BIOCHEMISTRY MODULE 1_Introduction to Biochemistry
Summary
TLDRThis lecture introduces biochemistry as the study of chemical processes in living organisms, highlighting its relevance to understanding life at the molecular level. It covers the principal biomolecules—carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids—and their roles in metabolism, energy storage, and genetic information. The script also touches on historical milestones in biochemistry, such as Pasteur's work on fermentation and the discovery of DNA, emphasizing the field's significance in diagnosing diseases and its applications in medicine and daily life.
Takeaways
- 📚 Biochemistry, also known as biological chemistry, studies chemical processes in living organisms, including plants and animals.
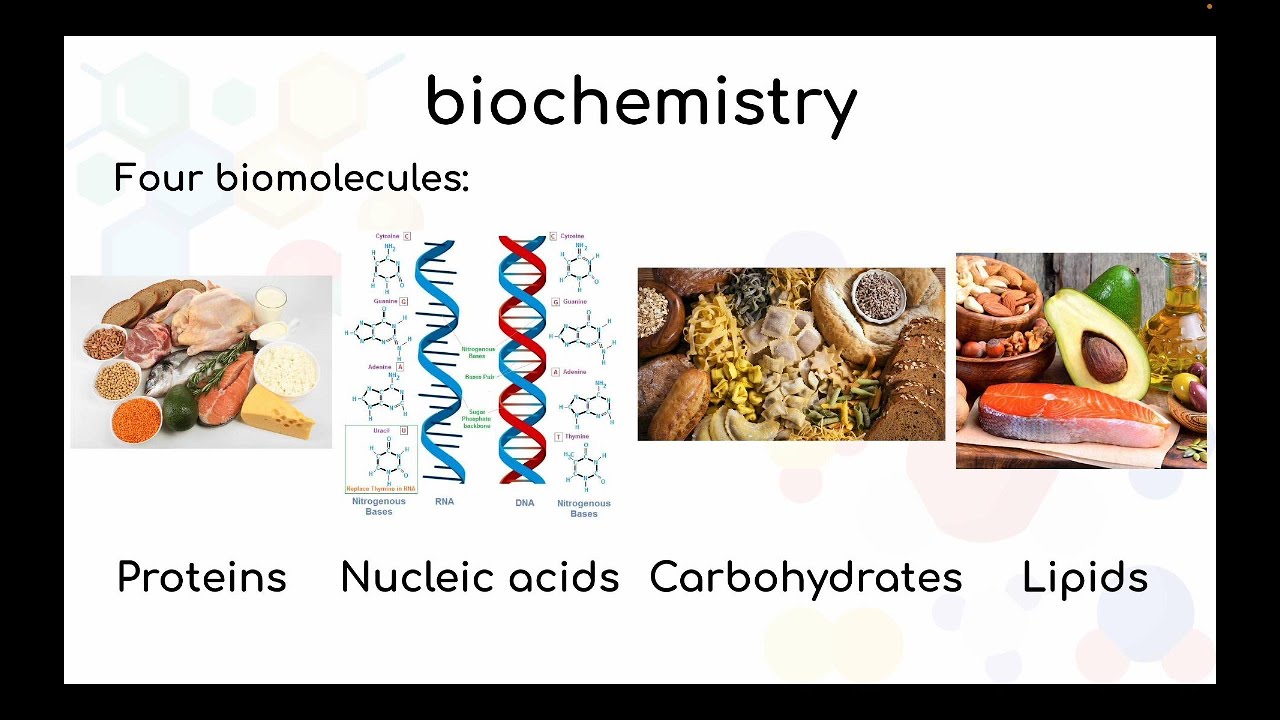
- 🧬 Biochemistry involves the study of key biomolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, which are essential for metabolism, absorption, and energy storage.
- 🧪 Louis Pasteur discovered that fermentation is carried out by microorganisms like bacteria and yeast, while Hans and Edward Buchner later demonstrated that fermentation can occur in cell-free extracts.
- 🧫 Key historical milestones in biochemistry include the synthesis of urea, the cell theory, the discovery of DNA, and the development of the kinetic theory of enzyme action.
- 🔬 Biochemistry studies chemical reactions at the molecular level, which can serve as indicators of abnormalities in the body, such as lipid profile tests detecting atherosclerosis.
- 💊 Biochemistry is applied in clinical settings to diagnose diseases and evaluate dietary needs, with biomolecules like lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids serving as markers for various conditions.
- 🍬 Carbohydrates, primarily composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, serve as the body's primary energy source, with glucose being the most common form.
- 🥚 Proteins, composed of amino acids, are crucial for transporting molecules, controlling chemical reactions, and making up the structure of living organisms, including hair, nails, and muscles.
- 💧 Lipids, or fats, are essential for energy storage, insulation, and making up cell membranes, with examples including saturated and unsaturated fats.
- 🧬 Nucleic acids, primarily found in the cell nucleus, provide genetic information and instructions to make proteins, with DNA containing the genetic code and RNA acting as a recipe for protein synthesis.
Q & A
What is the definition of biochemistry?
-Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. It is also the science concerned with the chemical constituents of living cells and the reactions and processes they undergo.
What are the principal classes of biomolecules in biochemistry?
-The principal classes of biomolecules in biochemistry include proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids.
What is the significance of Louis Pasteur's work in the history of biochemistry?
-Louis Pasteur demonstrated that fermentation is carried out by microorganisms such as bacteria and yeast, which was a major breakthrough in understanding biochemical processes.
What did Hans and Edward Buchner prove about fermentation that contradicted Pasteur's view?
-Hans and Edward Buchner proved that fermentation can occur in free cell extracts, meaning it can happen in non-living cells, which contradicted Pasteur's view that it was solely carried out by microorganisms.
What is the role of carbohydrates in the human body?
-Carbohydrates are the most common organic molecules and serve as the primary energy source for the body.
What are the main functions of lipids in the body?
-Lipids primarily function as energy storage and insulate the body. They also make up the cell membrane, which is crucial for cell structure and function.
How do proteins contribute to the body's structure and function?
-Proteins are involved in the transport of molecules in and out of cells, control the speed of chemical reactions, and are essential for growth and repair. They also make up the structure of living tissues such as hair, nails, skin, bones, and muscles.
What is the primary function of nucleic acids?
-Nucleic acids provide genetic information and hold the instructions for making proteins, which is essential for the replication and functioning of cells.
How can biochemical processes serve as indicators of abnormalities in the body?
-Biochemical processes can serve as indicators of abnormalities when certain biomolecules, such as lipids, proteins, or carbohydrates, are present in abnormal levels or forms, which can be detected through various tests like lipid profile tests or blood sugar tests.
What is the importance of the human genome project in the context of biochemistry, biology, and medicine?
-The human genome project has had a significant impact on biochemistry, biology, and medicine by providing a deeper understanding of genetic information and its role in various diseases, which aids in diagnosis, treatment, and the development of new therapies.
How do the hydrophobic properties of lipids relate to their role in cell membranes?
-Lipids are hydrophobic, meaning they do not dissolve in water. This property allows them to form the lipid bilayer of cell membranes, which is essential for maintaining cell integrity and function.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Introduction to Biochemistry: Definition, Scope, History, and Key Biomolecules

Biochem Intro Lecture
What is Biochemistry? What do Biochemists study? 🦋 Biology

Fundamentos Básicos de Sistemas Biológicos (Aula 1, parte 1)

INTRODUÇÃO À BIOQUÍMICA - Bioquímica | Biologia com Samuel Cunha

Biochemistry Basics
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)