are not separate but can be warped by massive objects.
How does Einstein’s concept of space-time bending explain gravity?
-According to Einstein, massive objects like the sun bend the fabric of space-time around them. Planets, including Earth, follow these curves, not because they are being pulled by a force, but because they are moving along the warped space-time.
Can you explain the trampoline analogy in relation to gravity?
-The trampoline analogy demonstrates how gravity works according to general relativity. A heavy object like a bowling ball placed on a trampoline creates a dip, and smaller objects like marbles roll toward the ball not because of a direct force, but because of the curve in the surface.
What real-world evidence supports Einstein's theory of general relativity?
-Real-world evidence supporting Einstein's theory includes the existence of black holes, which warp space-time into deep pits, and the functioning of GPS satellites, which adjust for the bending of time caused by Earth's gravity.
Why do GPS satellites need to account for general relativity?
-GPS satellites need to account for general relativity because time moves faster in space due to the weaker gravitational pull. If adjustments weren't made, GPS calculations would be inaccurate.
What is the significance of Einstein's theory in understanding the universe?
-Einstein's theory of general relativity transformed our understanding of the universe by showing that gravity is the result of space-time bending. This insight has allowed scientists to understand phenomena like black holes and the motion of planets with greater accuracy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

The True Nature of Gravity: Einstein vs. Newton

What is Gravity? | Singularity
If light has no mass, why is it affected by gravity? General Relativity Theory

Do you really understand Einstein’s theory of relativity? - BBC News

What is the General Theory of Relativity?

Teori Yang Membuat Kalian Berfikir Ulang Tentang Arti "JATUH" | TEORI RELATIVITAS UMUM EINSTEIN
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)