Hybrid Cloud Explained
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Sai Vennam from IBM explores the concept of hybrid cloud, blending private and public cloud environments for optimal application performance. Using 'Acme Freight' as a case study, he illustrates how a company can leverage the scalability and flexibility of the public cloud while maintaining security for sensitive data on-premises. The video covers the transition from monolithic ERP applications to microservices in the cloud, enhancing interoperability and utilizing cognitive services like Watson for improved operations. It highlights the benefits of hybrid cloud in security, scalability, portability, and vendor independence.
Takeaways
- 🌐 Hybrid cloud combines private and public cloud environments to run workloads and applications together.
- 🏢 The example of 'Acme Freight' illustrates how a company can integrate on-premises and public cloud applications.
- 📱 Acme Freight created a new BFF (Back-end For Front-end) layer in the public cloud for their mobile application.
- 🔗 Interoperability is key in hybrid cloud, allowing public and private components to work together seamlessly.
- 🚚 During peak times, Acme Freight experienced performance issues, highlighting the need for scalable infrastructure.
- 💻 They addressed this by breaking down their ERP application into microservices and moving it to the public cloud using container technologies like Docker and Kubernetes.
- 📈 Public cloud offers scalability, allowing applications to handle increased loads during peak demand periods.
- 🛍️ With the public cloud, Acme Freight benefits from the flexibility to use various open-source projects and programming languages.
- 🧠 They integrated their ERP application with Watson for cognitive capabilities in delivery rerouting during adverse weather conditions.
- 🔒 Security remains a priority, with sensitive data like user registry kept on-premises behind firewalls.
- 🛡️ Hybrid cloud offers the advantage of maintaining security for critical data while leveraging the benefits of public cloud for other applications.
Q & A
What is the role of the person presenting the video?
-The presenter is a developer advocate with IBM, tasked with explaining the concept of hybrid cloud.
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video focuses on explaining the concept of hybrid cloud and how it fits into a company's architecture.
What is the definition of hybrid cloud as presented in the video?
-Hybrid cloud is a mixture of private and public cloud environments working together to run workloads and applications.
What is the example company used to illustrate the concept of hybrid cloud?
-The example company is 'Acme Freight,' a fictional company that manages shipments.
What is the purpose of the BFF (Back-end For Front-end) in the context of the ERP application?
-The BFF handles front-end requests to ensure the web dashboard functions properly and serves the needs of the mobile application.
How does Acme Freight address the issue of system slowdown during peak hours?
-Acme Freight decides to break down the monolithic ERP application into microservices and move it to the public cloud for better scalability.
What technologies does Acme Freight use to facilitate the move to microservices in the public cloud?
-Acme Freight uses Linux container technologies like Docker and container orchestration tools like Kubernetes.
What are the advantages of using public cloud resources mentioned in the video?
-Public cloud resources offer scalability, the ability to avoid vendor lock-in, and the opportunity to use a variety of open-source projects and programming languages.
How does Acme Freight enhance its delivery rerouting capabilities?
-Acme Freight integrates its ERP application with Watson to take advantage of cognitive capabilities for improved delivery rerouting during adverse weather conditions.
Why does Acme Freight choose to keep the user registry on-premises?
-Acme Freight keeps the user registry on-premises for enhanced security, preferring to maintain it within their own infrastructure and hardware.
What are the key features of hybrid cloud mentioned in the video?
-The key features of hybrid cloud are interoperability, scalability, portability, and security.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
2 3 1 Hybrid multi-cloud
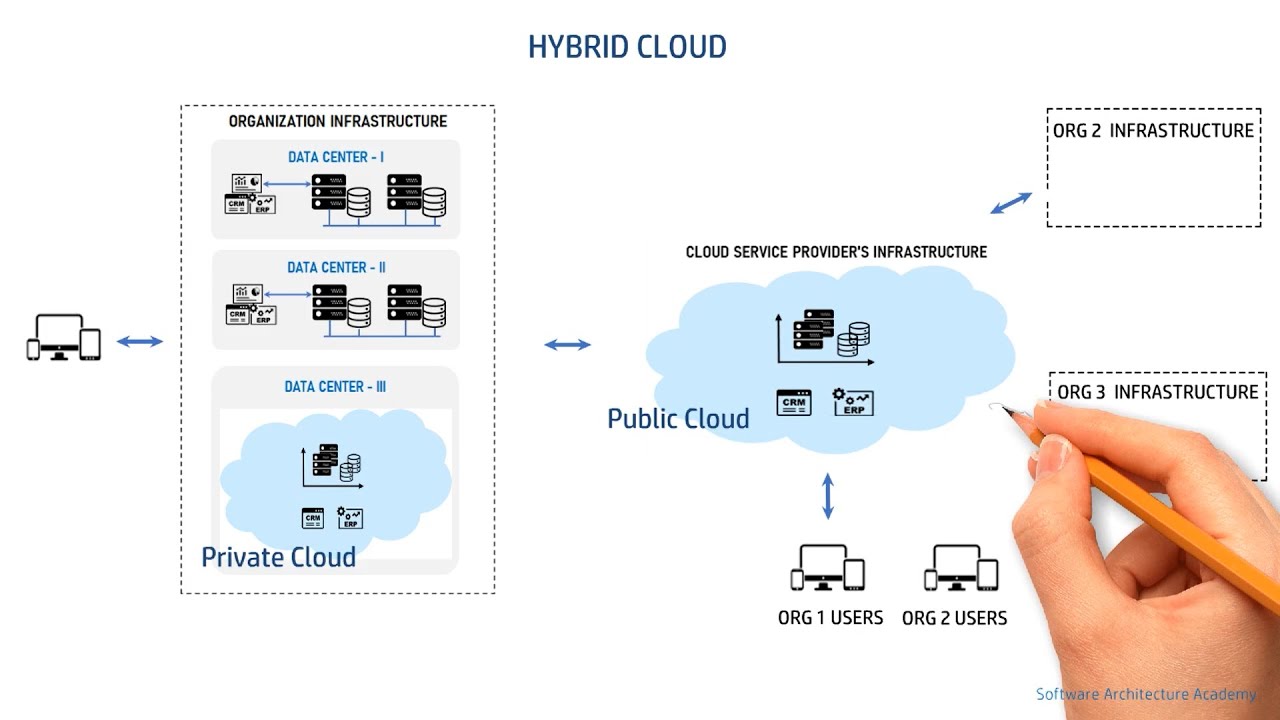
Cloud Deployment Models - Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud & Community Cloud
Blockchain Explained

What Is Cloud Bursting, and Why Is It Important? Hybrid cloud

Mengenal Apa itu Cloud Computing bagi Pemula

Cloud Engineer: Apache CloudStack - Install, Build and Run IaaS Cloud
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)