Fundamentos Básicos de Sistemas Biológicos (Aula 1, parte 1)
Summary
TLDRThis video script introduces the field of biochemistry, emphasizing its importance in understanding biological systems at the molecular level. It explains how bioinformatics seeks to connect simple molecular components, such as amino acids and sugars, to complex biological processes like metabolism and molecular regulation. The script discusses the organization of life into cellular systems and the fundamental principles of bioquímica, exploring the roles of various biomolecules. It highlights the relevance of studying these components to better understand living systems while bridging the gap between chemistry and biology. The video encourages students to grasp both the simplicity and complexity of life at the molecular scale.
Takeaways
- 😀 The course is an introduction to biochemistry, focusing on essential concepts needed to understand metabolism, regulation, and molecular biology.
- 😀 Bioochemistry bridges the gap between chemistry and biology, studying the molecular mechanisms that underlie biological processes.
- 😀 Living systems are defined by characteristics such as high chemical complexity, the ability to extract energy from the environment, and mechanisms for self-replication.
- 😀 Cells are the basic unit of life, and all living organisms are cellular. However, some organisms, like viruses, do not meet all the criteria for being classified as living.
- 😀 The most common elements in living organisms are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen, which form the majority of biological molecules.
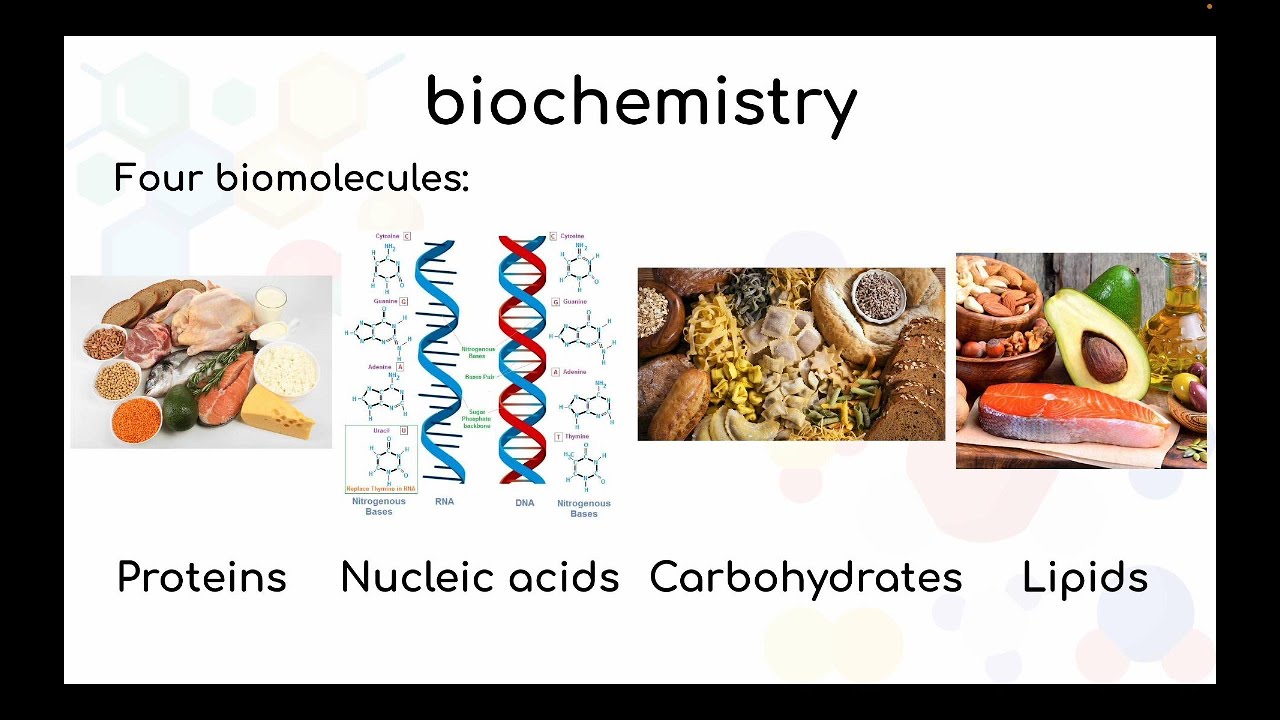
- 😀 Despite the complexity of biological systems, they are made up of simple molecules, such as amino acids, sugars, and nucleotides, that interact in highly organized ways.
- 😀 Biological processes obey the same laws of chemistry and physics as non-living systems, with no process violating the laws of thermodynamics.
- 😀 The course will help students understand how biological molecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, and carbohydrates, are organized and function at the molecular level.
- 😀 Biological systems are incredibly diverse, and this diversity is often rooted in the differences between prokaryotic (bacteria and archaea) and eukaryotic organisms.
- 😀 Biochemistry uses reductionist and holistic approaches to study biological systems, focusing on either individual components or the system as a whole.
- 😀 The course encourages students to examine biological molecules both in isolation (in vitro) and within the living system (in vivo) to understand their functions in context.
Q & A
What is the focus of the course 'Introduction to Biochemistry'?
-The course focuses on contextualizing various concepts that are necessary for understanding metabolism, regulation, and molecular biology, which will be studied in later biochemistry and molecular biology courses.
Why is biochemistry considered an intersection between chemistry and biology?
-Biochemistry attempts to describe molecular structures and mechanisms shared by all living organisms, organizing principles common to all forms of life. It looks at life from a molecular perspective, aiming to understand how life functions at this level.
What are the key characteristics of a living system?
-Living systems must have high chemical complexity, mechanisms for extracting energy from the environment, the ability to replicate and assemble itself faithfully, mechanisms to perceive and respond to the environment, defined functions for each component, and an evolutionary history of change.
What makes viruses different from other living organisms?
-Viruses are not considered cellular and do not fit the usual characteristics of living systems. They lack the organizational complexity and ability for self-replication. However, recent studies suggest some viruses may exhibit traits that align with certain definitions of life.
What is the basic unit of a living organism?
-The basic unit of a living organism is the cell, which can either be prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Most living organisms are cellular, although there are exceptions, such as viruses.
What are prokaryotic cells, and how do they differ from eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria and archaea, do not have a membrane-bound nucleus, while eukaryotic cells, like those in plants and animals, have a defined nucleus containing genetic material.
What is the significance of bacteria in the context of Earth's biomass?
-Bacteria represent about 80% of the Earth's living biomass. Despite the smaller number of species in prokaryotes compared to eukaryotes, bacteria make up the majority of life in terms of mass and diversity.
What role do macromolecules like proteins and DNA play in cells?
-Macromolecules like proteins and DNA are crucial in the structure and function of cells. DNA, made up of nucleotides, stores genetic information, while proteins, composed of amino acids, perform a variety of functions within the cell, including structural support and catalysis of biochemical reactions.
How does biochemistry study the complexity of living systems?
-Biochemistry uses reductionist methods, where living systems are broken down into simpler, isolated components to study them individually. This helps understand each component's role and function before synthesizing the information to understand the system as a whole.
What is the difference between in vitro and in vivo studies in biochemistry?
-In vitro refers to studies conducted outside a living organism, typically in controlled laboratory conditions. In vivo refers to studies conducted within a living organism, focusing on how biological systems operate in their natural environment.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)