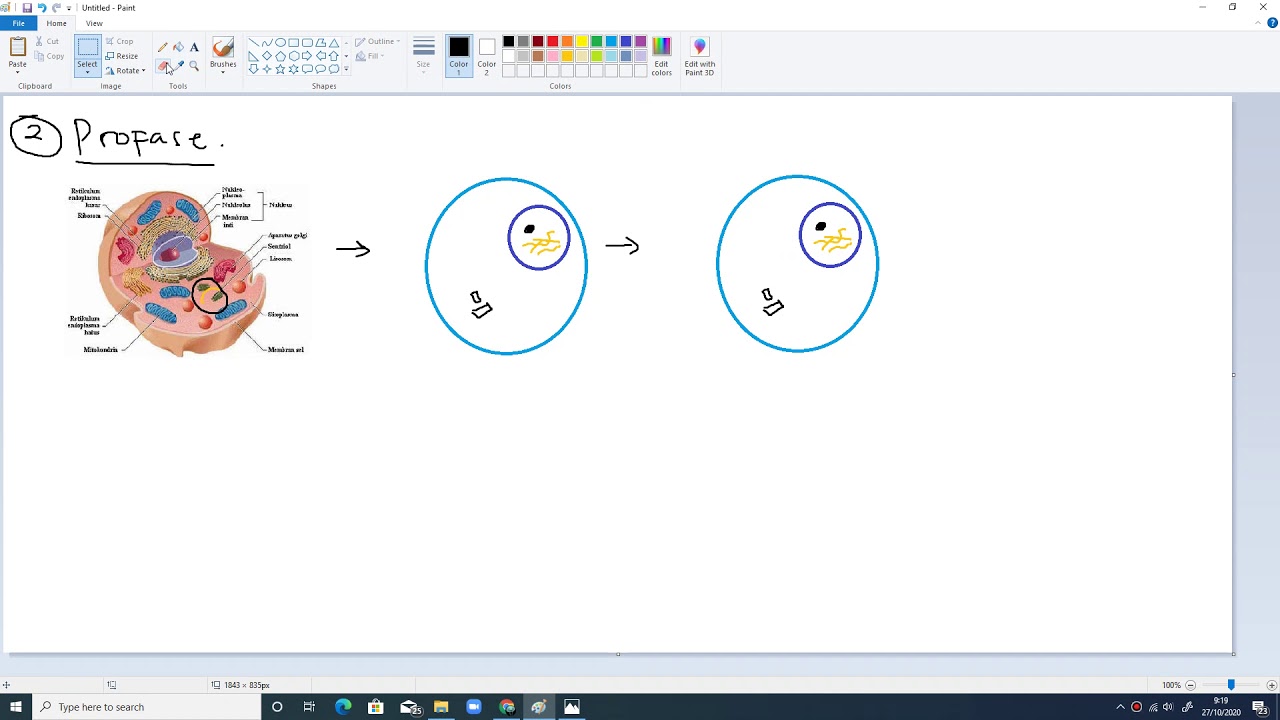
Pertumbuhan Sel
Summary
TLDRThe video script explains the concept of cell growth during interphase, which prepares cells for division. Interphase accounts for around 90% of the cell cycle and consists of three phases: G1 (first gap), S (synthesis), and G2 (second gap). G1 and G2 are periods of cell growth, while S is when DNA synthesis occurs. The duration of each phase varies based on the cell type and cycle length. For a 24-hour cell cycle, the G1 phase lasts about 11 hours, the S phase 8 hours, and G2 about 4 hours. Cells with slower generation times can have G1 phases lasting from days to years.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cell growth, also known as interphase, is a crucial stage for preparing cells for division.
- 😀 Interphase accounts for about 90% of the total cell cycle time, indicating high cellular activity.
- 😀 The interphase consists of three phases: G1 (Growth), S (Synthesis), and G2 (Gap 2).
- 😀 G1 (Gap 1) is the first phase, where the cell undergoes growth and organelle synthesis.
- 😀 S phase involves the synthesis and replication of DNA in preparation for division.
- 😀 G2 (Gap 2) is the phase where the cell prepares for division by ensuring all organelles and DNA are ready.
- 😀 The G1 and G2 phases are called 'gap' phases because they reflect the periods between DNA synthesis and division.
- 😀 Cell growth in interphase includes an increase in organelles, protein synthesis, and cell size.
- 😀 The length of each phase in the cell cycle varies, with G1 phase being the most variable.
- 😀 A 24-hour cell cycle typically sees G1 lasting around 11 hours, S phase around 8 hours, and G2 around 4 hours.
- 😀 The duration of the G1 phase can range from several days to years, depending on the type of cell.
Q & A
What is cell growth, and why is it important?
-Cell growth, also known as interphase, is the stage where a cell increases its mass and prepares for cell division. This process is crucial as it ensures that the cell has enough resources, such as organelles and DNA, to divide successfully.
How much of the total generation time does the interphase stage occupy?
-The interphase stage occupies around 90% of the total generation time, indicating that it is a period of very high cell activity.
What are the primary activities that occur during interphase?
-During interphase, several activities occur, including increasing organelles in the cytoplasm, protein synthesis, cell size growth, and DNA replication.
What are the three phases of interphase?
-The three phases of interphase are G1 (first gap interval), S (synthesis phase), and G2 (second gap interval).
What does the term 'gap intervals' refer to in the context of G1 and G2 phases?
-The term 'gap intervals' refers to periods of relative inactivity in terms of cell division, but during these phases, the cell grows and prepares for DNA synthesis (G1) and cell division (G2).
What is the role of the G1 phase in the cell cycle?
-The G1 phase, or first gap interval, is the stage where the cell grows in size and prepares the necessary organelles and proteins before DNA synthesis begins.
What occurs during the S phase of interphase?
-During the S phase (synthesis), the cell replicates its DNA in preparation for cell division.
Why is the G2 phase considered the 'division preparation phase'?
-The G2 phase is called the division preparation phase because the cell continues to grow and synthesizes proteins required for cell division.
How does the length of each phase in the cell cycle vary?
-The length of each phase varies depending on the cell type and its specific generation time. For example, in a 24-hour cell cycle, G1 might last around 11 hours, S phase around 8 hours, and G2 about 4 hours.
Why does the G1 phase have such variation in generation time across different cells?
-The length of the G1 phase can vary greatly, ranging from several days to several years, depending on how long a cell takes to prepare for DNA synthesis. Cells with slow generation times will have a longer G1 phase.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)