Types of DC Motor | Classification, Working, and Applications | VTU Electrical Engineering| GATE
Summary
TLDRIn this lecture on basic electrical engineering, the focus is on the classification and working principles of various types of DC motors. The lecturer discusses separately excited and self-excited DC motors, including DC series motors, DC shunt motors, and compound motors (both cumulative and differential). The video provides an in-depth look at their construction, how they function, and relevant equations for each motor type. The session is geared towards providing fundamental understanding, supported by visual aids and mathematical formulas, making it ideal for beginners in electrical engineering.
Takeaways
- 😀 DC motors are broadly classified into two types: separately excited DC motors and self-excited DC motors.
- 😀 A separately excited DC motor has a separate field excitation circuit, making it more complex and expensive.
- 😀 In a self-excited DC motor, the magnetic field is generated through residual magnetism and requires no external field excitation.
- 😀 A DC series motor connects the armature and field windings in series, meaning the same current flows through both.
- 😀 DC series motors are ideal for applications requiring high starting torque, such as traction systems.
- 😀 A DC shunt motor connects the armature and field windings in parallel, with the field winding receiving a portion of the current.
- 😀 Compound motors combine both series and shunt field windings, offering a mix of both motor types' characteristics.
- 😀 Long shunt compound motors have the field winding connected in parallel with the armature.
- 😀 Short shunt compound motors have the field winding connected in series with the armature.
- 😀 Compound motors are used in applications like elevators, where both high starting torque and stable speed are required.
- 😀 Key formulas, such as the KVL equations for terminal voltage, are critical for understanding DC motor operation and performance.
Q & A
What are the two main types of DC motors discussed in the lecture?
-The two main types of DC motors discussed are separately excited DC motors and self-excited DC motors.
What is a key characteristic of a separately excited DC motor?
-A separately excited DC motor requires an external field excitation circuit to generate the magnetic field, which makes it more complex and costly to operate.
Why are separately excited DC motors rarely used?
-Separately excited DC motors are rarely used because their setup is complicated and costly due to the need for external field excitation circuits.
What role does residual magnetism play in self-excited DC motors?
-Residual magnetism provides the initial magnetic field in self-excited DC motors, allowing them to operate even before full excitation.
How are the field winding and armature connected in a DC series motor?
-In a DC series motor, the field winding and armature are connected in series, meaning the same current flows through both.
What is the key difference between a DC shunt motor and a DC series motor?
-In a DC shunt motor, the field winding is connected in parallel with the armature, while in a DC series motor, the field winding is connected in series with the armature.
What equation is used to describe the voltage in a DC series motor?
-The voltage equation for a DC series motor is: V = E + I_A (R_A + R_{SC}), where V is the supply voltage, E is the back electromotive force (EMF), I_A is the armature current, and R_A and R_{SC} are the armature and field resistance, respectively.
What is the significance of the long shunt and short shunt configurations in compound DC motors?
-In a long shunt compound motor, both the series field and shunt field windings are connected in parallel with the armature, while in a short shunt compound motor, the shunt field winding is placed in parallel with the armature but not with the series field.
What types of applications would benefit from using a compound DC motor?
-Compound DC motors are useful in applications like elevators, where both series and shunt motor characteristics are required to handle varying loads efficiently.
What are the general advantages of self-excited DC motors compared to separately excited DC motors?
-Self-excited DC motors are simpler and more cost-effective because they use residual magnetism and do not require a separate excitation circuit, unlike separately excited DC motors.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Electrical Machine 1 | Introduction | B.Tech 2nd Year | Abdul Kalam Technical University | AKTutor
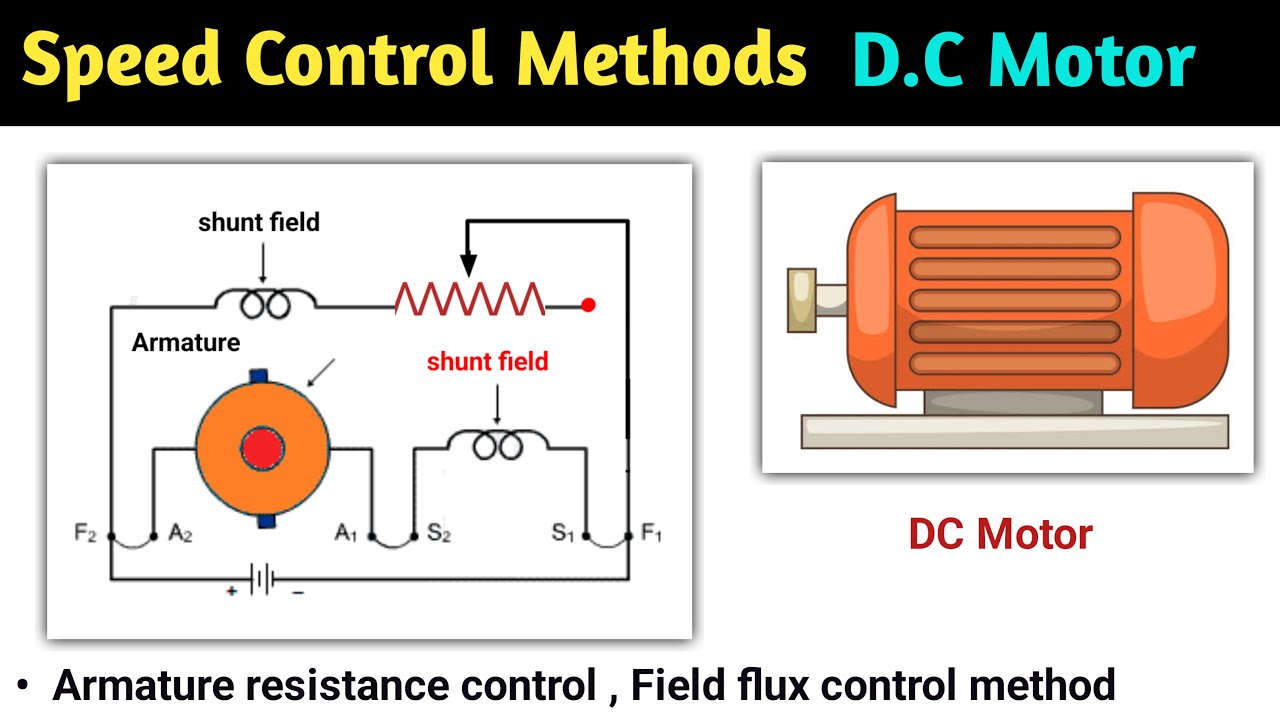
speed control of dc motor | speed control of dc shunt motor | dc motor speed control | series motor

PID control of BLDC motor
Motor VS Generator VS Alternator || How Generator, Motor And Alternator Works || In Hindi
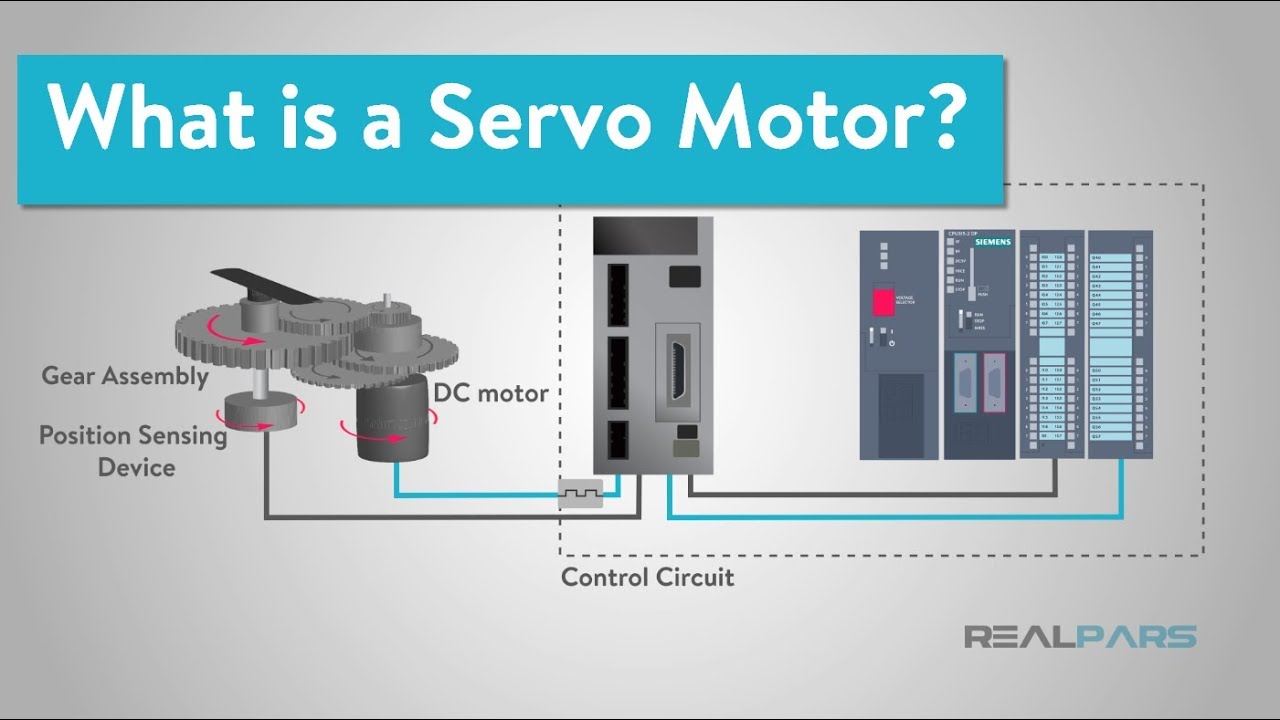
What is a Servo Motor and How it Works?

Module: Power Converter I BEE I 1Ph VSI (Half Bridge)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)