O Discreto Charme das Partículas Elementares Parte II - Aula de física - Ensino médio
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses complex topics related to particle physics, focusing on concepts such as photons, protons, neutrons, and quarks. It explains the nature of elementary particles, their interactions, and the forces that govern them, including the strong nuclear force and electromagnetic force. The conversation also touches on the Standard Model of particle physics, the importance of understanding these particles, and their real-world applications in technologies like lasers and touchscreens. The narrative incorporates an engaging blend of scientific explanation and real-world relevance, making advanced physics concepts accessible to a general audience.
Takeaways
- 😀 The photon is an elementary particle that mediates electromagnetic interactions and is responsible for the way we see light.
- 😀 Hydrogen is the simplest and most abundant element in the universe, with a single proton in its nucleus and one electron in its electron shell.
- 😀 More complex atoms like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus have more protons, neutrons, and electrons in their structure.
- 😀 Protons within the nucleus of an atom do not repel each other due to the strong nuclear force, which overpowers the electromagnetic force.
- 😀 The electron is sensitive only to the electromagnetic force, while it does not interact with the strong nuclear force.
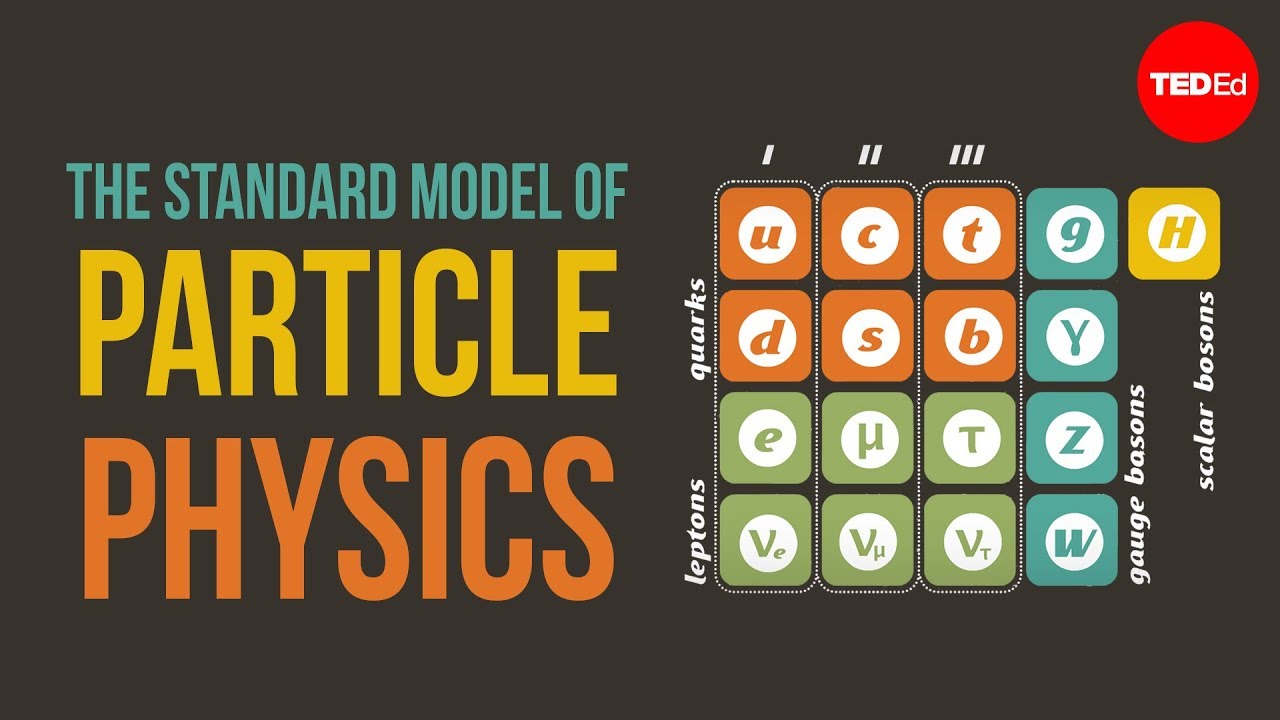
- 😀 Neutrinos are elementary particles that accompany leptons, such as electrons, and belong to the Standard Model of particle physics.
- 😀 The Standard Model of particle physics categorizes six types of leptons, including electrons and their corresponding neutrinos.
- 😀 Particles in the Standard Model are abstract and represented mathematically, often using complex equations.
- 😀 The book 'The Discrete Charm of Elementary Particles' explains the importance of understanding elementary particles and their influence on modern technology.
- 😀 Modern technology, like lasers, smartphones, and even supermarket conveyor belts, are based on knowledge of elementary particles.
- 😀 The uncertainty principle in quantum mechanics states that it is impossible to simultaneously know a particle's exact position and velocity, which applies to the microscopic world.
Q & A
What is a photon, and why is it important in understanding light?
-A photon is an elementary particle that acts as the mediator of the electromagnetic interaction. It is a packet of energy that allows us to see things, as the light we perceive is carried by photons.
Why does the script mention hydrogen as the simplest and most abundant element in the universe?
-Hydrogen is the simplest element because it consists of only one proton and one electron, making it the most abundant element in the universe, playing a key role in various chemical and physical processes.
What is the role of the strong nuclear force in atoms?
-The strong nuclear force is responsible for holding protons together in the nucleus, despite their positive charge, which would otherwise cause them to repel each other due to the electromagnetic force.
Why is the electron not sensitive to the strong nuclear force?
-Electrons are not sensitive to the strong nuclear force because they are not located in the nucleus where the strong force operates. Instead, they are part of the atom's electron cloud, affected only by electromagnetic forces.
What is the neutrino of the electron?
-The neutrino of the electron is an elementary particle that accompanies the electron in the family of leptons within the Standard Model of particle physics. It has little to no mass and interacts very weakly with other matter.
How are the families of leptons organized in the Standard Model?
-There are three families of leptons in the Standard Model: the first family contains the electron and its neutrino, the second family includes the muon and its neutrino, and the third family is made up of the tau and its neutrino.
What are quarks and how are they related to protons and neutrons?
-Quarks are elementary particles that combine to form protons and neutrons. A proton consists of two up quarks and one down quark, while a neutron consists of two down quarks and one up quark.
Why are strange and charm quarks significant?
-Strange and charm quarks belong to the second family of quarks and are important for understanding particle physics. They are highly unstable and can only be observed under specific conditions in particle accelerators.
What makes the top quark unique?
-The top quark is the heaviest quark, and it is so massive that it could only have existed in the early universe under extreme conditions. Due to its mass, it decays very quickly and is difficult to observe directly.
What is the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle, and how does it apply to particles?
-The Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle states that it is impossible to simultaneously know the exact position and velocity of a particle. This principle is crucial in quantum mechanics and explains the uncertainty in the behavior of subatomic particles.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
What’s the smallest thing in the universe? - Jonathan Butterworth

Fisika Inti • Part 1: Defek Massa dan Energi Ikat Inti
We1 sterke&zwakke ww

All of PARTICLES & QUANTUM in 15 mins - AS & A-level Physics
Struktur atom, Lambang Unsur, isotop, isoton, dan isobar- Kimia SMA kelas 10 semester 1

Programa "O Discreto Charme das Partículas Elementares" Parte 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)