Refrigerasi03
Summary
TLDRThe script explains the process of refrigeration, focusing on the flow of refrigerant through different components like the condenser and evaporator. It discusses temperature changes and phase transitions (from gas to liquid and vice versa) as the refrigerant absorbs and releases heat. The process includes pressure and temperature adjustments, often using expansion valves, to achieve the desired cooling effect. The script also mentions the importance of understanding each component's role in the cycle and hints at further analysis using a temperature-entropy diagram. A deeper breakdown and calculations will be addressed in future videos.
Takeaways
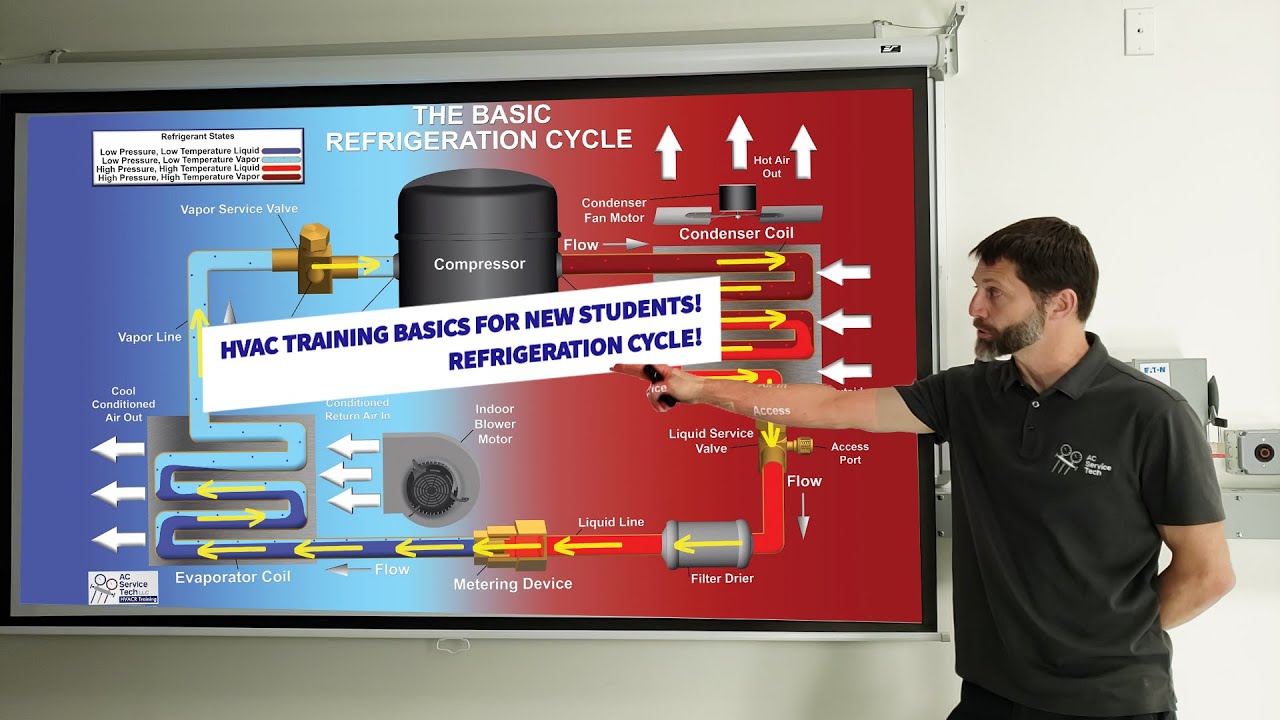
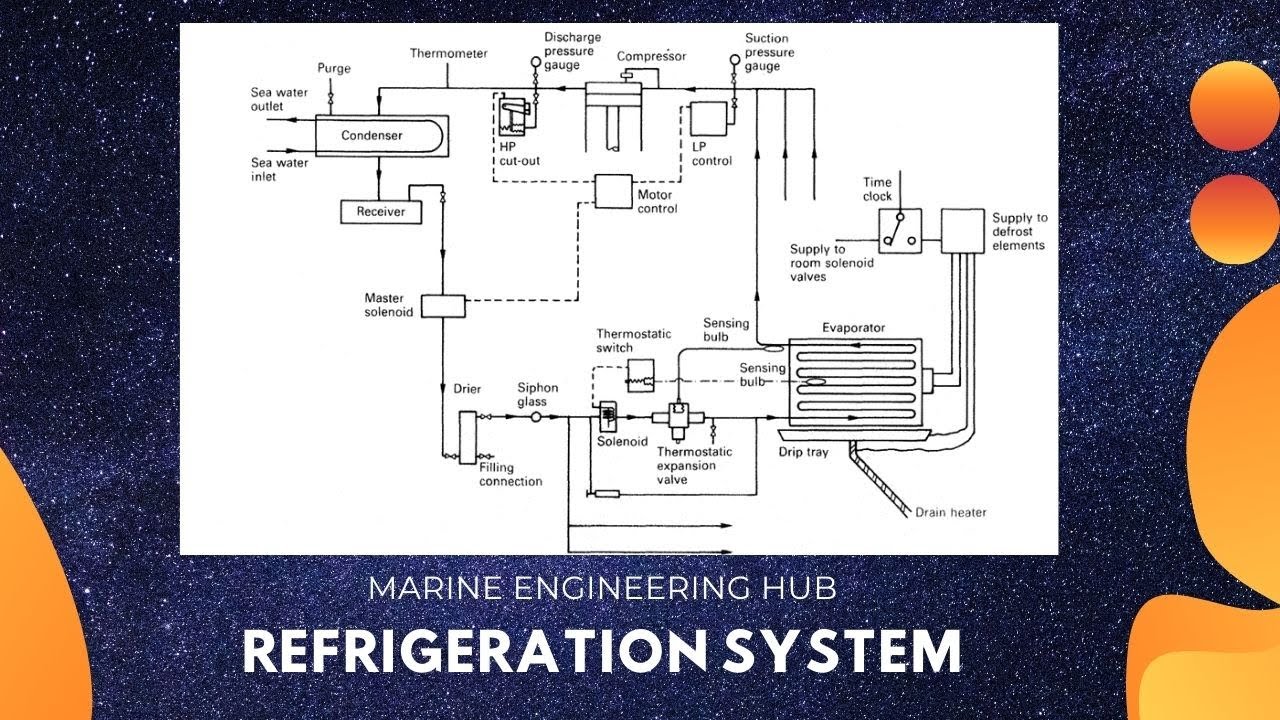
- 😀 The refrigerant entering the condenser has a higher temperature than the environment, often around 70-86°C.
- 😀 Heat is dissipated from the refrigerant in the condenser, which is why components like car air conditioners feel hot to the touch.
- 😀 The refrigerant undergoes cooling, transitioning from superheated gas to a saturated liquid at constant pressure.
- 😀 At the saturated phase, the refrigerant's temperature drops, but it remains at a higher temperature than the evaporator input.
- 😀 The transition from superheated gas to saturated liquid occurs in the condenser, where the refrigerant releases heat.
- 😀 The refrigerant cycle must return to its starting point after completing the heat exchange in the condenser.
- 😀 To complete the cycle, the refrigerant must undergo a pressure drop from the high-pressure line to the low-pressure line.
- 😀 An expansion valve is typically used to lower the refrigerant's pressure, causing its temperature to drop.
- 😀 The expansion valve process results in the refrigerant cooling down and returning to a mixture of liquid and vapor.
- 😀 The refrigerant then absorbs heat from the target area, continuing the cycle of heat transfer and cooling.
- 😀 Each component of the refrigeration cycle, including the expansion valve and condenser, plays a crucial role in maintaining the efficiency of the system.
Q & A
What happens to the refrigerant when it enters the condenser?
-When the refrigerant enters the condenser, its temperature is higher, and it begins to release heat as it changes from a superheated gas to a saturated liquid under constant pressure.
Why does the environment near the condenser feel hot?
-The environment near the condenser feels hot because the refrigerant is releasing heat during the condensation process, causing the surrounding area, such as a parking lot or iPhone, to absorb this excess heat.
What is the state of the refrigerant when it reaches the evaporator?
-The refrigerant arrives at the evaporator in a saturated state, where it absorbs heat from the surroundings and evaporates into a superheated gas.
What happens to the refrigerant's temperature and pressure when it goes through the expansion valve?
-When the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, both its temperature and pressure decrease, leading to a drop in energy and enabling it to absorb heat from the environment during the evaporation phase.
What role does the expansion valve play in the refrigeration cycle?
-The expansion valve reduces the pressure of the refrigerant, which lowers its temperature. This allows the refrigerant to continue absorbing heat as it evaporates inside the evaporator.
Why does the refrigerant undergo a phase change at the condenser?
-At the condenser, the refrigerant undergoes a phase change from a superheated gas to a saturated liquid as it releases heat, which helps maintain the refrigeration cycle's efficiency.
What is meant by 'saturated gas' and 'saturated liquid' in the context of refrigeration?
-'Saturated gas' refers to refrigerant that is at its boiling point and is about to condense, while 'saturated liquid' refers to refrigerant that has fully condensed into liquid form at its boiling point.
How does the temperature of the refrigerant compare at different points in the cycle?
-The temperature of the refrigerant is highest at the condenser, where it releases heat. As it moves through the cycle to the evaporator and through the expansion valve, the temperature decreases significantly, enabling it to absorb heat from the environment.
What is the significance of the refrigerant being in a superheated state?
-In a superheated state, the refrigerant is a gas that has absorbed more heat than its boiling point. This allows it to carry heat efficiently and maintain its gas form until it enters the condenser.
Why is understanding the Temperature-Entropy (T-S) diagram important for analyzing refrigeration cycles?
-The T-S diagram helps visualize and understand the relationships between temperature, entropy, and the various states of the refrigerant during the cycle. It is essential for analyzing the system's efficiency and behavior at each stage.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)