Klasifikasi Virus Biologi Kelas 10 | Materi UTBK Biologi
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Kak Isma introduces the classification of viruses, explaining six key categories: presence or absence of an envelope on the nucleocapsid, the number of capsomeres, host cell type, genome type and replication method, nucleic acid type, and basic structural form. The video highlights examples for each classification, such as herpesvirus, polio, and HIV, while covering the difference between enveloped and naked viruses, as well as the variations in capsomeres and host specificity. Viewers gain a comprehensive understanding of viral classification, which is essential for further study in virology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Viruses can be classified into six categories based on their characteristics: presence or absence of a sheath, number of capsomeres, type of host cell, type of genome and replication method, type of nucleic acid, and basic form.
- 😀 The first classification is based on whether the virus has a sheath around its nucleocapsid. Viruses with sheaths are called enveloped viruses, while those without are called naked viruses.
- 😀 Examples of enveloped viruses include pox viruses, herpes viruses, togaviruses, and rhabdoviruses, whereas naked viruses include popo virus, adenovirus, picornavirus, and reovirus.
- 😀 The second classification is based on the number of capsomeres in the virus. This can range from 32 capsomeres in parvovirus to 252 in adenovirus.
- 😀 The third classification categorizes viruses according to the type of host cell they infect: bacteria (bacteriophage), plants (e.g., tobacco mosaic virus), animals (e.g., rabies virus), and humans (e.g., HIV, influenza, and coronavirus).
- 😀 The fourth classification focuses on the type of genome and replication method. Viruses are grouped based on their DNA or RNA structure and how they reproduce.
- 😀 Type 1 viruses have double-stranded DNA and replicate by replication (e.g., herpesvirus), while type 6 viruses have single-stranded positive RNA and intermediate DNA, with reproduction via reverse transcription (e.g., HIV).
- 😀 Type 2 viruses feature single-stranded DNA and replicate by replication, whereas type 5 viruses have single-stranded negative RNA and replicate similarly (e.g., rabies virus).
- 😀 The fifth classification divides viruses into DNA and RNA viruses based on their nucleic acid type. DNA viruses include parvovirus, while RNA viruses include picornavirus.
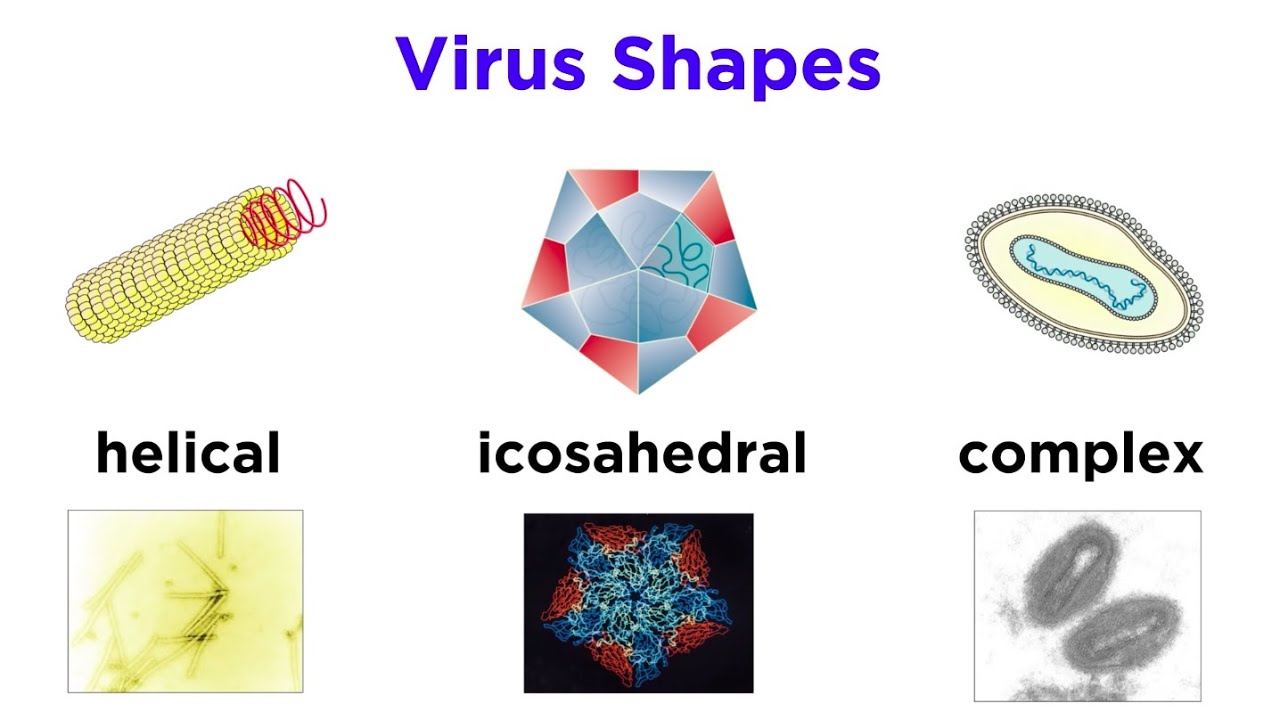
- 😀 The sixth and final classification concerns the basic shape of the virus: icosahedral (e.g., polio virus), helical (e.g., flu virus), and complex (e.g., smallpox virus).
Q & A
What are the main classifications of viruses discussed in the video?
-The video discusses six classifications of viruses: 1) Classification based on the presence or absence of a sheath on the nucleocapsid, 2) Classification based on the number of capsomeres, 3) Classification based on the type of host cell, 4) Classification based on the type of genome and replication method, 5) Classification based on the type of nucleic acid, and 6) Classification based on their basic form.
What is the difference between enveloped and naked viruses?
-Enveloped viruses have a sheath made of lipoproteins and glycoproteins surrounding the nucleocapsid, such as poxviruses and herpesviruses. Naked viruses do not have this sheath, and examples include picornavirus and reovirus.
How are viruses classified based on the number of capsomeres?
-Viruses are classified into five groups based on their number of capsomeres: 32 capsomeres (parvovirus), 60 capsomeres (picornavirus), 72 capsomeres (poxvirus), 162 capsomeres (herpesvirus), and 252 capsomeres (adenovirus).
What are the four categories of host cells viruses can attack?
-Viruses are classified based on the type of host cell they attack: 1) Bacteria (bacteriophages), 2) Plants (e.g., tobacco mosaic virus), 3) Animals (e.g., rabies virus), and 4) Humans (e.g., HIV, influenza, and coronavirus).
What are the different types of viruses based on genome and replication method?
-There are seven types of viruses based on genome and replication method: Type 1 (double-stranded DNA), Type 2 (single-stranded DNA), Type 3 (double-stranded RNA), Type 4 (single-stranded positive RNA), Type 5 (single-stranded negative RNA), Type 6 (single-stranded positive RNA with intermediate DNA, reverse transcription), and Type 7 (double-stranded RNA with intermediate RNA, reverse transcription).
What is the difference between DNA viruses and RNA viruses?
-DNA viruses have nucleic acid in the form of DNA, like parvovirus, while RNA viruses have nucleic acid in the form of RNA, like picornavirus.
Can you explain the three basic forms of viruses?
-Viruses can have three basic forms: 1) Icosahedral viruses, with 20 equilateral triangles and a double axis of rotation (e.g., polio virus), 2) Helical viruses, with a single axis of rotation and a rod-like shape (e.g., flu virus), and 3) Complex viruses, which have more complex structures (e.g., smallpox virus).
What is the replication process for viruses with single-stranded negative RNA?
-Viruses with single-stranded negative RNA, like the rabies virus, replicate through the process of replication, where the RNA is transcribed into complementary RNA for protein synthesis and replication.
How does reverse transcription occur in certain viruses?
-In viruses like HIV (Type 6) and hepatitis B (Type 7), reverse transcription occurs where RNA is first converted into DNA by the enzyme reverse transcriptase, enabling integration into the host genome for replication.
Why is classification based on host cell important?
-Classifying viruses based on their host cell helps in understanding which organisms they affect, and aids in the development of targeted treatments for bacterial, plant, animal, and human viral infections.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)