What Are the Hidden Properties of Stuff?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores various mechanical properties of materials, highlighting how they behave under stress and deformation. It covers concepts like elasticity, plasticity, malleability, ductility, hardness, stiffness, strength, toughness, durability, and resilience. The video provides examples of materials like steel, gold, diamonds, and rubber, explaining their unique characteristics and applications in engineering. It emphasizes how understanding these properties helps in selecting the right materials for different tasks, such as using durable concrete for skyscrapers or elastic rubber for slingshots. The video serves as an insightful introduction to material science, demonstrating the hidden 'stats' that define each material's performance.
Takeaways
- 😀 Elasticity is the ability of a material to return to its original shape after being deformed, like elastic bands and trampoline springs.
- 😀 Plasticity is the ability of a material to be deformed without breaking, with examples like Saran wrap and clay.
- 😀 Brittle materials, like glass and ceramics, break easily when deformed, unlike plastic materials.
- 😀 Malleability refers to a material's ability to be made into sheets, with gold being a highly malleable material.
- 😀 Ductility is the ability to turn materials into wires, with silver being one of the most ductile materials.
- 😀 Hardness refers to a material's resistance to being scratched or penetrated, with diamonds being extremely hard.
- 😀 Stiffness measures how much a material resists being deformed, with glass and ceramics being stiff but easily broken.
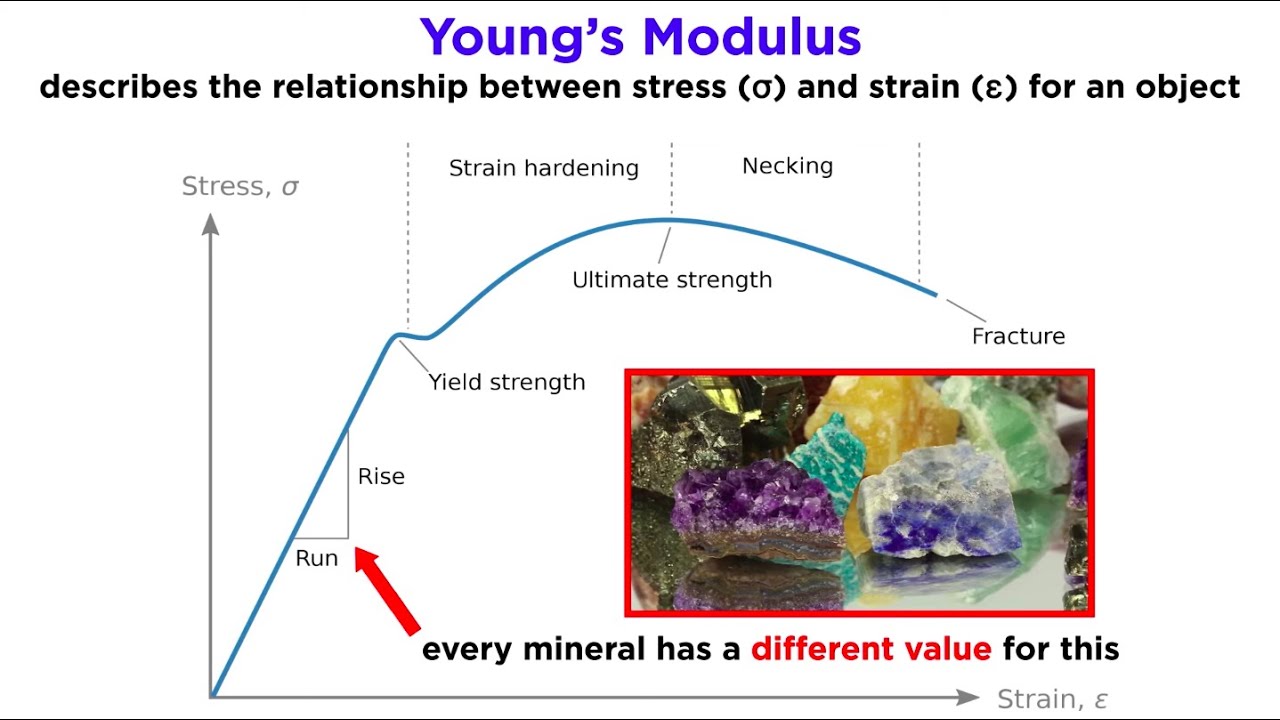
- 😀 Strength, or ultimate strength, is the amount of force a material can withstand before breaking, with titanium and tungsten being strong materials.
- 😀 Toughness refers to how much energy a material can absorb before breaking, combining strength and plasticity, with stainless steel and aluminum being tough materials.
- 😀 Durability is how well a material can withstand wear and tear, with materials like wood, bricks, and concrete used for building structures.
- 😀 Resilience is the ability of a material to absorb and store energy, with rubber being an example of a resilient material used in slingshots.
Q & A
What is elasticity in materials?
-Elasticity refers to how well a material can return to its original shape after being deformed. Materials like elastic bands, bowstrings, and trampoline springs are highly elastic.
What is the difference between plasticity and brittleness?
-Plasticity is the ability of a material to be deformed without breaking, while brittleness refers to materials that break easily when deformed. Plastic materials include Saran wrap and clay, while brittle materials include glass and diamonds.
What is the significance of malleability and ductility?
-Malleability is the ability of a material to be formed into sheets, and ductility is the ability to be drawn into wires. Malleable materials like gold and ductile materials like silver are examples of materials that are both plastic in nature.
How do hardness and brittleness relate to each other?
-Hardness refers to how resistant a material is to being scratched or penetrated, while brittleness refers to how easily a material breaks when deformed. A material can be hard but brittle, like diamonds.
What is stiffness in materials?
-Stiffness is the ability of a material to resist being deformed when a force is applied. Materials like glass and ceramics are stiff, but they are prone to breaking when deformed.
What is the difference between tensile strength and compressive strength?
-Tensile strength is the ability of a material to withstand pulling or tension, while compressive strength is the ability to withstand compression or squeezing. Both are types of strength that materials may have.
What is ultimate strength, and how does it differ from yielding strength?
-Ultimate strength is the maximum force a material can withstand before breaking, while yielding strength is the force at which a material starts to permanently deform. A material can still withstand additional force after it starts to deform.
What makes materials like stainless steel and aluminum tough?
-Toughness refers to a material's ability to absorb energy before breaking. Stainless steel and aluminum are tough because they combine strength and plasticity, allowing them to endure high stress without breaking.
Why is durability important in materials?
-Durability is the ability of a material to withstand wear and tear. Materials like wood, bricks, and concrete are durable, making them ideal for construction, as they can handle environmental stress over time.
What is resilience, and which material is a good example?
-Resilience is the ability of a material to store and absorb energy, combining strength and elasticity. Rubber is a highly resilient material, often used in applications like slingshots to store and release elastic energy.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Mechanics of Materials Lecture 01: Introduction and Course Overview
Overview of Geologic Structures Part 1: Rock Deformation, Stress and Strain
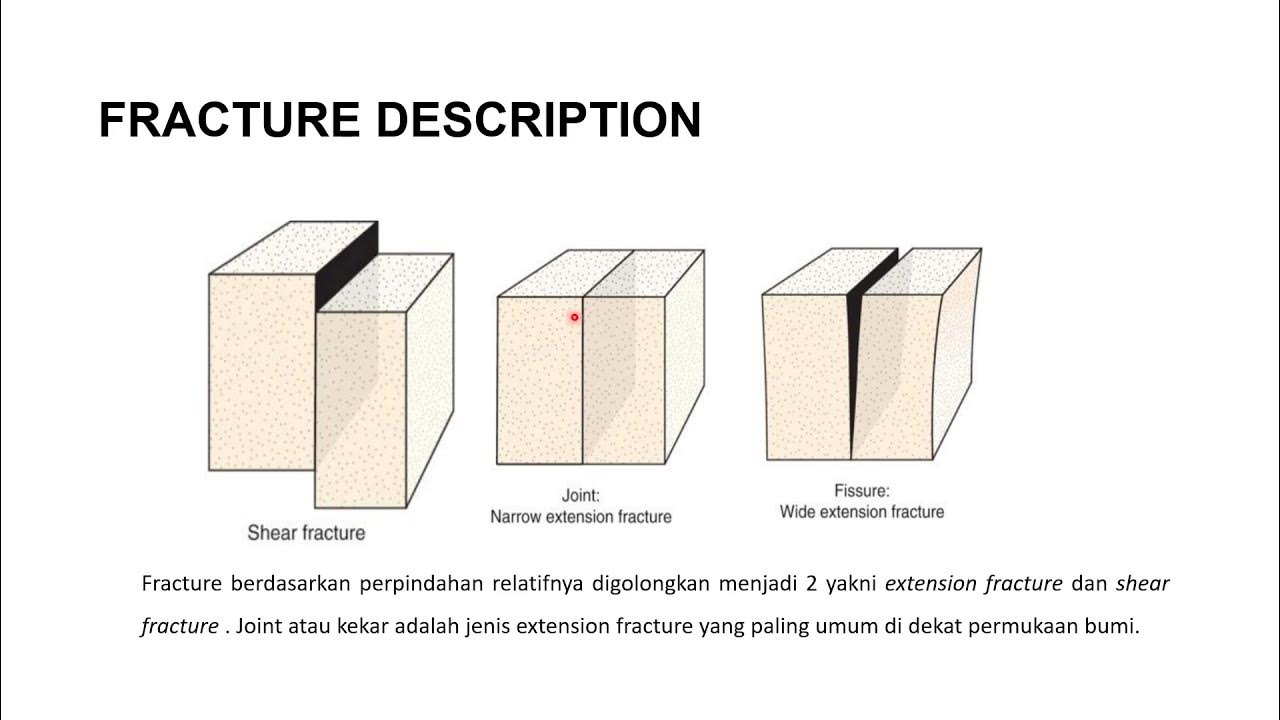
Deformasi Batuan II KEKAR

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Propriedades do Materiais

Pitch sobre Curva de Escoamento

Pitch sobre Discordâncias
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)