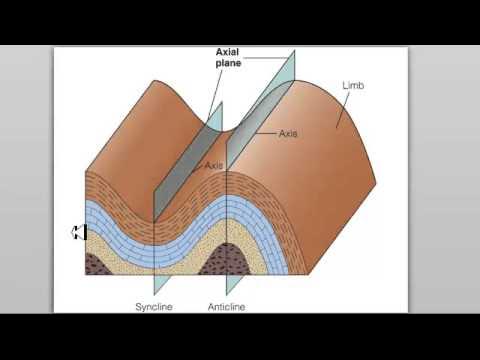
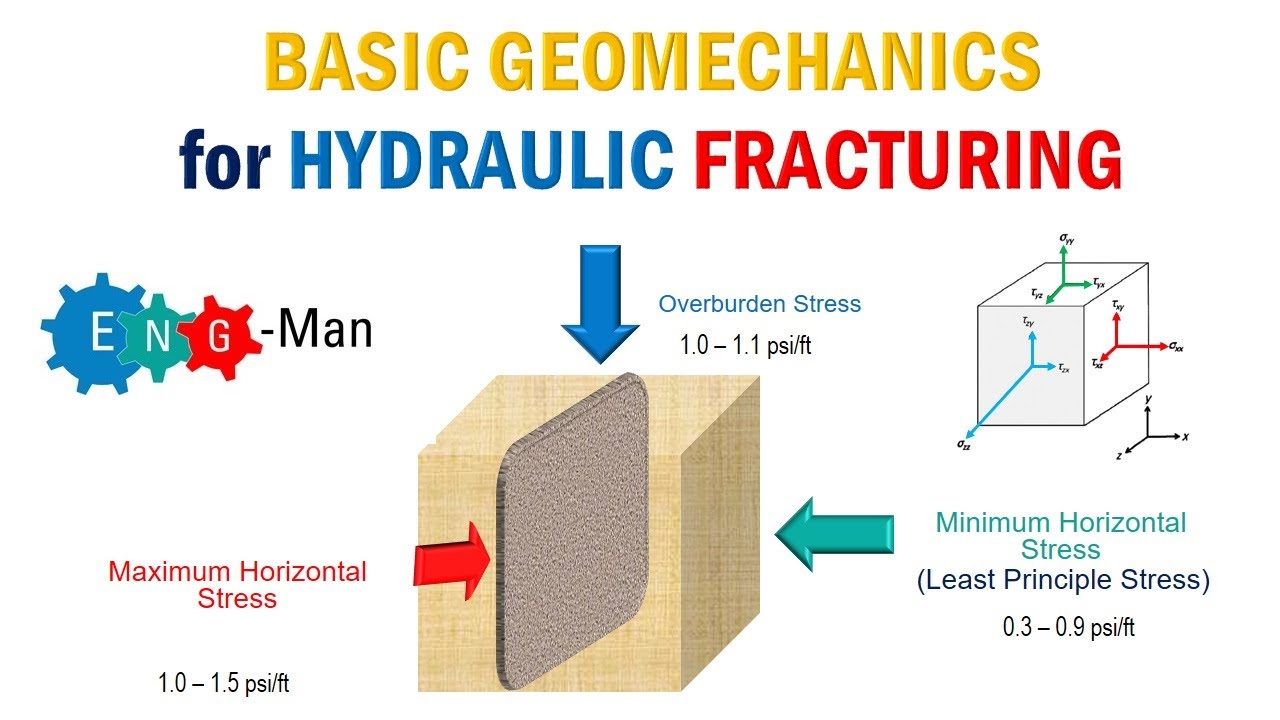
Deformasi Batuan II KEKAR
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the formation of fractures in rocks under different stress conditions. It explains the transition from brittle deformation, where fractures are formed, to ductile deformation, where rocks undergo significant internal changes. The types of fractures, including joint and extension fractures, are categorized and analyzed. The impact of temperature, pressure, and stress direction on rock deformation is explored. Additionally, it covers the significance of fractures in construction, mineral exploration, and how they affect the mechanical properties of rocks, highlighting their importance in geological studies and their practical implications in various industries.
Takeaways
- 😀 Fractures in rocks form as a result of differential stress, with their characteristics changing based on temperature and pressure conditions.
- 😀 When stress exceeds a rock's elastic limit, it undergoes permanent deformation, leading to fractures or other changes in its structure.
- 😀 At higher pressures and temperatures, fractures may transform into ductile behavior, where the rock deforms without breaking.
- 😀 Fractures are commonly found near the surface, where temperature and pressure are lower, and they are a key structure in geological studies.
- 😀 Two main types of fractures are identified: shear fractures and extension fractures, which have different movements and causes.
- 😀 Joints, a specific type of fracture, are common in rocks and can be categorized into systematic and non-systematic types based on their geometric patterns.
- 😀 Extension fractures can form fissures or joins, depending on the degree of opening or displacement between the fracture surfaces.
- 😀 Fractures are critical in fields like construction and mineral exploration, as they can weaken rocks and facilitate the flow of fluids or mineralization.
- 😀 The classification of fractures depends on the direction of stress applied, leading to different deformation modes, such as opening, sliding, or tearing.
- 😀 Fractures can result from both tectonic (internal) and non-tectonic (external) processes, including cooling, contraction, and reduction of overburden pressure.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video script is about fractures and joints in rocks, which are products of rock deformation. It discusses how these structures form under various stress, temperature, and pressure conditions.
How does differential stress affect rocks during deformation?
-Differential stress causes rocks that initially do not have fractures to form them as stress increases. When the stress exceeds the elastic limit of the rock, it undergoes permanent deformation, leading to fractures.
What is the difference between fractures formed in brittle and ductile zones?
-In brittle zones, fractures form under low temperature and pressure conditions, often resulting in visible cracks. In ductile zones, where higher temperature and pressure exist, rocks deform without forming visible fractures, and changes are more plastic in nature.
What are the two main types of fractures discussed in the video?
-The two main types of fractures discussed are 'joint fractures' and 'extension fractures'. Joint fractures have minimal displacement, while extension fractures involve larger displacement, often resulting from tectonic processes.
What is a 'joint' in geological terms?
-A joint is a type of fracture with little to no displacement. It is commonly found in rocks, often occurring in pairs, and can be systematic (with consistent geometry and spacing) or non-systematic (irregular in shape and spacing).
How do fractures influence the strength and behavior of rocks?
-Fractures weaken rocks by providing planes of weakness that can make them more susceptible to further deformation. Additionally, fractures can facilitate fluid flow, which is important in various construction and mining processes.
What role do fractures play in mineral exploration?
-Fractures are crucial in mineral exploration because they can serve as pathways for fluid migration. These fluids often carry valuable minerals, such as gold, which can accumulate in the fracture zones.
How are different types of fractures classified based on their displacement?
-Fractures are classified into two main types: 'slip' fractures, which involve significant displacement, and 'joint' fractures, which exhibit little to no displacement. Fractures with larger displacement are generally referred to as 'large fractures'.
What are the three main modes of fracture deformation?
-The three main modes of fracture deformation are Mode 1 (opening due to extension), Mode 2 (sliding due to shear), and Mode 3 (tearing, which is also a shear mode). These modes are based on the direction and nature of the applied stress.
What is the significance of the stress orientation on fracture formation?
-The orientation of the principal stress plays a critical role in determining the type of fracture that forms. For instance, tension-oriented stresses cause opening fractures, while shear stresses lead to sliding fractures, affecting the rock’s overall deformation pattern.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade Now5.0 / 5 (0 votes)