Pengantar Spektroskopi FTIR
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Syahril Siregar introduces infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and its practical applications. He explains the foundational concepts of FTIR, highlighting its role in fields like forensics, medicine, and diagnostics. By referencing real-life scenarios such as the Jessica Sianida case and the use of oximeters, he illustrates how FTIR can detect substances like cyanide or monitor oxygen saturation in blood. The video also covers the basic physics behind light dispersion and molecular vibrations, laying the groundwork for understanding how FTIR works in detecting various compounds and even detecting cancer in the future.
Takeaways
- 😀 FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) is a type of spectroscopy that studies the interaction between light and matter at the atomic or molecular level.
- 😀 The lecture aims to teach students the basics of FTIR and its practical applications in various fields, particularly in forensics and medicine.
- 😀 FTIR can be used to detect substances like cyanide in a body, as demonstrated in a real-life case where it helped solve a murder mystery.
- 😀 The working principle of FTIR can also explain how devices like oximeters measure oxygen saturation in blood.
- 😀 FTIR technology is being explored for potential uses in non-invasive real-time glucose monitoring, such as through devices like the Apple Watch.
- 😀 FTIR could play a significant role in future medical applications, such as cancer detection using blood samples or bodily fluids.
- 😀 The concept of light dispersion is essential in understanding spectroscopy, where white light splits into different colors based on wavelength.
- 😀 Spectroscopy emerged from the study of light dispersion, first observed by Isaac Newton in the 17th century, highlighting the diverse wavelengths in light.
- 😀 Infrared light, which is a key component of FTIR, falls between visible light and microwaves on the electromagnetic spectrum, with three subcategories: near-infrared, mid-infrared, and far-infrared.
- 😀 The unit 'cm⁻¹' (wave number) is used in FTIR to represent the energy or frequency of the infrared radiation, which can be converted into energy using specific formulas.
- 😀 Molecules like water have specific vibrational modes (symmetric, asymmetric, and bending), which can be studied using FTIR to understand molecular behavior in various environments.
Q & A
What is the focus of the script?
-The script focuses on introducing and explaining Infrared Spectroscopy, particularly FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy), its applications, and its importance in various fields such as forensics, medical diagnostics, and monitoring devices like oximeters.
Why is Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) important in forensics?
-FTIR is important in forensics because it can be used to detect substances like cyanide in the human body, as demonstrated in the case of Jessica and Mirna, where FTIR could potentially identify the presence of cyanide in forensic investigations.
How does FTIR play a role in the development of medical devices like oximeters?
-FTIR plays a role in the development of medical devices such as oximeters by helping measure oxygen saturation levels in the blood. By analyzing the absorption of light at specific wavelengths, it can distinguish between oxygenated hemoglobin and deoxygenated hemoglobin to calculate oxygen levels.
What is the significance of FTIR in detecting blood glucose levels?
-FTIR is proposed as a method for real-time, non-invasive monitoring of blood glucose levels, which is a potential feature for future devices like the Apple Watch, enabling continuous health monitoring.
How does FTIR contribute to cancer detection?
-FTIR contributes to cancer detection by analyzing biological samples like tissue, saliva, urine, or plasma. Its ability to detect molecular vibrations allows for the identification of specific biomarkers associated with cancer.
What is the basic principle behind Spectroscopy?
-The basic principle behind Spectroscopy is the interaction of light with matter at the atomic or molecular level. When light passes through a prism, it gets dispersed into different wavelengths, which allows for the analysis of various substances based on their unique spectral patterns.
What is the relationship between light dispersion and Spectroscopy?
-The relationship between light dispersion and Spectroscopy is that light dispersion (first observed by Isaac Newton) helps in understanding that light consists of various wavelengths. This forms the basis for Spectroscopy, where different wavelengths interact with substances in distinct ways, creating unique spectra for analysis.
What does the wave number in FTIR represent?
-The wave number in FTIR represents the number of waves per centimeter and is inversely related to the wavelength of light. It is a measure of the energy of the infrared light being absorbed by a molecule, which can help identify molecular structures.
How are vibrational modes of molecules related to FTIR?
-Vibrational modes of molecules are key to FTIR because they determine how a molecule will absorb infrared light at specific frequencies. Different molecules vibrate in various ways (e.g., symmetric, asymmetric, and bending), and these vibrations can be detected by FTIR to identify the substance.
What is the formula to determine vibrational modes in a molecule?
-The formula to determine vibrational modes in a molecule depends on the type of molecule. For linear molecules, the formula is 3n - 5, where 'n' is the number of atoms. For non-linear molecules, like water, the formula is 3n - 6.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Introduction to Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)

Back to Basics: Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
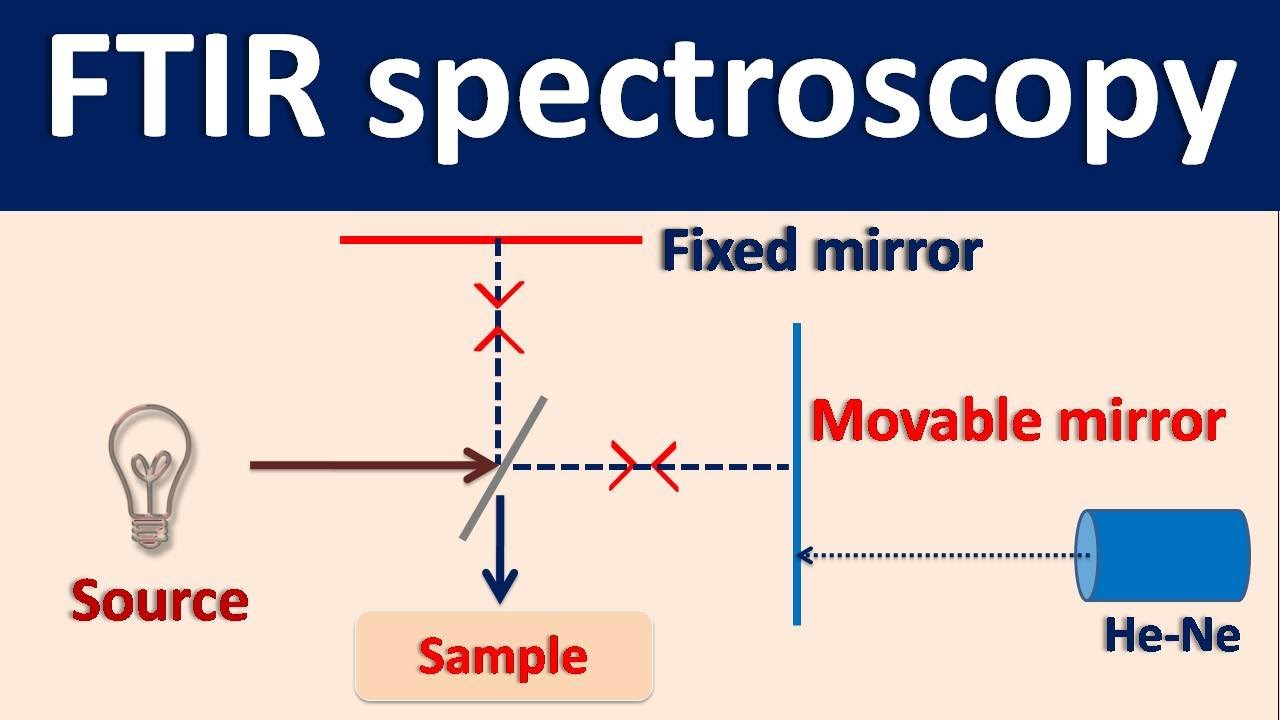
Fourier Transform IR spectroscopy (FTIR) - How it works?

What is FTIR Spectroscopy? – Technology Introduction – METTLER TOLEDO - EN
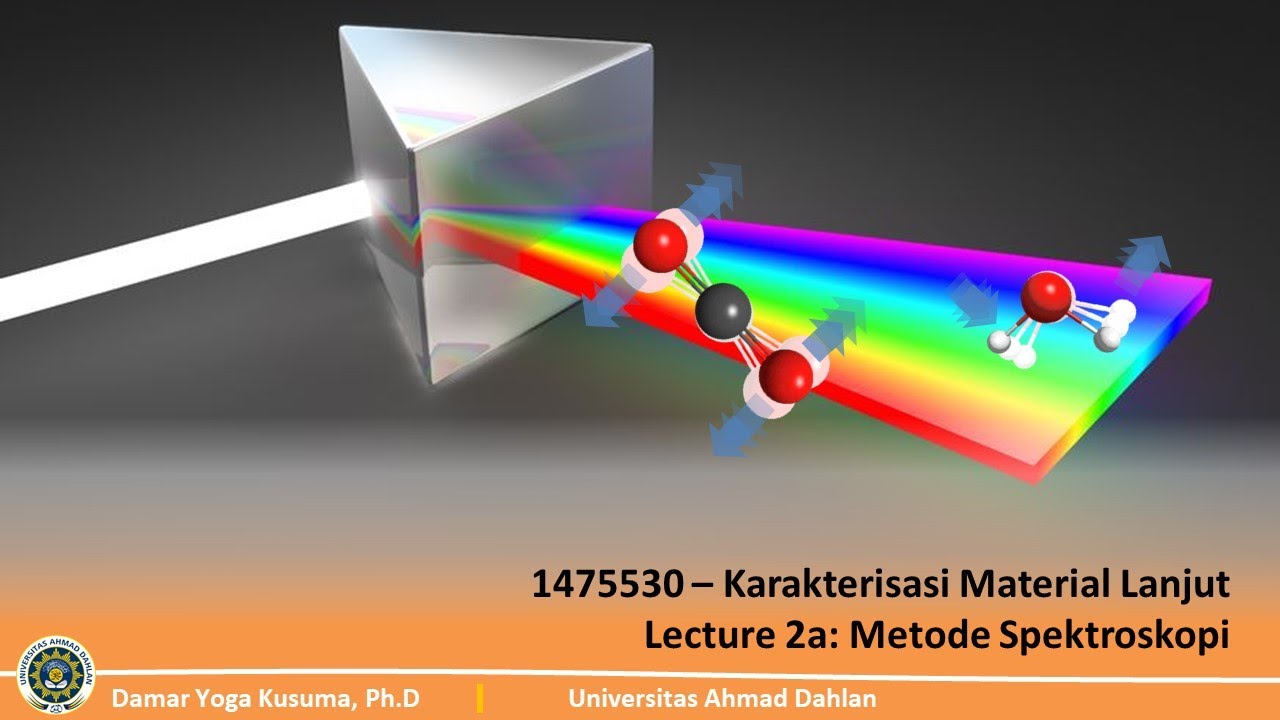
UAD - Kuliah Online 1475530 Karakterisasi Material Lanjut (Lecture 2a - part 1)

(16) IR Spectroscopy | Introduction to Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy | Instrumental Method of Analysis
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)