The True Nature of Gravity: Einstein vs. Newton
Summary
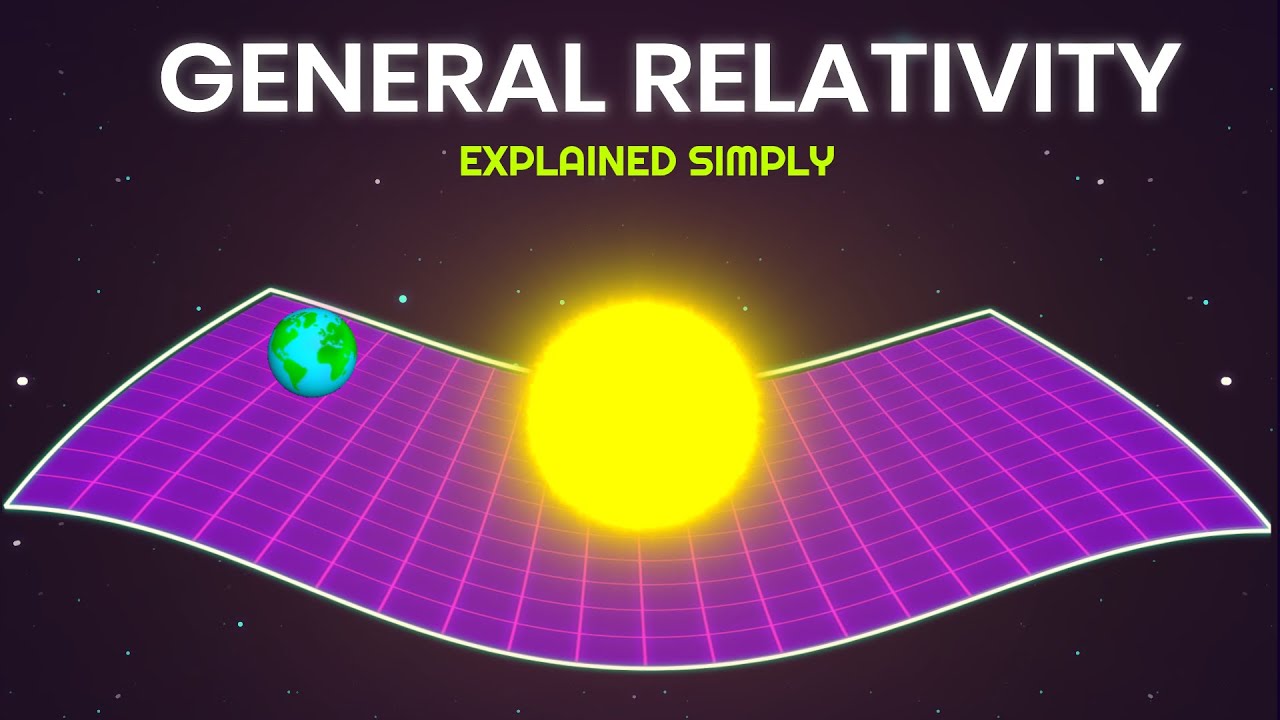
TLDRThis video explores the revolutionary concept of gravity according to Einstein's theory of General Relativity, contrasting it with Newton's view. Unlike Newton, who described gravity as a force between masses, Einstein explained gravity as the curvature of space-time caused by massive objects. The video delves into how this curvature influences the movement of planets and other objects, and how the fall of objects is not due to a force but the natural movement through curved space-time. It also highlights key concepts like geodesics, space-time curvature, and the principle of equivalence.
Takeaways
- 😀 Newtonian gravity views gravity as a force between masses that attract each other.
- 😀 Einsteinian gravity, in contrast, sees gravity as a curvature of spacetime caused by massive objects.
- 😀 Massive objects like the Earth and Sun cause spacetime to curve, and this curvature influences planetary orbits.
- 😀 The curvature of spacetime is the key factor behind gravity, not a traditional force between objects.
- 😀 The principle of equivalence states that all objects fall the same way, regardless of their mass.
- 😀 In Einstein's theory, free fall is not caused by a force but by the natural motion of bodies through curved spacetime.
- 😀 Objects moving through curved spacetime follow geodesics, the most direct paths in curved geometry.
- 😀 The curvature of spacetime around massive bodies like the Earth and Sun is subtle and often undetectable by common measurements.
- 😀 According to general relativity, gravity is not a force but the result of moving through curved spacetime.
- 😀 The geometry of spacetime in the presence of mass distorts the straight lines (geodesics), creating what we perceive as gravitational effects.
- 😀 The idea of gravity in general relativity fundamentally changes our understanding of orbits and the movement of objects in space.
- 😀 In relativity, objects move in straight lines in spacetime, but these lines appear curved when projected into regular 3D space due to spacetime curvature.
- 😀 The gravitational effect of the Sun causes spacetime to curve, and planets move along these curved paths, creating elliptical orbits.
- 😀 The force of gravity is no longer a concept in the dynamics of objects, but rather a manifestation of spacetime curvature.
- 😀 While gravity is not a force in general relativity, using the term 'force' remains practical for everyday discussions.
Q & A
What is the key difference between Newtonian gravity and Einsteinian gravity?
-In Newtonian gravity, gravity is seen as a force between masses that attract each other. In Einsteinian gravity, gravity is not a force but the curvature of space-time caused by the presence of mass.
How does Einstein’s theory of relativity explain the Earth’s orbit around the Sun?
-Einstein’s theory explains that the Sun’s mass distorts space-time, causing the Earth to move along a curved geodesic path through space-time. This results in an elliptical orbit, which is perceived as a curved trajectory in ordinary space.
What is the concept of space-time in general relativity?
-Space-time in general relativity is a four-dimensional construct combining three spatial dimensions and one temporal dimension. Objects move within this space-time, and gravity is understood as the curvature of this space-time, not a force.
What does the principle of equivalence state in Einstein's theory?
-The principle of equivalence states that all objects, regardless of their mass, fall in the same way under gravity. This means that the motion of objects in free fall is the natural motion, and gravity is not a force but the result of curved space-time.
How does mass affect space-time according to general relativity?
-Mass distorts the fabric of space-time. The more massive an object, the greater the curvature of the space-time around it. This curvature dictates the movement of objects nearby, explaining gravitational attraction.
What is a geodesic in the context of general relativity?
-A geodesic is the straightest possible path in curved space-time. In general relativity, objects move along these paths, and their motion is determined by the curvature of space-time rather than a force acting on them.
Why does an object in free fall appear to be accelerating towards the Earth?
-An object in free fall follows a geodesic in curved space-time. The curvature around Earth causes the object to appear as though it is accelerating toward the ground, even though it is simply moving along a straight path in curved space-time.
How does Einstein’s theory redefine the concept of gravity?
-Einstein’s theory of general relativity redefines gravity as the curvature of space-time rather than a force between masses. The presence of mass distorts space-time, and objects move along the curved paths (geodesics) dictated by this curvature.
Why did humans once believe that space was Euclidean, and how did Einstein’s theory change this view?
-For centuries, humans believed space was Euclidean because the curvature of space-time caused by Earth and the Sun was too subtle to detect with everyday measurements. Einstein’s theory revealed that space is not strictly Euclidean, but rather curved, especially around massive objects like the Sun.
Why is the term 'gravity' still used, despite the fact that it is not a force in general relativity?
-The term 'gravity' is still used for convenience, as a shorthand for the effects of space-time curvature. While gravity is not a force in the traditional sense, referring to it as gravity is useful in everyday language and understanding of the phenomenon.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is Gravity? | Singularity

Einstein's Theory Of Relativity | The Curvature of Spacetime | General Relativity | Dr. Binocs Show

Newtonian physics and relativity

#AghamUnite: Relativity and the Big Bang

Teori Yang Membuat Kalian Berfikir Ulang Tentang Arti "JATUH" | TEORI RELATIVITAS UMUM EINSTEIN
If light has no mass, why is it affected by gravity? General Relativity Theory
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)