Refrigerasi02
Summary
TLDRThis script explains the process of refrigerant flow in a refrigeration system, starting with the evaporator where refrigerant absorbs heat and evaporates. It moves on to describe how the refrigerant is compressed in the compressor, increasing its temperature and pressure. Finally, the refrigerant releases heat and condenses in the condenser. This cycle—evaporation, compression, and condensation—efficiently transfers heat, ensuring cooling in systems like air conditioners, freezers, and refrigerators. The explanation covers key principles such as latent heat, pressure, and temperature control, illustrating how each component plays a crucial role in the refrigeration process.
Takeaways
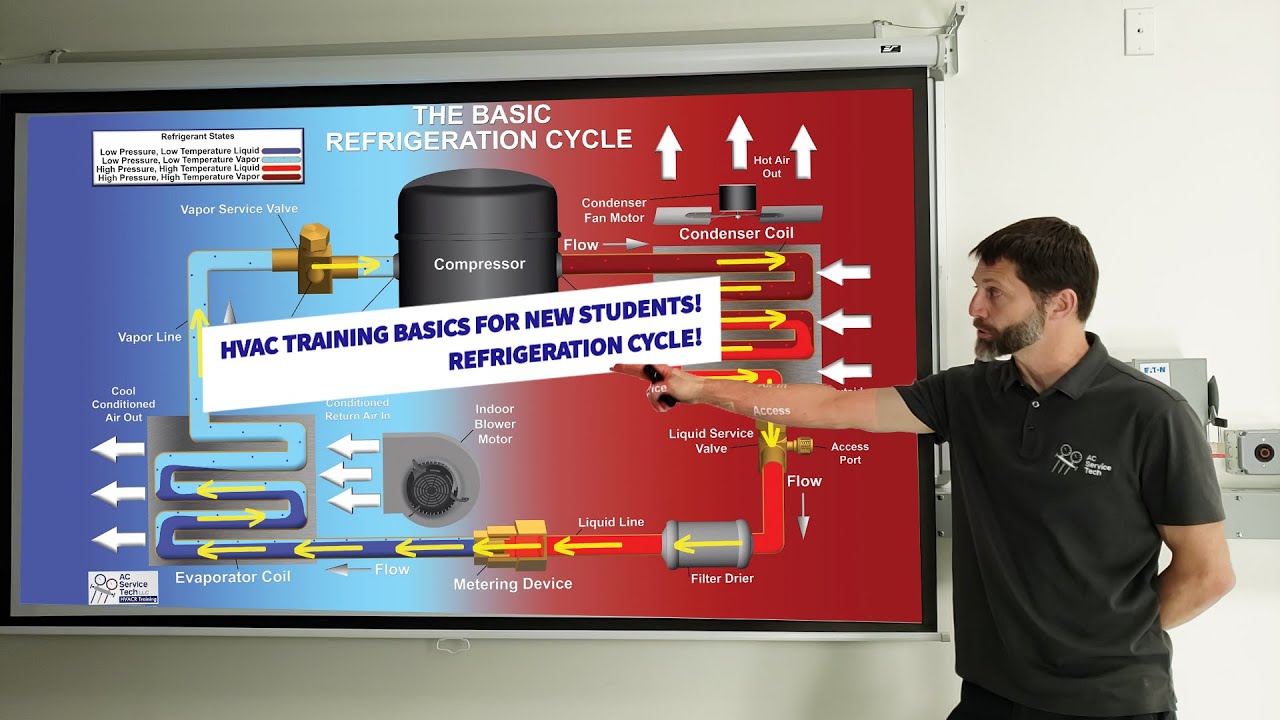
- 😀 The refrigerant flow begins in the evaporator, where it absorbs heat from the environment to lower the temperature of the room or object.
- 😀 The refrigerant enters the evaporator at a much lower temperature than the environment (around 5°C or even lower) to facilitate efficient heat absorption.
- 😀 In the evaporator, the refrigerant undergoes a phase change from a liquid-gas mixture to saturated vapor, absorbing latent heat during the process.
- 😀 The phase change in the evaporator occurs at constant temperature and pressure, with the refrigerant leaving the evaporator as saturated vapor.
- 😀 The compressor increases both the temperature and pressure of the refrigerant by compressing it, making it a superheated vapor.
- 😀 The compressor performs mechanical work to compress the refrigerant, transitioning it from a low-pressure vapor to a high-pressure, superheated gas.
- 😀 After compression, the refrigerant is in a superheated vapor state with high temperature and pressure, preparing to release the absorbed heat in the condenser.
- 😀 The condenser releases the heat absorbed by the refrigerant in the evaporator by cooling and condensing the refrigerant back into a high-pressure liquid state.
- 😀 The condenser operates at a constant pressure while the refrigerant temperature decreases, releasing heat to the surrounding environment.
- 😀 The cycle is a continuous process where refrigerant flows through the evaporator, compressor, and condenser, repeatedly absorbing and releasing heat to maintain the desired temperature in the cooled space.
Q & A
What is the role of the evaporator in a refrigeration system?
-The evaporator's role is to absorb heat from the environment or space to be cooled. It does this by circulating refrigerant at a temperature lower than the room temperature, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and absorb heat in the process.
Why does the temperature of the refrigerant in the evaporator need to be lower than the room temperature?
-The refrigerant temperature must be lower than the room temperature to facilitate heat transfer from the room to the refrigerant. This ensures that the room is cooled as heat flows from the warmer space to the cooler refrigerant.
What happens to the refrigerant as it passes through the evaporator?
-As the refrigerant passes through the evaporator, it absorbs heat from the environment, which causes it to evaporate from a liquid to a gas phase. This process occurs at constant temperature and pressure.
What is the significance of 'latent heat' in the refrigeration cycle?
-Latent heat is the heat absorbed or released during a phase change, such as from liquid to gas. In the evaporator, the refrigerant absorbs latent heat, which allows it to transition from a liquid to a gas without a change in temperature.
How does the pressure of the refrigerant change as it flows through the system?
-The pressure of the refrigerant is low in the evaporator but increases significantly when it reaches the compressor. The compressor increases the refrigerant's pressure and temperature, preparing it for the next stage of heat rejection in the condenser.
What is the role of the compressor in the refrigeration cycle?
-The compressor increases the refrigerant's pressure and temperature by compressing the refrigerant gas. This process is essential because it ensures that the refrigerant reaches a high enough temperature to release heat in the condenser.
What is the purpose of the condenser in the refrigeration system?
-The condenser's role is to reject the heat absorbed by the refrigerant. After the refrigerant is compressed, it is much hotter than the surrounding environment. In the condenser, the refrigerant cools down and releases heat to the outside air or another cooling medium.
What happens to the refrigerant in the condenser?
-In the condenser, the refrigerant, which is in a high-pressure, high-temperature gaseous state, cools down and undergoes a phase change from gas to liquid. This process occurs at constant pressure, as the refrigerant releases heat to the surrounding environment.
How does the refrigerant change state in the evaporator and condenser?
-In the evaporator, the refrigerant changes from liquid to gas as it absorbs heat from the environment. In the condenser, the refrigerant changes from gas to liquid as it releases heat to the environment. These phase changes are essential for the refrigerant to absorb and release heat in the system.
What is the importance of keeping the pressure constant in the evaporator and condenser?
-Maintaining constant pressure in the evaporator and condenser is important for ensuring stable and efficient heat exchange. In the evaporator, constant pressure allows for consistent heat absorption, while in the condenser, it allows for effective heat rejection.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)