Rangkaian Listrik - Analisis Mesh (Genap 2019/2020)
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture on electrical circuits, the speaker explains the process of Mesh Analysis (also known as loop analysis) in electrical networks. The discussion covers key concepts like Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL), assumptions for loop currents, and the method for calculating currents and voltages using Mesh Analysis. The speaker demonstrates the steps for analyzing circuits with DC and AC sources, providing practical examples and emphasizing the importance of consistency in assuming current directions. Additional topics include dealing with supermesh situations when current sources are involved. The video is geared toward helping students better understand circuit analysis techniques for upcoming exams.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mesh analysis is a method used to analyze electrical circuits, particularly focusing on the currents in closed loops or meshes.
- 😀 Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL) is a core principle in mesh analysis, stating that the sum of voltages in any closed loop equals zero.
- 😀 The mesh analysis method can be applied to both DC and AC sources in circuit analysis.
- 😀 When performing mesh analysis, it is essential to define the direction of mesh currents. The lecturer prefers clockwise direction for simplicity.
- 😀 The number of mesh equations corresponds to the number of independent loops in the circuit, minus any dependent loops.
- 😀 Mesh analysis involves setting up equations for each loop based on the voltage drops across resistive elements and sources.
- 😀 For circuits with current sources, the concept of 'supermesh' is used, where two loops are combined to avoid directly dealing with the current source.
- 😀 In mesh analysis, substitution or elimination methods are used to solve the simultaneous equations derived from the mesh loop analysis.
- 😀 The lecturer demonstrates examples using both resistive elements and current sources, showing how to simplify equations for easier computation.
- 😀 Mesh analysis can be used for both simple and complex circuits, and while it may seem complex at first, practice helps in mastering the method.
- 😀 The lecturer emphasizes that understanding mesh analysis requires not just theoretical knowledge but also hands-on practice with different circuit problems.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture discussed in the transcript?
-The main topic of the lecture is the analysis of electrical circuits using mesh analysis (or loop analysis) and its various techniques, including how to apply Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) to solve for unknown currents in a circuit.
What is mesh analysis in electrical circuits?
-Mesh analysis involves assuming currents that flow through closed loops (meshes) in a circuit. These currents are used to analyze and solve for unknown values in the circuit using Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL).
What is Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL), and how does it relate to mesh analysis?
-Kirchhoff's Voltage Law states that the sum of all voltages around any closed loop in a circuit must be zero. In mesh analysis, KVL is applied to each loop in the circuit to set up equations that allow solving for unknown currents.
What is the difference between mesh analysis and nodal analysis?
-Mesh analysis focuses on currents in the loops (meshes) of a circuit, applying Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL). Nodal analysis, on the other hand, focuses on the voltages at various nodes in the circuit, applying Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL).
What does the term 'supermesh' refer to in mesh analysis?
-A supermesh occurs when two loops share a current source, requiring the analysis of the combined loop as a single entity while taking into account the current source's influence between the two loops.
How are currents in mesh analysis assumed to flow in the loops?
-The current in each mesh is typically assumed to flow in a clockwise direction, though the direction can be arbitrary. This assumption helps in applying Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and solving the circuit equations.
What is the purpose of selecting a reference direction for currents in mesh analysis?
-Selecting a reference direction for currents helps in defining a consistent approach for applying Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) and ensures clarity in forming equations for solving the circuit.
Why is it important to simplify the analysis process by combining resistances in mesh analysis?
-Combining resistances in mesh analysis helps to simplify the circuit and makes it easier to form equations, reducing the complexity of solving for unknown currents.
What happens if there is a current source in the circuit during mesh analysis?
-If there is a current source in the circuit, it is handled by creating a supermesh, which is a combination of the two loops affected by the current source. This requires solving the equations for the combined loop while considering the current source's impact.
How is the value of unknown currents determined in mesh analysis?
-The value of unknown currents in mesh analysis is determined by setting up and solving a system of equations based on Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) for each loop in the circuit. Techniques like substitution or elimination are often used to solve these equations.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
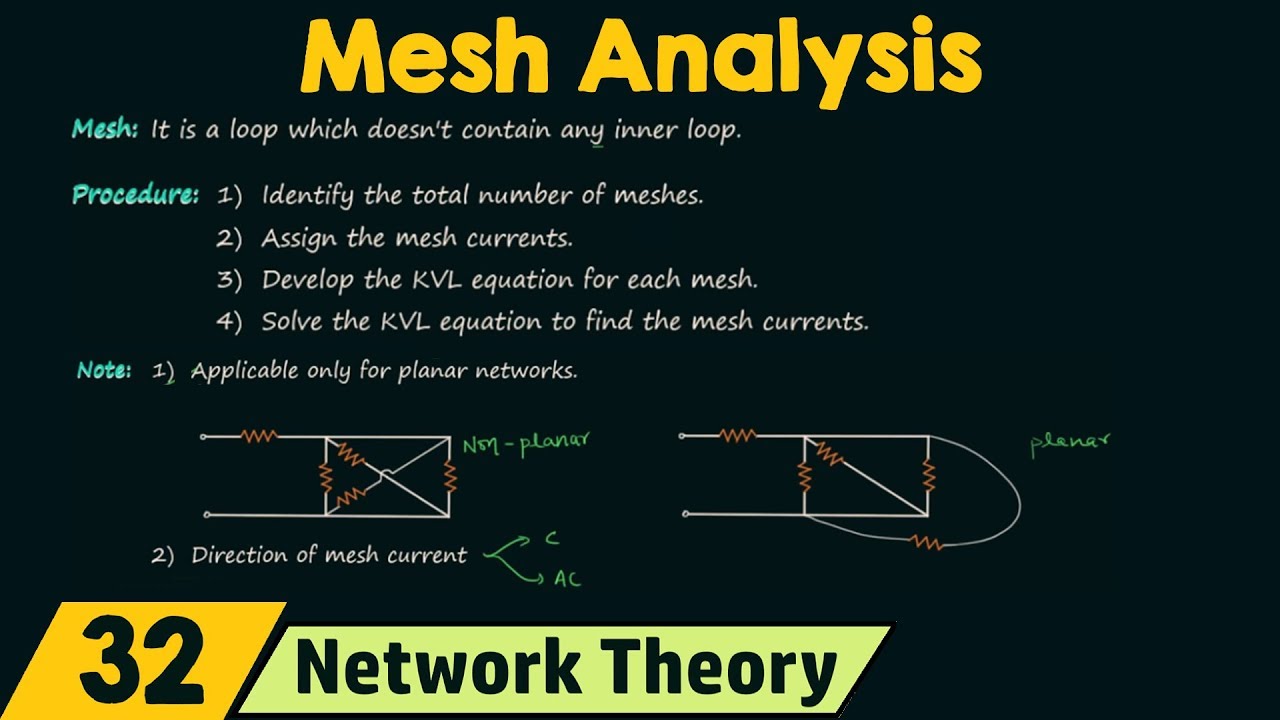
Mesh Analysis

Video Pembelajaran Modul 2 & 3 Praktikum Rangkaian Listrik 2024/2025 (DK)
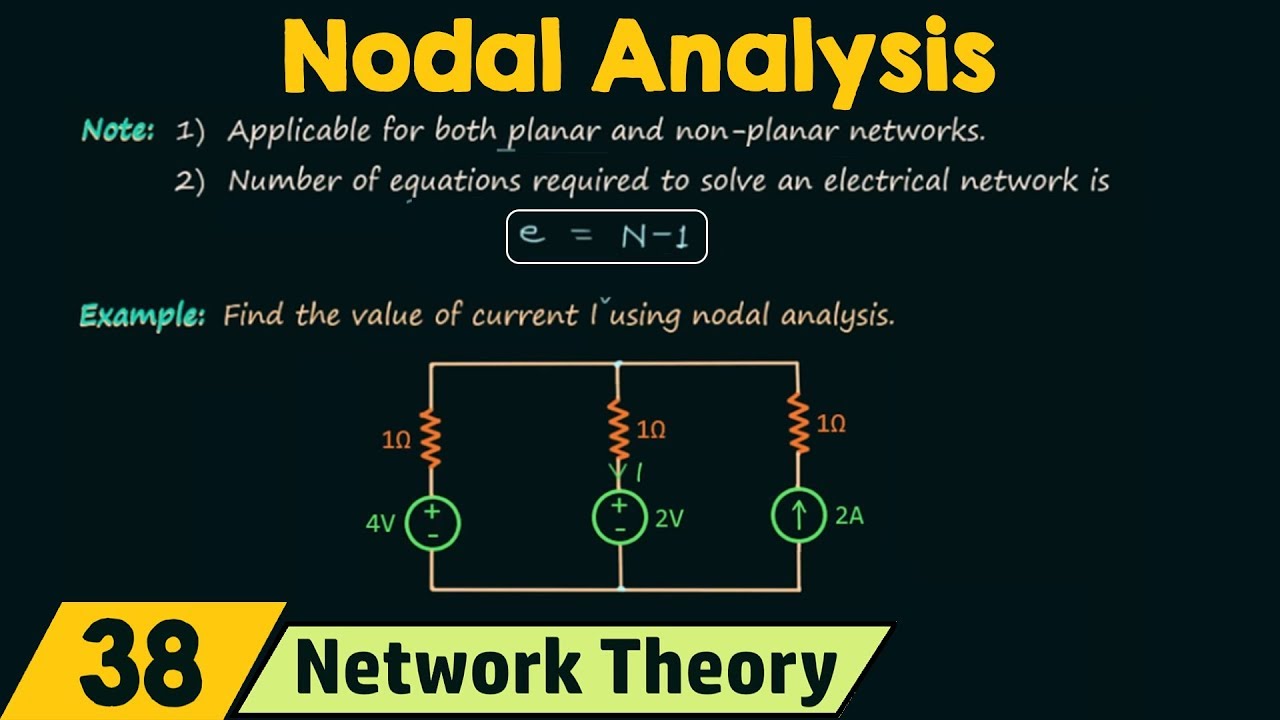
Nodal Analysis

Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) - How to Solve Complicated Circuits | Basic Circuits | Electronics

metode analisa node

Network Theory Introduction | Synthesis of Circuit | Difference in between Network and Circuit
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)