DNA e RNA (Ácidos Nucleicos) - LEIA A DESCRIÇÃO
Summary
TLDRIn this biology lesson, the teacher, Guilherme, explores the essential topic of nucleic acids, specifically focusing on the differences between DNA and RNA. He explains the structure of nucleotides, including phosphate groups, sugars (ribose and deoxyribose), and nitrogenous bases, highlighting how these components form the backbone of DNA and RNA. The video also covers the importance of these molecules in protein synthesis, with DNA acting as a genetic blueprint for proteins. The lesson touches on the processes of transcription and translation, which are crucial for cellular functions. The teacher invites viewers to follow along with the series for deeper understanding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Acids nucleic are molecules formed by nucleotides, which consist of three components: a phosphate group, a sugar (pentose), and a nitrogenous base.
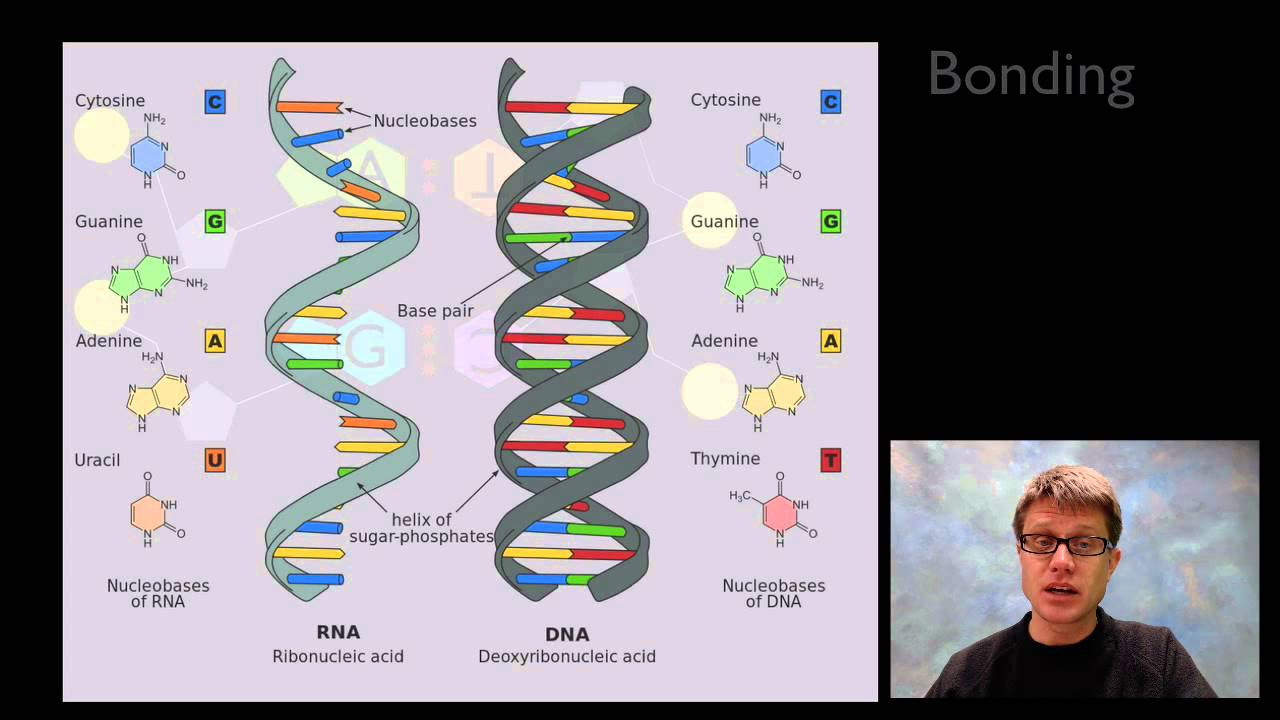
- 😀 DNA stands for deoxyribonucleic acid, while RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. The key difference is that DNA lacks an oxygen atom in its sugar (deoxyribose), making it more stable than RNA.
- 😀 The term 'nucleic acid' was coined because these molecules were first discovered in the nucleus of cells.
- 😀 DNA has a double-helix structure, discovered by Watson and Crick in the mid-20th century, with complementary strands resembling a twisted ladder.
- 😀 RNA is a single-stranded molecule, unlike DNA, and has a different sugar molecule (ribose) compared to DNA's deoxyribose.
- 😀 The nitrogenous bases in DNA are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T), and cytosine (C), whereas in RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil (U).
- 😀 The phosphate group in nucleotides gives DNA its acidic properties by releasing hydrogen ions (H+), contributing to the acidic nature of nucleic acids.
- 😀 Nucleotides are the building blocks of both DNA and RNA, with a key role in genetic information storage and transmission.
- 😀 The DNA molecule is much more stable than RNA due to its deoxyribose sugar, which lacks an oxygen atom, preventing degradation.
- 😀 The central function of DNA is to store genetic information that codes for proteins, which are essential for various biological functions in the body.
Q & A
What are nucleic acids and how are they structured?
-Nucleic acids are molecules made up of smaller units called nucleotides. These nucleotides consist of a phosphate group, a sugar (pentose), and a nitrogenous base. Nucleic acids like DNA and RNA are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
Why are nucleic acids called 'nucleic'?
-Nucleic acids are called 'nucleic' because they were first discovered inside the nucleus of a cell. Although they can be found outside the nucleus, the name was derived from their initial discovery.
What are the main differences between DNA and RNA?
-DNA is double-stranded, forming a double helix structure, while RNA is single-stranded. Another key difference is the sugar: DNA contains deoxyribose (which lacks one oxygen atom), while RNA contains ribose. Additionally, RNA contains uracil (U) instead of thymine (T), which is found in DNA.
Why does DNA have greater stability than RNA?
-DNA is more stable than RNA due to the absence of one oxygen atom in the sugar deoxyribose. This small difference makes DNA more resistant to degradation, ensuring it maintains genetic information over time.
What are the nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA?
-In DNA, the nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), thymine (T), and cytosine (C). In RNA, the bases are adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U) instead of thymine.
How do the nitrogenous bases pair in DNA?
-In DNA, adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C). These base pairs form the rungs of the DNA 'ladder' structure.
What role do nucleotides play in DNA and RNA?
-Nucleotides form the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. In DNA, nucleotides create the two strands of the double helix, while in RNA, they form a single strand. The sequence of these nucleotides carries genetic information.
What is the significance of the pentose sugar in DNA and RNA?
-The pentose sugar in DNA is deoxyribose, and in RNA, it is ribose. The difference in their structures (the presence or absence of an oxygen atom) influences the stability of each molecule, with DNA being more stable due to its deoxyribose sugar.
How does the process of transcription work in relation to DNA and RNA?
-Transcription is the process in which a segment of DNA is copied into RNA. During transcription, the DNA sequence is used as a template to produce messenger RNA (mRNA), which then carries genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis.
What is the main function of DNA in cells?
-DNA serves as a blueprint for building proteins. It contains the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms. When proteins need to be made, the information in DNA is copied to RNA, which then guides the protein synthesis process.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Me Salva! CIT11 - Citologia - Substâncias orgânicas - Ácidos nucleicos

Biologia Molecular – Ácidos Nucleicos - Biologia Básica - Me Salva! Saúde

Ácidos nucleicos (DNA e RNA) - resumo professor Gustavo

6-1 Nucleic Acids and Nucleotides (Cambridge AS & A Level Biology, 9700)

Bioquímica - Aula 09 - Ácidos Nucleicos
Nucleic Acids
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)