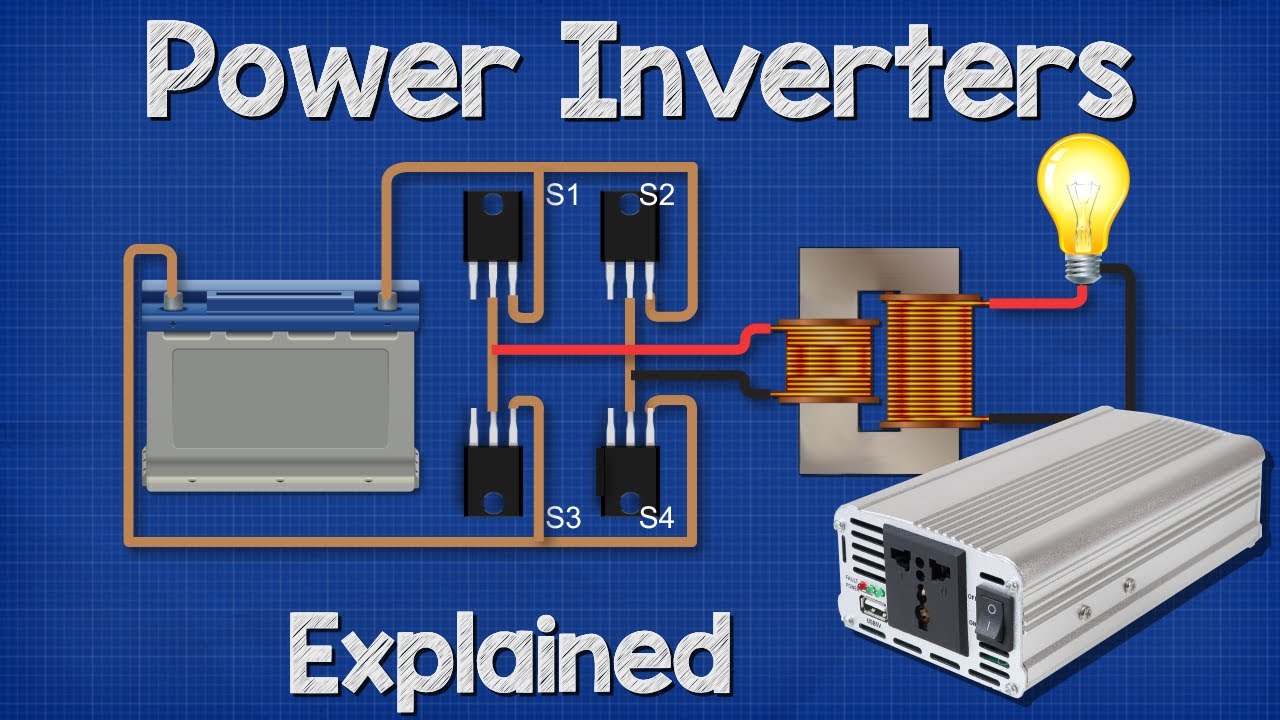
Module: Power Converter I BEE I 1Ph VSI (Half Bridge)
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial covers the essential concepts of inverters in power conversion, focusing on DC to AC inverters. It explains the working principles of different inverter types, including single-phase and three-phase voltage source inverters (VSI). The video also delves into the calculation of output voltages such as RMS and average voltage, crucial for understanding inverter performance. With a focus on power semiconductors and advanced control techniques, the tutorial equips electrical engineering students with the knowledge to understand, calculate, and improve inverter operation for various applications. Ideal for those seeking foundational knowledge in power electronics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Inverters are crucial devices used in power applications, converting DC to AC.
- 😀 Inverters are commonly used in various applications, including powering motors and battery-operated devices.
- 😀 A basic inverter operates by using semiconductor devices such as diodes and transistors.
- 😀 The tutorial focuses on single-phase inverters, specifically the voltage source inverters (VSI).
- 😀 Single-phase voltage source inverters come in two types: half-bridge and full-bridge inverters.
- 😀 The operation of inverters involves creating alternating current (AC) from direct current (DC).
- 😀 The circuit diagram of a half-bridge inverter is used to demonstrate how switches function in generating AC.
- 😀 The output voltage from the inverter can be calculated using RMS (Root Mean Square) and average voltage formulas.
- 😀 Control techniques are important for enhancing the efficiency and output quality of inverters.
- 😀 The video targets electrical engineering students and provides an introductory understanding of inverters.
- 😀 The knowledge of inverters, including their working and output voltage calculation, is fundamental for students in power electronics.
Q & A
What is the primary function of an inverter?
-An inverter's primary function is to convert DC (Direct Current) into AC (Alternating Current), typically by using power semiconductor devices like diodes and transistors. This conversion is essential for applications like battery-powered systems, solar energy, and industrial machinery.
How does an inverter work?
-An inverter works by taking DC input voltage and converting it into AC output through a series of switches and semiconductors. The switches alternately connect and disconnect the DC supply, creating an AC waveform at the output.
What types of inverters are mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions several types of inverters: single-phase voltage source inverters, three-phase voltage source inverters, and specifically, single-phase half-bridge inverters. These inverters can have different configurations like 180-degree mode and 120-degree mode.
What role do semiconductor devices play in inverters?
-Semiconductor devices, such as diodes and transistors, are crucial in inverters because they act as switches that regulate the flow of current, enabling the conversion of DC to AC. These devices allow for precise control of the output waveform.
What is the significance of control techniques in inverter operation?
-Control techniques are critical in ensuring that inverters operate efficiently. Advanced control methods help generate a smoother AC waveform by minimizing distortion and improving the quality of the output voltage. The more advanced the control technique, the better the inverter's performance.
Why is a pure sine wave not always achievable in basic inverters?
-In basic inverters, the output waveform may not be a pure sine wave due to limitations in switching and control techniques. The waveform can be more distorted, resembling a square wave or a stepped wave. However, with advanced control techniques, it is possible to approach a pure sine wave.
What is the importance of RMS and average voltage calculations in inverter operation?
-RMS (Root Mean Square) and average voltage calculations are essential for understanding the power delivered by the inverter. These calculations provide a way to quantify the effectiveness of the voltage output in terms of its energy content, which is crucial for determining efficiency and compatibility with devices.
How is the switching behavior of the inverter controlled?
-The switching behavior of the inverter is controlled using electronic switches that alternate between on and off states, based on the desired waveform. The timing and sequence of these switches are crucial for determining the waveform's characteristics, such as frequency and waveform shape.
What challenges are mentioned when attempting to improve the quality of the AC output?
-One challenge in improving the AC output quality is the limitation of basic inverters to produce a pure sine wave. However, by applying advanced techniques, such as pulse-width modulation (PWM) or other forms of control, the waveform can be smoothed out to improve its quality and reduce distortion.
What is the practical use of single-phase and three-phase inverters in the market?
-Single-phase inverters are often used in residential applications, such as powering household appliances and solar systems, while three-phase inverters are used in industrial applications requiring higher power levels, such as machinery and large motors.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)