Back to Basics: Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Summary
TLDRIn this video, The Madison Group introduces Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR), a key analytical technique for identifying and investigating materials' chemical composition, especially in the plastics industry. The video explains how FTIR works, what results to expect, and its primary uses, including material identification, contamination analysis, and polymer degradation studies. It also highlights the limitations of FTIR, such as difficulty distinguishing similar materials and quantifying components. Viewers gain foundational knowledge to effectively interpret FTIR results, with practical insights on when this powerful tool can solve polymer-related problems.
Takeaways
- 😀 FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) is a powerful analytical technique used to investigate a substance's chemical composition, especially useful for organic liquids and solids.
- 😀 FTIR works by exposing a sample to infrared light, causing molecular motion, and analyzing how much energy is absorbed by the sample at different wavelengths.
- 😀 The FTIR results are presented as a graphical absorption spectrum, which helps identify materials by comparing them to known reference spectra.
- 😀 The spectrum shows intensity on the y-axis and wave number on the x-axis, indicating energy absorption at different wavelengths, with the peaks corresponding to chemical bonds in the material.
- 😀 FTIR is commonly used for material identification, quality control, and investigating contamination sources, providing a quick and effective analysis.
- 😀 FTIR can identify modifications in polymeric materials due to environmental factors and monitor reaction rates in thermosetting resins and adhesives.
- 😀 FTIR's limitations include difficulty in distinguishing materials with similar structures (e.g., different polyamides), and a reliance on reference libraries, which may not include all substances.
- 😀 FTIR may struggle to detect weak overlapping absorption bands, which can confound spectrum interpretation, and it has detection limits of about 1-5% for additives.
- 😀 FTIR cannot easily quantify components, requiring additional methods or development for accurate measurements of component ratios.
- 😀 To interpret FTIR results accurately, an experienced analyst may combine multiple spectra and use their knowledge of material chemistry for more complex cases.
Q & A
What is FTIR and how is it used in polymer analysis?
-FTIR (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) is an analytical technique used to investigate the chemical composition of materials, primarily organic solids and liquids. It provides a unique 'fingerprint' of a material, allowing analysts to identify chemical bonds and functional groups within the polymer, which is essential in problem-solving within the plastics industry.
How does FTIR work to identify the components of a material?
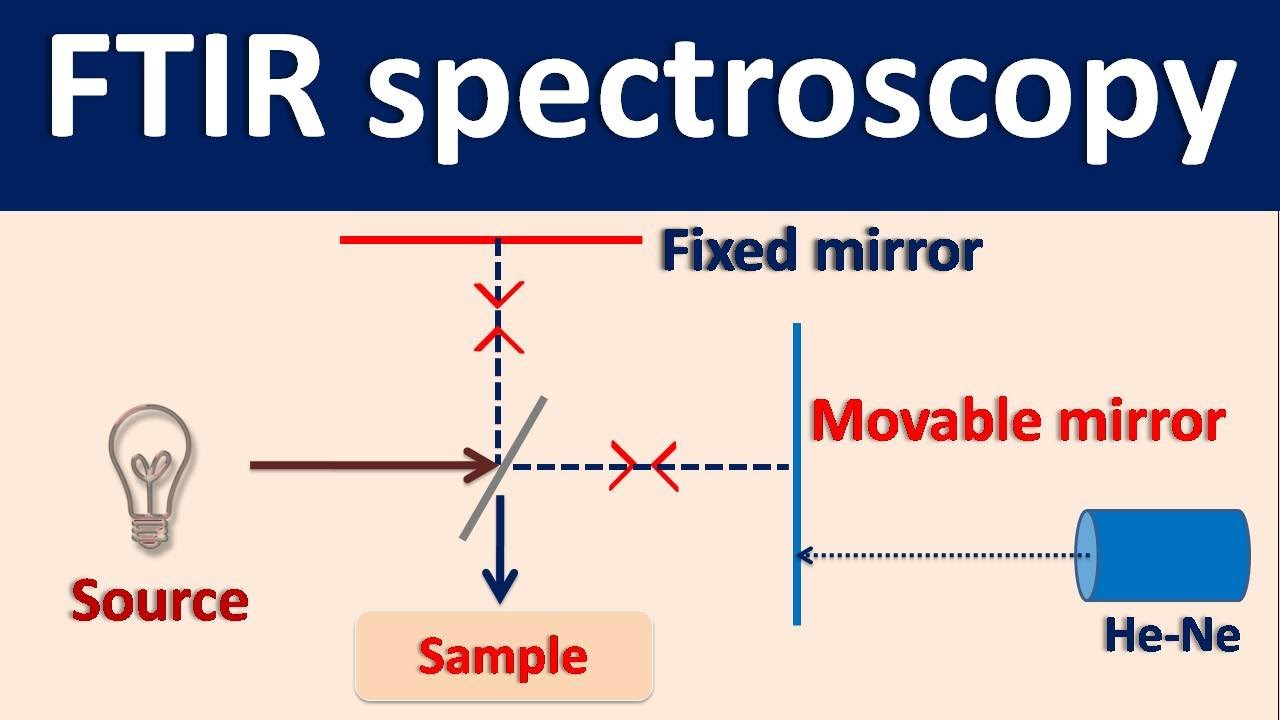
-FTIR works by exposing a sample to infrared light at various frequencies. Some wavelengths are absorbed by the material, causing molecular motion, while the remaining light passes through the sample and is detected. The resulting spectrum is then analyzed, with peaks representing the energy absorbed at different wavelengths, which corresponds to the material's chemical bonds and functional groups.
What does the absorption spectrum from FTIR represent?
-The absorption spectrum from FTIR represents the amount of infrared energy absorbed by the sample at different wavelengths. The peaks in the spectrum correspond to specific chemical bonds and functional groups in the material, which are used to identify the substance.
How is the FTIR spectrum used for material identification?
-FTIR spectra are compared with a database of known reference spectra. The comparison helps identify the material by matching the unknown spectrum with the closest references. In complex cases, experienced analysts may combine multiple spectra to accurately identify the material.
What are some typical applications of FTIR analysis in the plastics industry?
-FTIR is commonly used for material identification, quality control, contamination detection, analyzing polymer modification due to environmental conditions, and monitoring reaction progress in processes such as thermosetting resins and adhesives.
What are the limitations of FTIR as a testing method?
-FTIR has several limitations, including difficulty in distinguishing materials with similar structures, reliance on reference libraries for accurate identification, challenges in detecting weak overlapping absorption bands, and limitations in quantifying components, especially in low concentrations.
How does FTIR help in identifying contamination in materials?
-FTIR can detect contaminants by analyzing the unique spectrum they produce. By identifying the chemical composition of the contamination, FTIR can help trace its source, aiding in quality control and failure analysis efforts.
What role does an experienced analyst play in interpreting FTIR results?
-An experienced analyst plays a crucial role in interpreting FTIR results, especially when the spectrum is complex or does not perfectly match a reference. They use their knowledge of the material and polymer chemistry to combine spectra or make informed conclusions.
Why is it difficult to differentiate between similar materials, like different polyamides, using FTIR?
-It is difficult to differentiate between similar materials, such as polyamide 6 and polyamide 6,6, because their chemical structures are nearly identical. Only slight differences in their backbones are visible in the FTIR spectrum, making them almost indistinguishable.
What is the detection limit of FTIR for additives in materials?
-FTIR typically has a detection limit of around 1 to 5 percent for most additives. This means that if an additive is present in concentrations lower than this range, FTIR may not detect it, requiring other testing methods for accurate identification.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)